Antenna housing based on wide-stop-band low-frequency multilayer frequency selective surface
A frequency selective surface, wide stopband technology, applied in the field of radome, can solve the problems of frequency selective surface cost increase, capacitance capacitance error capacitance effectiveness, inductance and capacitance failure, etc., to achieve wide stopband suppression capability, strong capacitance, etc. Inductive and inductive, the effect of low resonant frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
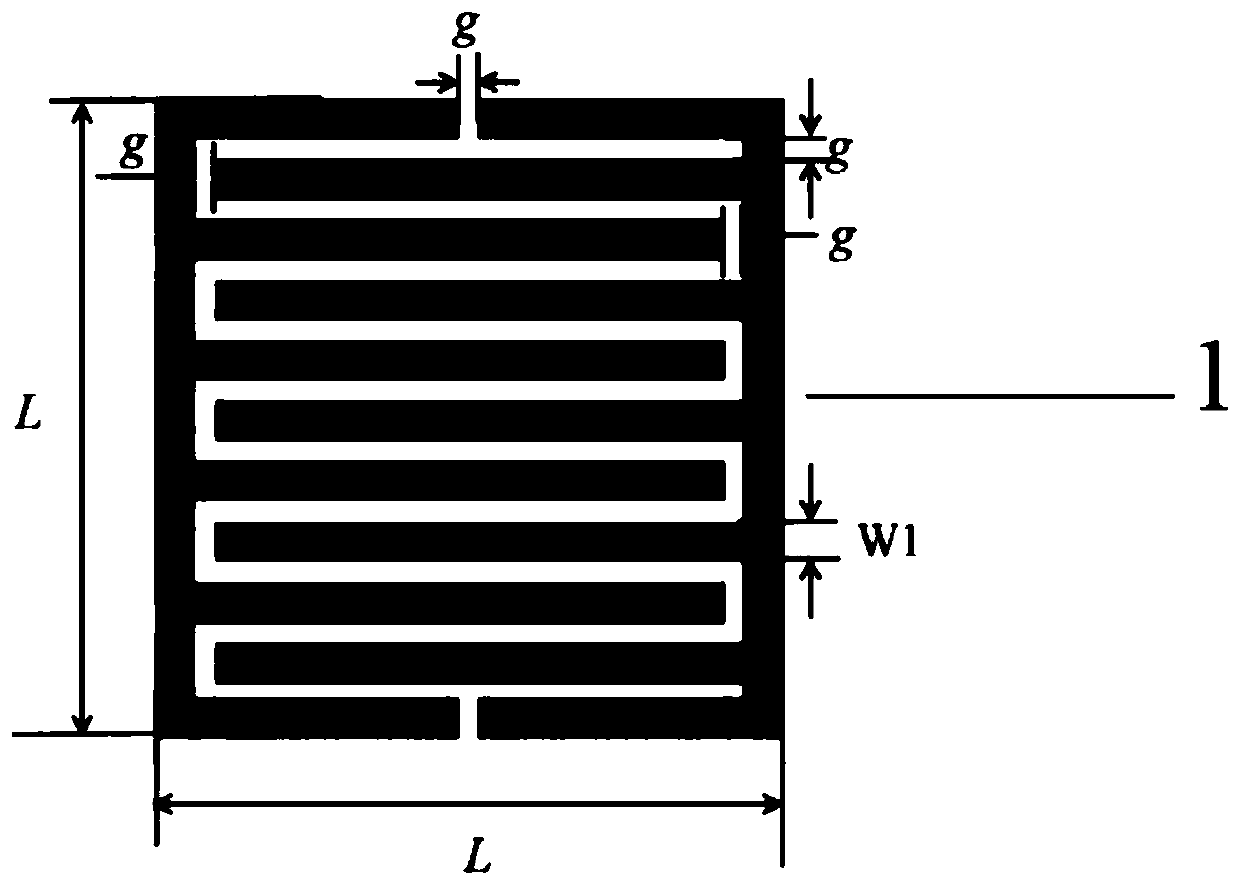
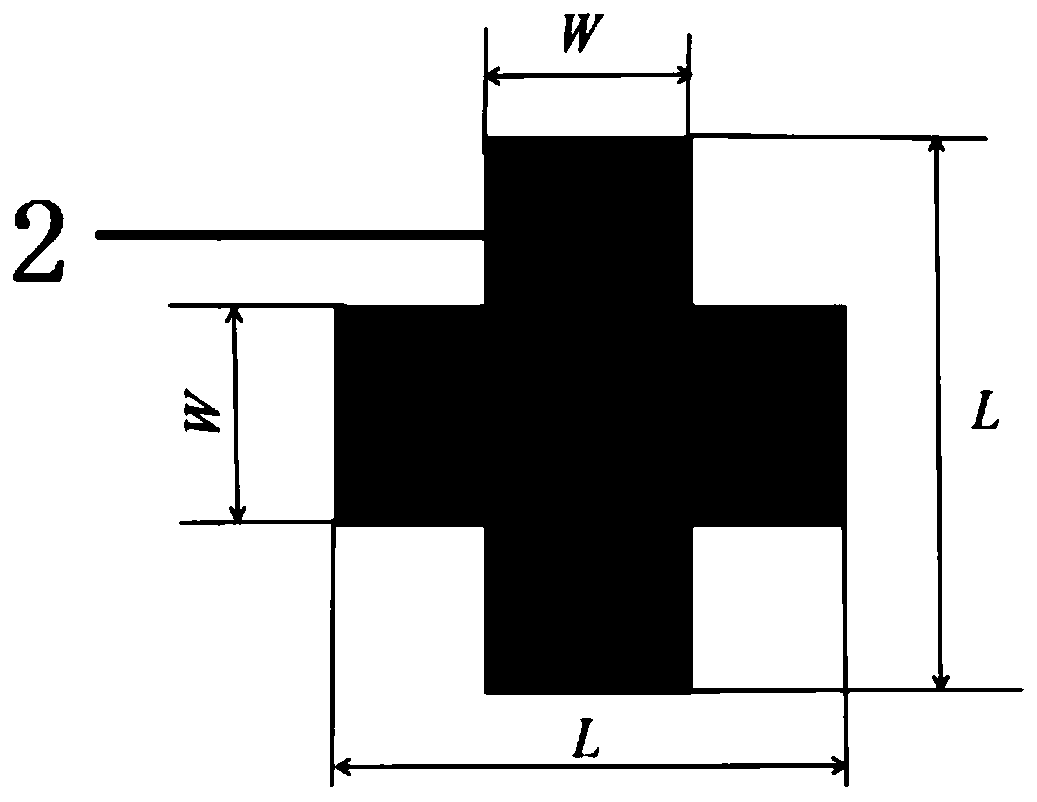
[0028] In this embodiment, the average side length of the upper fork finger structure unit 1 and the lower fork finger structure unit 3 is 6mm, the interfinger gap is 0.204mm, the finger width of the fork finger is 0.36mm, and the length of the fork finger is 5.006mm; The length of each protruding part in the structural unit 2 is 6 mm, the width is 2.4 mm, the thickness of the upper PCB board 4 and the thickness of the lower PCB board 5 are both 2 mm, and the dielectric constant is 3.2 mm. Figure 5 and Image 6 In order to simulate the structure, in the simulation results, it is assumed that the number of the upper interdigital structural unit 1, the cross-shaped structural unit 2 and the lower interdigital structural unit 3 is 30, from Figure 5 It can be seen from the simulation results that the resonant frequency of the radome can be as low as about 2500MHz, and the unit size is only equal to λ 0 / 20, lambda 0 is the free-space wavelength of the resonant frequency electr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com