Dual-motor transmission structure and wall cutting machine provided with the same
A transmission structure and dual-motor technology, which is applied in the direction of electric components, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of unreasonable setting of the dual-motor transmission structure, machine fragility, and small torque, so as to avoid machine failure and easy heat dissipation , the effect of increasing the torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
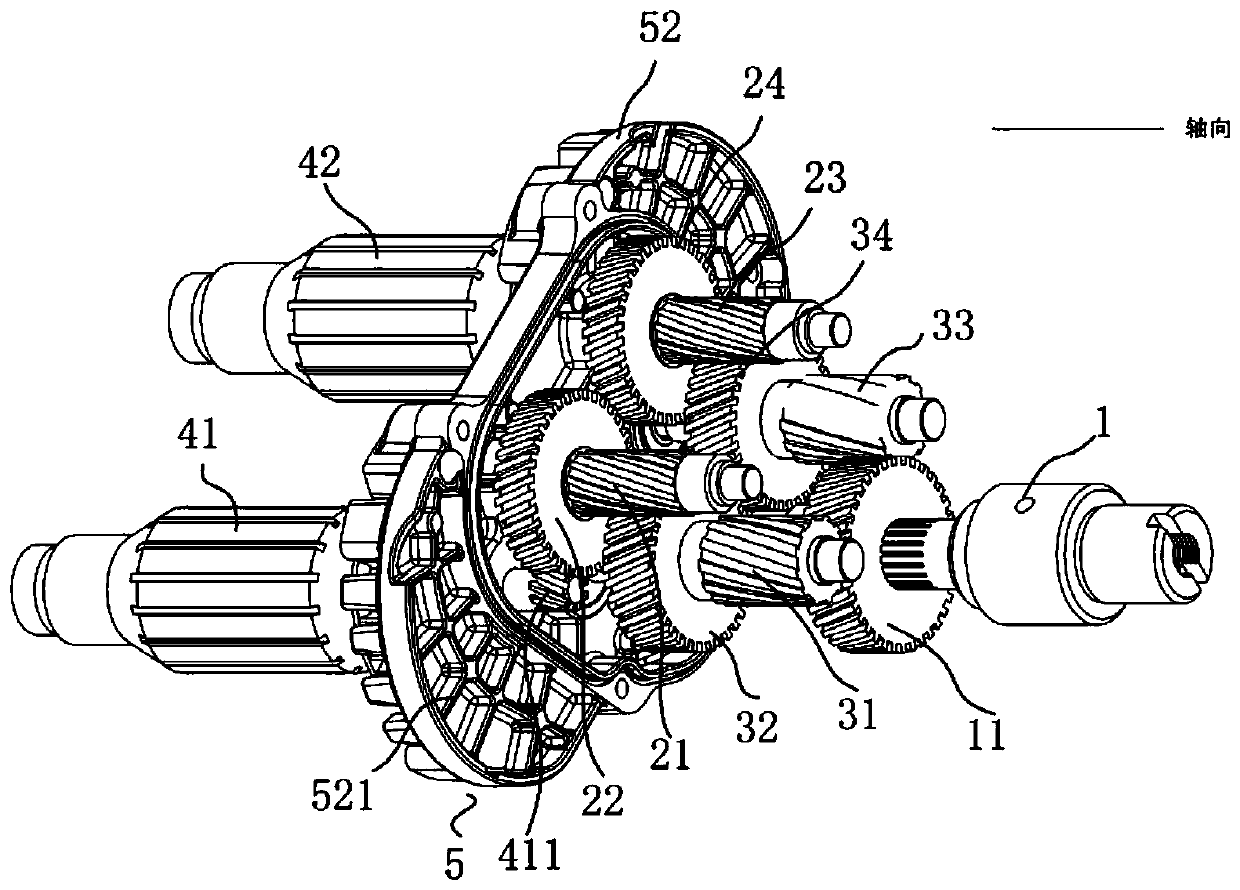
[0042] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a transmission structure of a double motor, the double motor includes a first motor (not shown in the figure) and a second motor (not shown in the figure), and the rotor (41, 42) is arranged in the motor, and the rotor Including the first rotor 41 in the first motor and the second rotor 42 in the second motor, the transmission structure is connected to the two motors, and the transmission structure includes the main shaft 1, the main shaft gear 11 and the transmission wheel set connected in sequence , the transmission wheel set includes at least two delivery wheel sets (21, 22, 23, 24 or 31, 32, 33, 34), and the transmission connection between adjacent delivery wheel sets, the delivery wheel set (21, 22 , 23,24 or 31,32,33,34) comprise the first gear shaft (21,31), the second gear shaft (23,33), the first plate gear connected with the first gear shaft (21,31) (22,32), the second plate gear (24,34) connected with the second gear...
Embodiment 2
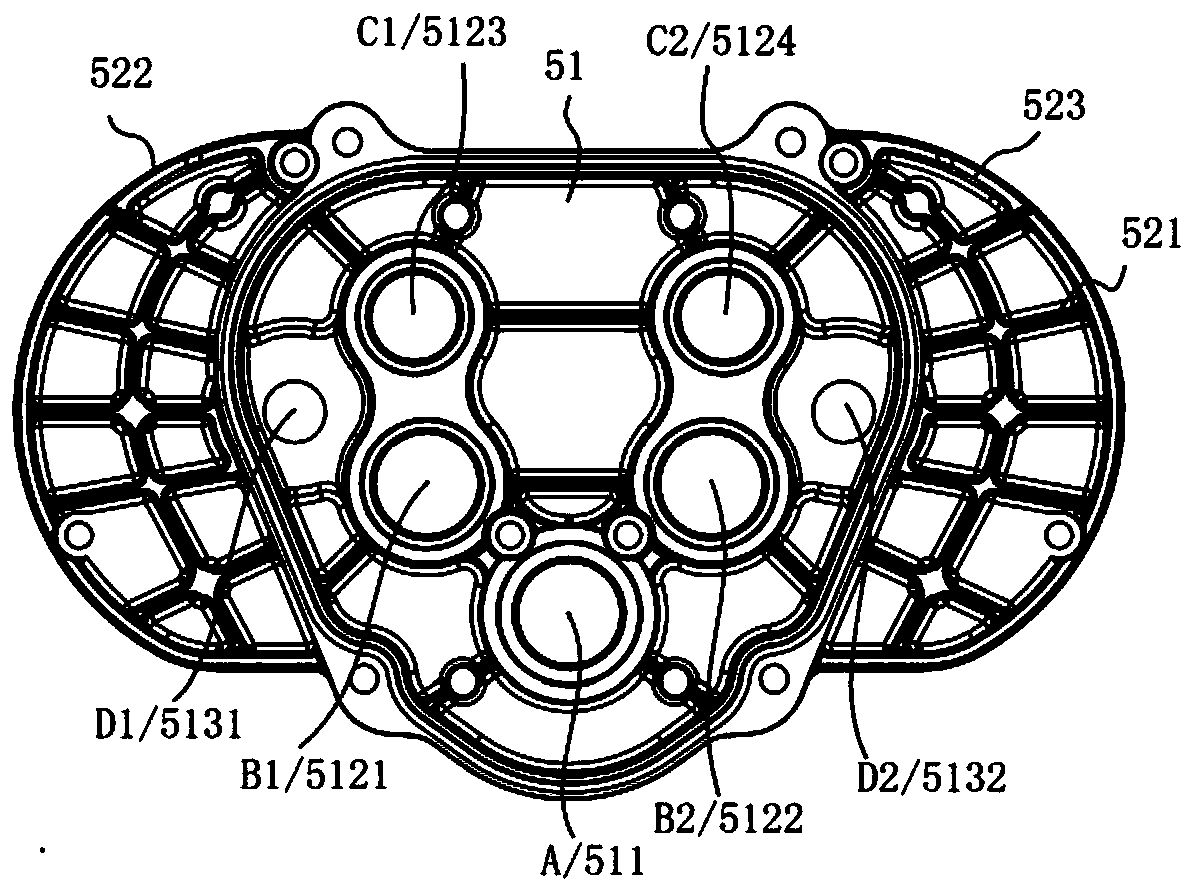
[0048] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, on the basis of Embodiment 1, there is also the following technical solution. On the same plane perpendicular to the axis of the main shaft 1, with the axis A of the main shaft 1 as the apex, the axis of the first stage gear shaft 21 C1, the axis A of the main shaft 1, and the axis C2 of the second-stage gear shaft 23 form an angle α1;
[0049] Taking the axis A of the main shaft 1 as the apex, the axis B1 of the first-stage gear shaft 31, the axis A of the main shaft 1, and the axis B2 of the second-stage gear shaft 33 form an included angle α2;
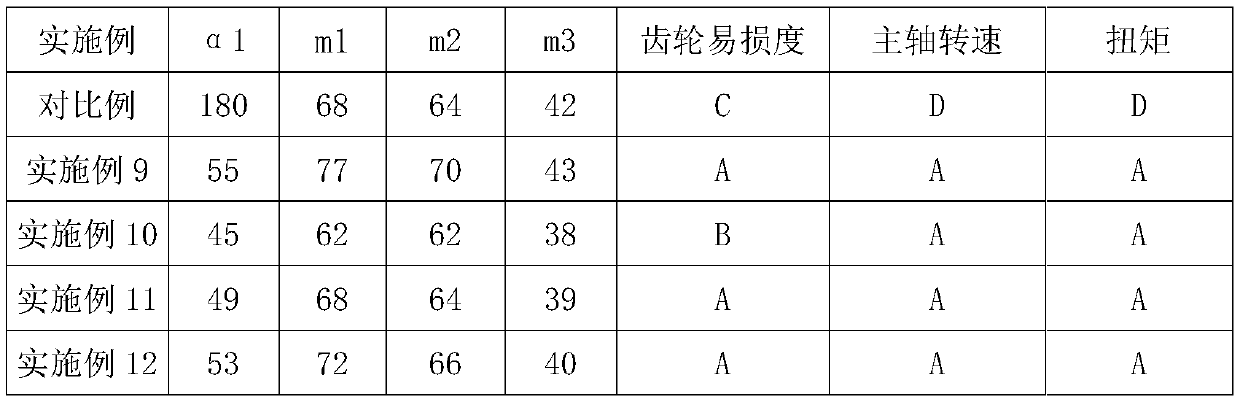
[0050] With the axis A of the main shaft 1 as the vertex, the angle α3 is formed between the axis D1 of the first rotor 41, the axis A of the main shaft 1, and the axis D2 of the second rotor 42; the degrees of α1 and α2 The relationship is, α1<α2<180 degrees, α3<180 degrees. In this embodiment, α1 is 120 degrees, α2 is 170 degrees, and α3 is 168 degrees.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, on the basis of Examples 1 and 2, there is also the following technical solution, the included angle α1, the included angle α2, 75 degrees ≤ α2 ≤ 115 degrees, 45 degrees ≤ α1 ≤ 65 degrees. 105°≤α3≤109°, the degree of α3 can be 105°, 106°, 107°, 108°, 109°. The degrees of α1 and α2 can be adjusted within the interval of 30 degrees ≤ α2-α1 ≤ 50 degrees, and the difference between α2-α1 can be 30 degrees, 32 degrees, 35 degrees, 40 degrees, 45 degrees, 50 degrees.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com