Novel method for rapidly detecting septicopyemia by using gram-negative bacterial infection
A technology for Gram-negative bacteria and sepsis, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, and analysis materials, and can solve the problem of undetectable blood endotoxin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Method for rapid detection of LPS in cultured blood of patients with suspected sepsis
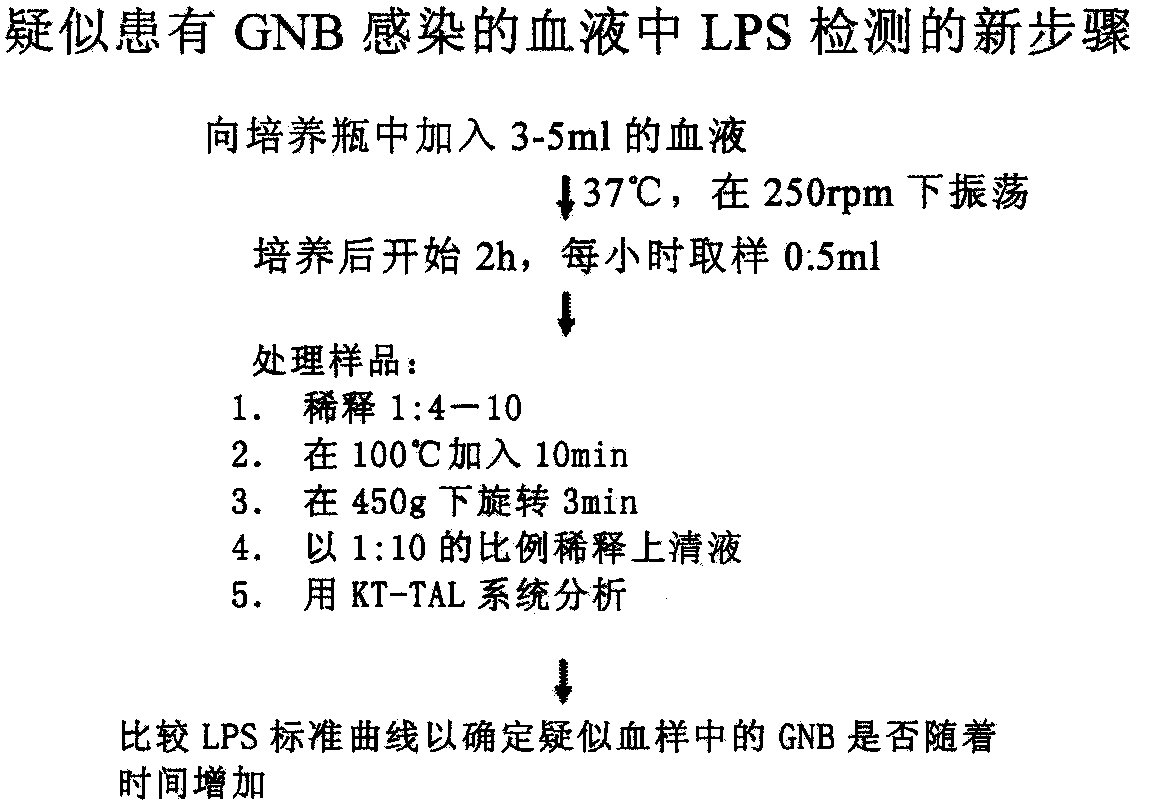
[0037] A new step in the detection of LPS in blood suspected of GNB infection. Briefly, 3-5 ml of blood was added to the culture flask. After 2 hours, 0.5 ml samples were taken every hour for dynamic testing of LPS. Samples were diluted, heated, spun, and diluted again prior to LPS quantification with the KT-TAL system.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 Formulation of reference standards
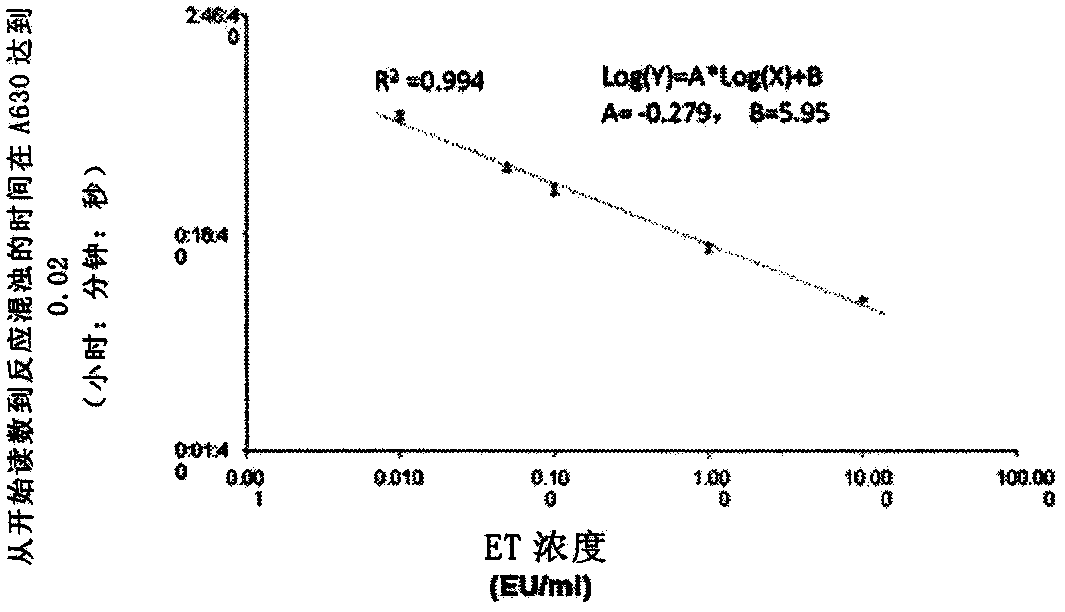
[0039] Lyophilized endotoxin standard stock solutions were reconstituted in endotoxin-free water, diluted to final concentrations of 50, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01 and 0 EU / ml, and three independent experiments were performed on microplates. After adding 100 μl of TAL reagent to each well, place the plate in a dynamic culture reader (BioTek TM ELx808IULALXH), and the reader immediately began to measure endotoxin levels using the kinetic assay procedure. Gel formation was recorded every 30 seconds for 30-60 minutes at a wavelength of 630 nm. For this set of studies, the resulting formula was Log(Y)=A*Log(X)+B, where Y=reaction time (onset time), A=Y intercept, X=endotoxin concentration, and B=regression curve The slope of. In this set of studies, A was -0.279, B was 5.95, and R 2 (correlation efficiency) was 0.994. If the standard curve is completed using the same batch of reagents and the same procedure, it can be stored in the...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Effect of heating on LPS released from GNB samples and assay specificity
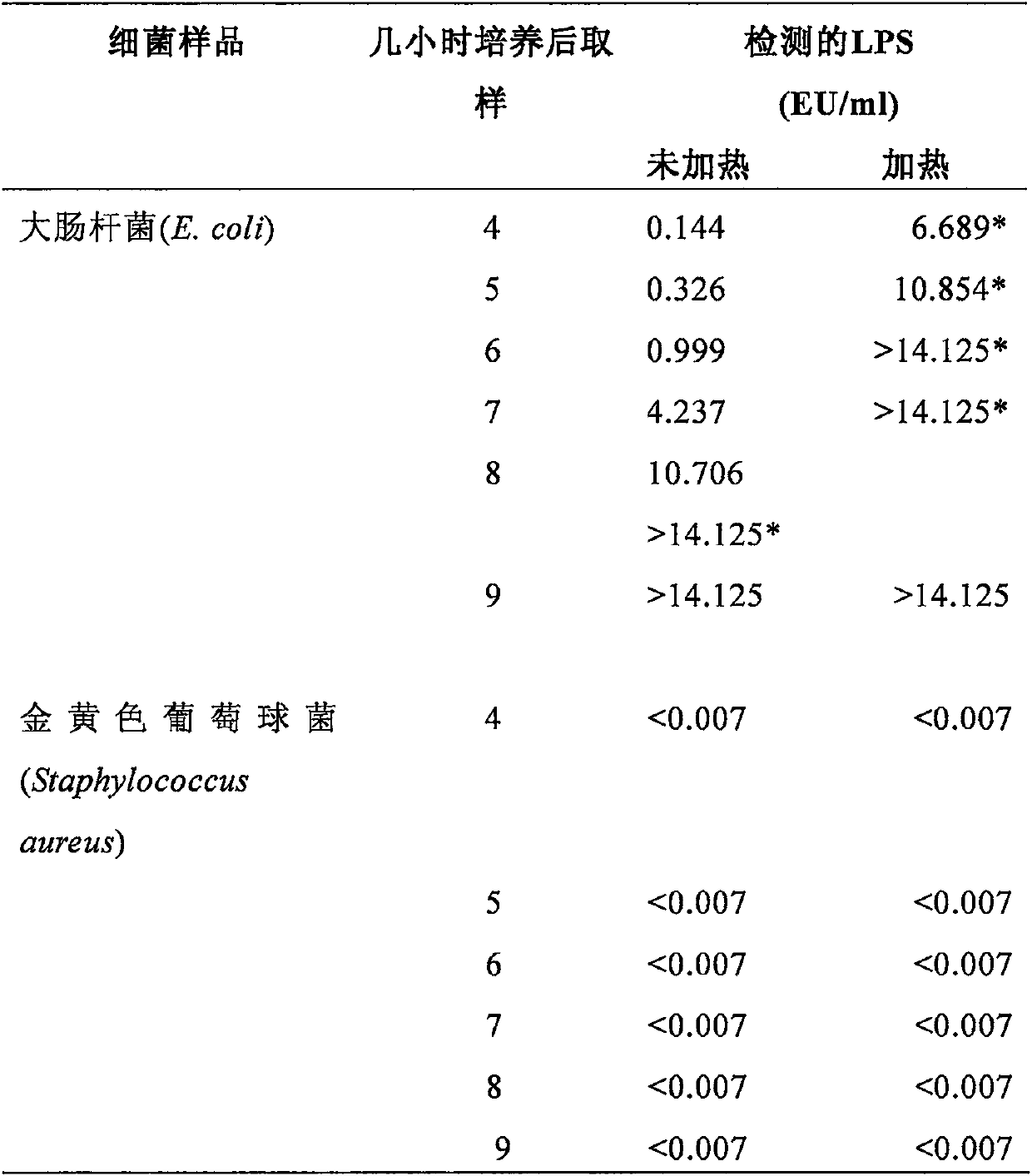
[0041]Based on the knowledge that (1) LPS has two forms, free LPS and LPS associated with intact cell walls (Jorgensen et al., 1973); and (2) heat can not only promote the release of LPS, but also denature / precipitate interfering substances , and contribute to more sensitive quantification of LPS, employing heat as a necessary step in sample preparation. As shown in Table 1, a series of cultured E. coli samples were collected at 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 hours, with or without heating, and the detected LPS levels were compared for concurrently prepared paired samples. At 4 hours, the LPS of the unheated sample was 0.144 EU / ml, while the LPS of the heated sample was 6.689 EU / ml. Similarly, unheated samples rose relatively slowly from 0.326, 0.999, 4.237 to 10.706 EU / ml at 5, 6, 7, 8 hours, and >14.125 EU / ml at 9 hours, while at 5 hours hour, the heating time reaches 10.854, which is equival...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com