Optical filter, and laser light source and optical transceiver using the same
An optical filter and laser source technology, applied in the field of optical filters, can solve problems such as difficulty in preventing mode hopping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0047] refer to Figure 1-8 The first embodiment will be described. In this embodiment mode, a laser light source using an optical filter is described.
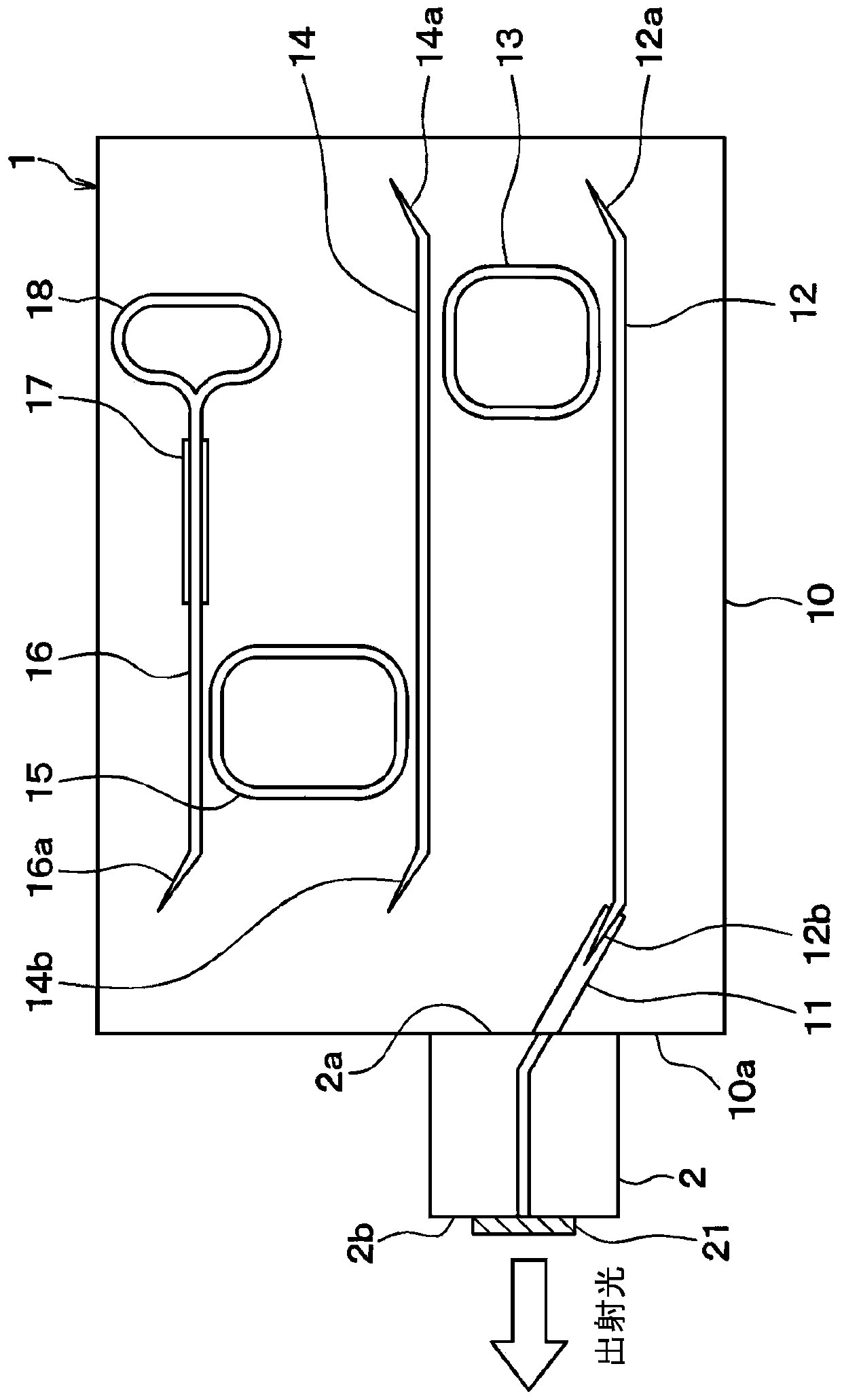
[0048] Such as figure 1As shown, the laser source includes an optical filter 1 and a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) 2 . The laser source emits inner outgoing light from SOA2 to filter 1, extracts intense light that has entered a resonance state in optical filter 1 and SOA, and outputs the intense light from SOA2 to the outside as outer outgoing light.
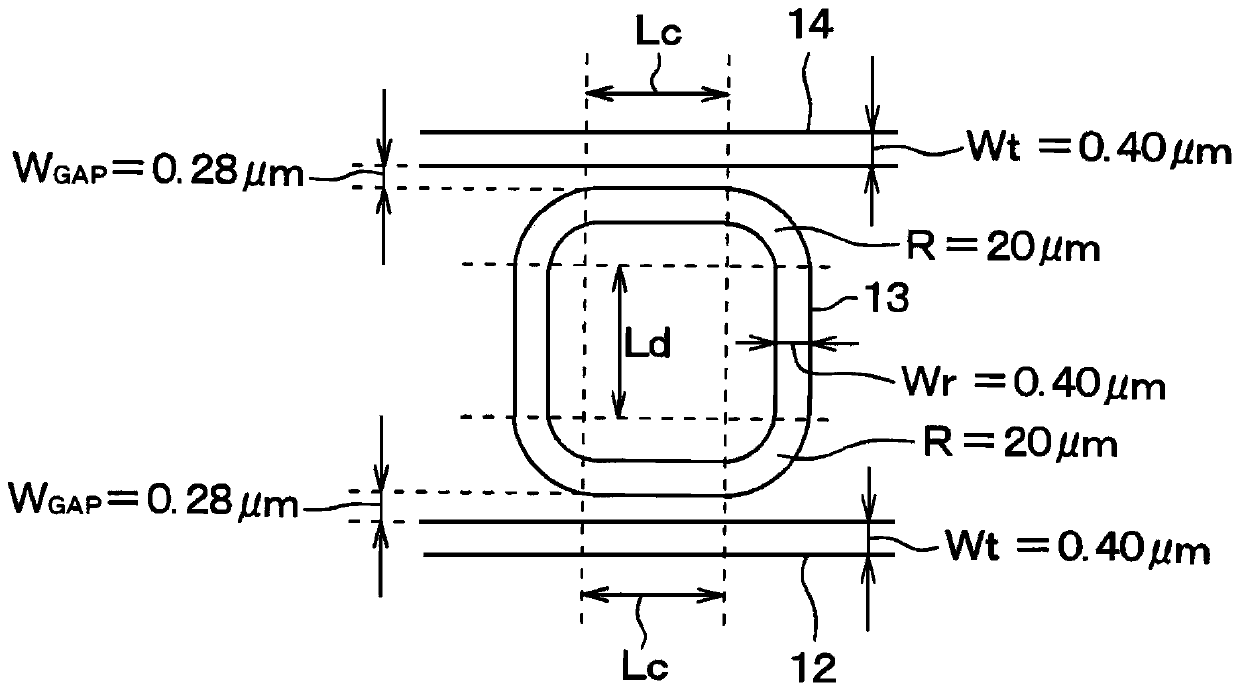
[0049] The optical filter 1 is formed, for example, by performing a semiconductor process using the semiconductor substrate 10 . Specifically, the semiconductor substrate 10 included in the optical filter 1 is equipped with a spot size converter (optical spot size converter, SSC for short) 11, a first waveguide 12, a first ring resonator 13, a second waveguide 14, a second A ring resonator 15, a third waveguide 16, a modulator 17, a ring mirror 18, and the like.
...
no. 2 approach
[0131] The second embodiment is described below. This embodiment differs from the first embodiment in the light extraction direction and the like. Other configurations are similar to those of the first embodiment. Only the parts different from the first embodiment will be described.
[0132] In the first embodiment, when laser oscillation occurs, light is output from the mirror 21 corresponding to the first reflector. In the present embodiment, light is output from a portion different from the mirror 21 .
[0133] In this embodiment, the second reflector is not the annular mirror 18 as in the first embodiment, but as Figure 20 A directional coupler 40 is shown. The directional coupler 40 is folded back from the third waveguide 16 in a meandering manner. In this embodiment, the tip of the directional coupler 40 is directed to the end face 10b of the semiconductor substrate 10, which is opposite to the end face 10a on which the SOA 2 is provided.
[0134] Specifically, th...
no. 3 approach
[0141] A third embodiment is described below. The present embodiment differs from the first and second embodiments in the configuration between the first ring resonator 13 and the second ring resonator 15 . Other configurations are similar to those of the first and second embodiments. Only the parts different from the first and second embodiments are described. In the present embodiment, an example in which light is output through the reflection mirror 21 of the SOA2 as in the first embodiment will be described. Light may be output from a portion different from the reflection mirror 21 as in the second embodiment.
[0142] In the present embodiment, the second waveguide 14 included in the first and second embodiments is omitted. Specifically, as Figure 22 As shown, the first ring resonator 13 and the second ring resonator 15 are adjacent to each other. One side of the first ring resonator 13 and one side of the second ring resonator 15 are opposed to each other with a pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| perimeter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com