A field comparative test method and application of a new fast-growing tree variety
A comparative test and new variety technology, applied in the field of field comparative test of new fast-growing tree varieties, can solve the problems of large test error, low breeding efficiency, long test cycle, etc., and achieve the advantages of easy operation, shortened rotation period, and shortened test cycle Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] A field comparison test method for fast-growing new varieties of forest trees, comprising the following steps:
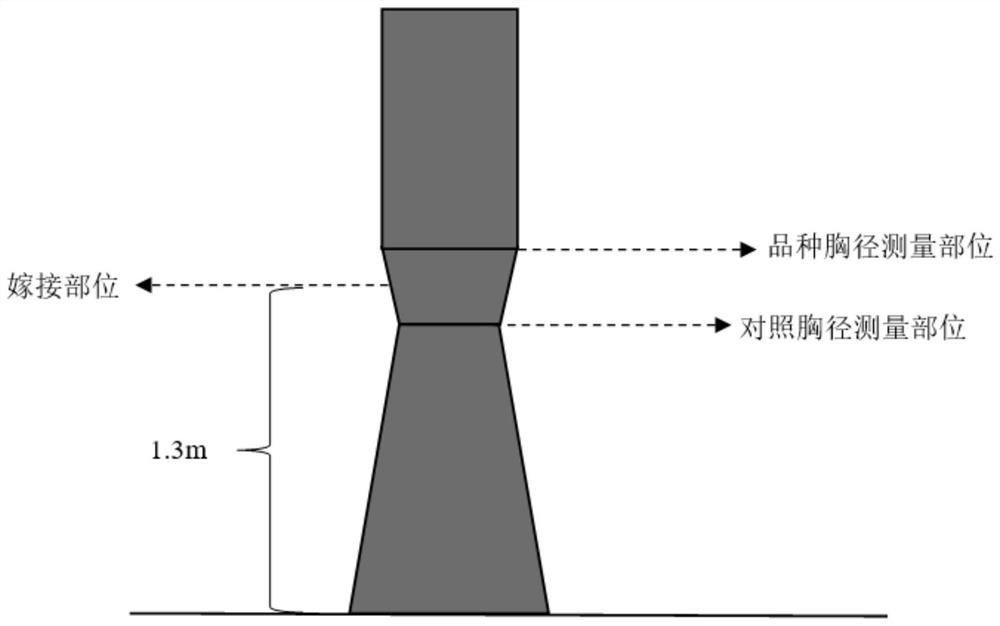
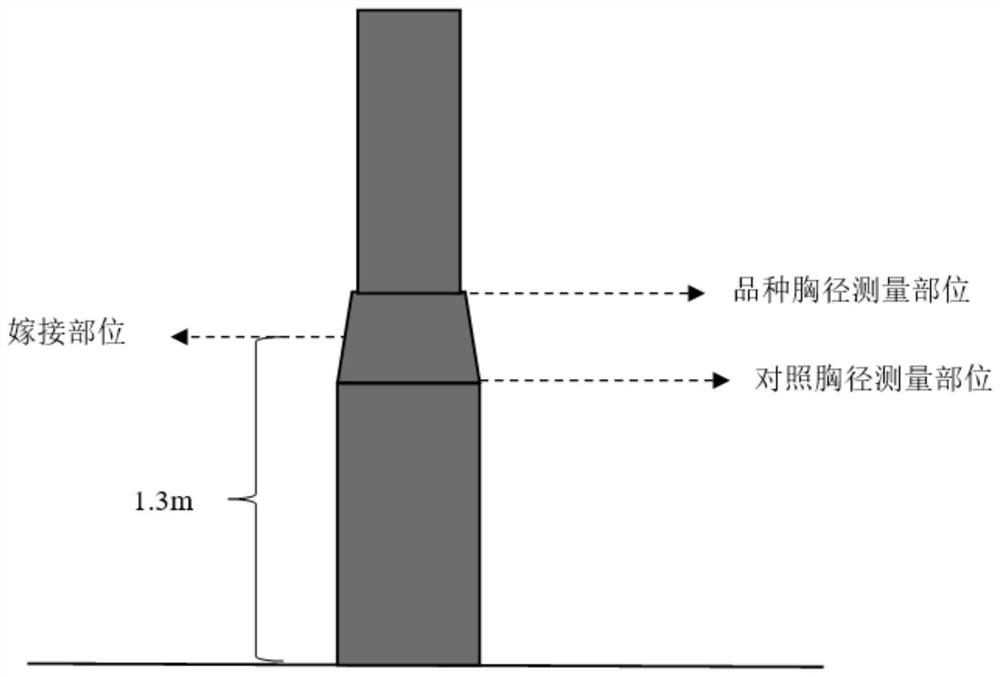
[0056] Step 1. Breeding of test materials: Cultivate control varieties as rootstocks 2 years in advance, use new varieties as scions, and carry out high-grafting at a height of 1.3m on rootstocks. The age and location of indirect ear materials of each variety should be consistent, and the grafting method should also be consistent. Nine plants were bred from each variety.
[0057] Step 2. Selection of experimental field: select 3 ecological experimental points, and the area of each experimental point is determined according to the number of varieties to be tested. Requires flat terrain, convenient drainage and irrigation, high and uniform soil fertility.
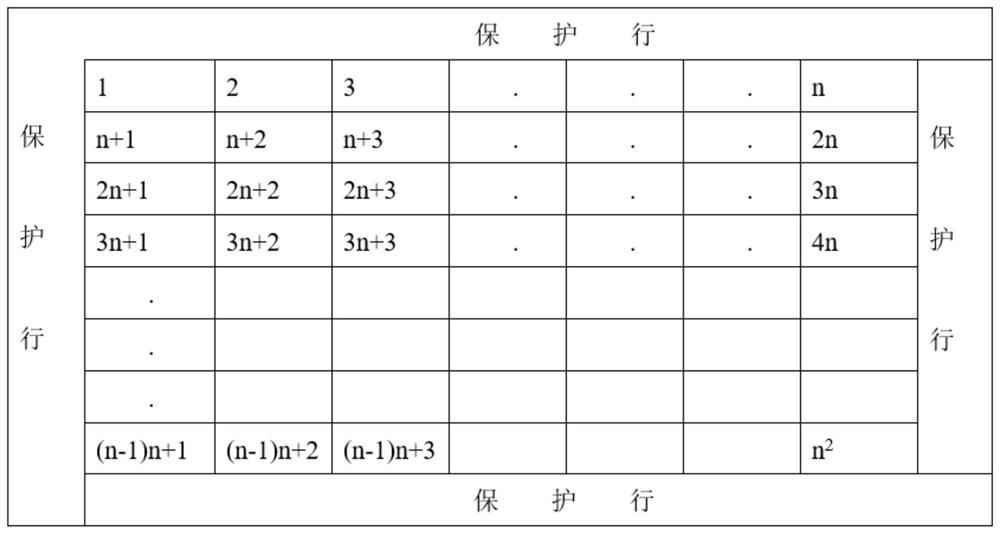
[0058] Step 3, plot design: 3 plots, arranged in a single row, the size of the row spacing is determined according to the cultivation technical requirements of the target forest species of the selected ne...
Embodiment 2
[0063] A field comparison test method for fast-growing new varieties of forest trees, comprising the following steps:
[0064] Step 1. Breeding of test materials: Cultivate the control variety one year in advance as the rootstock, use the new variety as the scion, and carry out high grafting at a height of 1.3m on the rootstock. 12 strains were bred for each variety.
[0065] Step 2. Selection of experimental field: select 3 ecological experimental points, and the area of each experimental point is determined according to the number of varieties to be tested. Requires flat terrain, convenient drainage and irrigation, high and uniform soil fertility.
[0066] Step 3, plot design: 3 plots, arranged in a single row, the size of the row spacing is determined according to the cultivation technical requirements of the target forest species of the selected new variety, and the area of a single plant is 30m 2 , each variety was randomly arranged, surrounded by 3 protective rows,...
Embodiment 3
[0071] A field comparison test method for fast-growing new varieties of forest trees, comprising the following steps:
[0072] Step 1. Breeding of test materials: Cultivate the control variety one year in advance as the rootstock, use the new variety as the scion, and carry out high grafting at a height of 1.3m on the rootstock. Nine plants were bred from each variety.
[0073] Step 2. Selection of experimental field: select 3 ecological experimental points, and the area of each experimental point is determined according to the number of varieties to be tested. Requires flat terrain, convenient drainage and irrigation, high and uniform soil fertility.
[0074] Step 3, plot design: 3 plots, arranged in a single row, the size of the row spacing is determined according to the cultivation technical requirements of the target forest species of the selected new variety, and the area of a single plant is 30m 2 , each variety was randomly arranged, surrounded by 3 protective row...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com