Ultra-thin wave absorber based on deep sub-wavelength slits
A deep subwavelength, wave absorber technology, applied in the field of ultra-thin wave absorbers, can solve the problem of poor wave absorption effect, and achieve the effect of light weight, simple structure and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
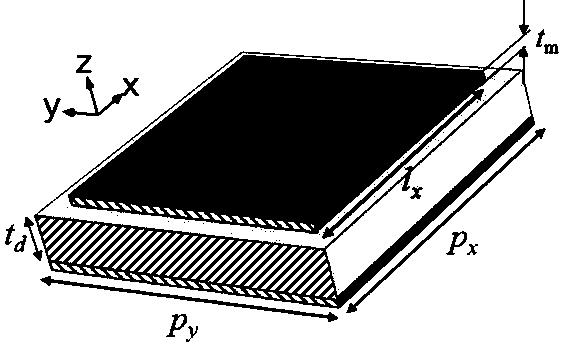
[0021] Set the working frequency to 2.21 GHz and the working wavelength to 135.7 mm. Low-loss doped PTFE plate is selected as the dielectric material, ε = 3.6, tan δ = 0.004. The metal material is copper, and the thickness is a typical value of 18 μm under the copper clad process. .
[0022] The side length of the metal patch is set to l ≈ lambda / 2 / √ ε = 34.3 mm, the thickness of the dielectric spacer is set to t d = lambda / 300 = 0.45 mm, and the width of the air slit between the patches was set to 0.5 mm. Scanning with CST t d and l , and after fine-tuning twice, the final scale parameter is obtained, t d = 0.25 mm, l = 35 mm.
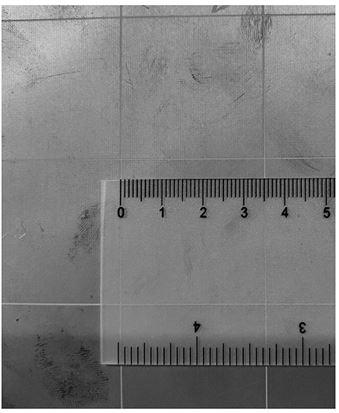
[0023] Both material production and structural processing can rely on mature board manufacturers and circuit board processors. Produced absorbers such as image 3 with 4 As shown, the width and thickness are in line with the design values. The simulated absorbing effect (magnitude of reflection coefficient) of this abso...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com