Anchoring part and anchoring device
An anchor and an anchoring technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as easy displacement, and achieve the effects of increasing roughness, slowing down speed, and improving effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
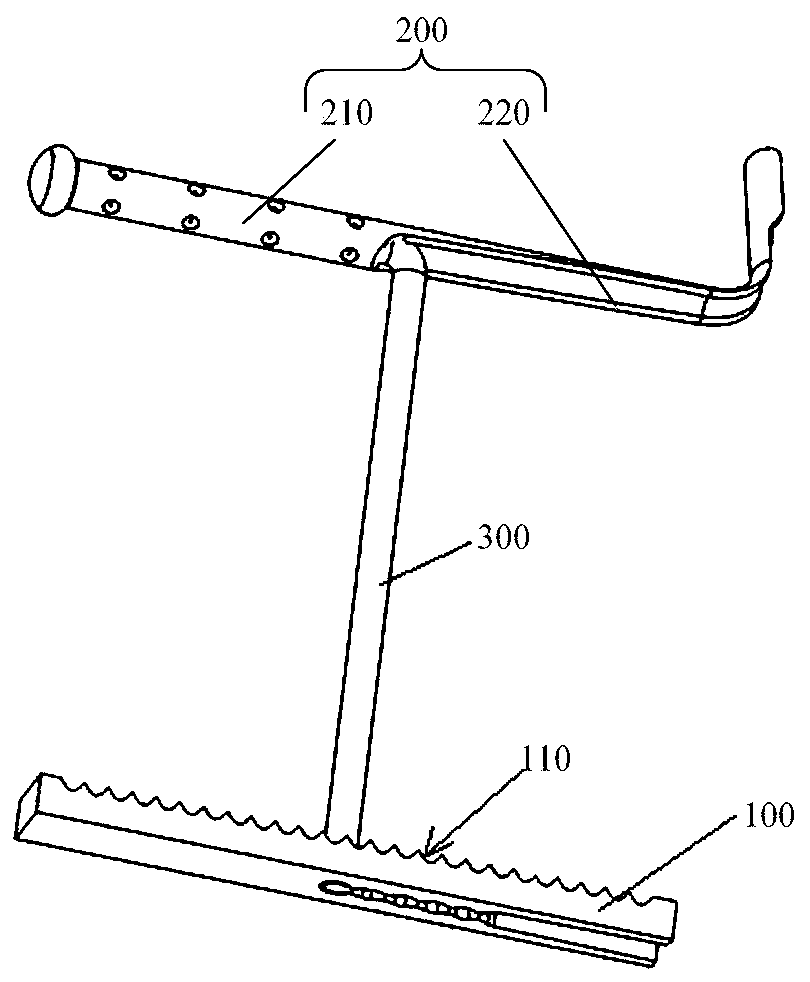
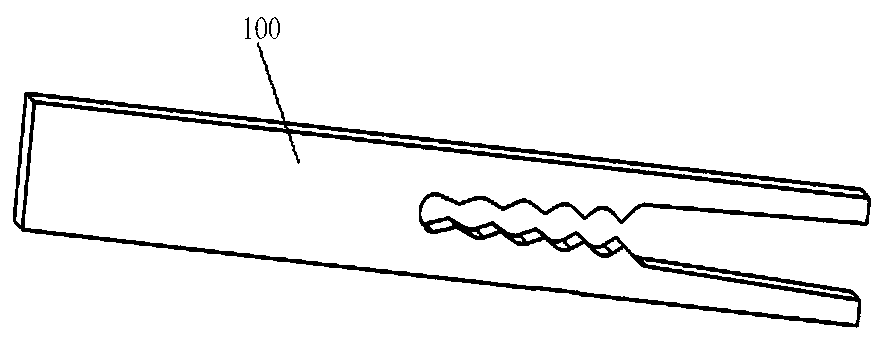
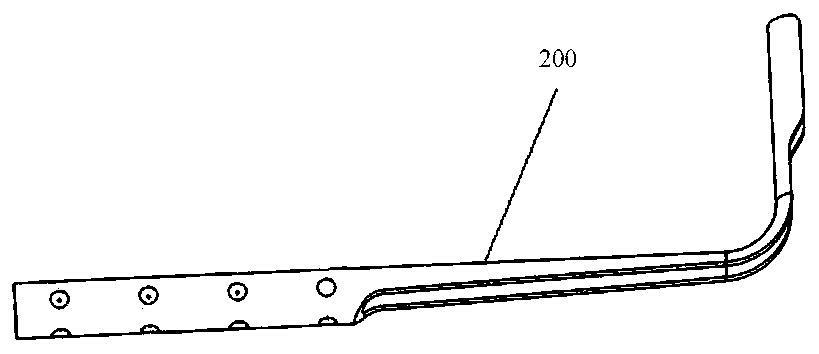
[0063] This embodiment provides an anchoring device. refer to figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 , figure 1 is a schematic structural view of the anchoring device in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 2 and image 3 They are schematic structural diagrams of the proximal anchor 100 and the distal anchor 200 in the anchoring device in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The anchoring device includes the proximal anchor 100, the distal anchor 200 and the connector 300. The end anchor 100 includes a contact surface 110 and a non-contact surface. The contact surface 110 is used to contact the tissue. The contact surface 110 includes at least one concave portion and / or at least one convex portion. The concave portion or the convex portion includes but is not limited to Groove, pattern, frosted surface, etc. The connecting part 300 includes a first connecting part and a second connecting part extending from one end of the first connecting part, the second connecti...
Embodiment 2
[0083] This embodiment provides an anchoring device, and the anchoring device in this embodiment is a further improvement on the anchoring device in Embodiment 1. refer to Figure 14 and Figure 15 , Figure 14 and Figure 15 They are two structural diagrams of the proximal anchor 100 in the anchoring device in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In this embodiment, the first protrusion 112 includes at least one second groove 113 .
[0084] Since the first protrusion 112 includes at least one second groove 113 . Therefore, the roughness of the contact surface 110 can be further increased, thereby further increasing the frictional resistance of the proximal anchor 100 relative to tissue movement, thereby further improving the wall-attachment performance of the proximal anchor 100 and reducing the relative resistance of the proximal anchor 100. The risk of tissue displacement further improves the anchoring stability of the anchoring device; the contact area between the co...
Embodiment 3
[0093] This embodiment provides an anchoring device. The difference between the anchoring device in this embodiment and the anchoring device in Embodiment 1 is that, refer to Figure 16 , Figure 16 It is a structural schematic diagram of the proximal anchor 100 in the anchoring device in the third embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the concave portion includes a plurality of third grooves 115 provided on the contact surface 110 .
[0094] Such as Figure 16 As shown, a plurality of third grooves 115 are distributed in a dot shape. The shape of the third groove 115 on a section perpendicular to the contact surface 110 may be V-shaped, U-shaped or rectangular. The third groove 115 has a circular shape on a cross section parallel to the contact surface 110 . In other embodiments, the shape of the third groove 115 on a cross section parallel to the contact surface 110 may be an ellipse. Preferably, the plurality of third grooves 115 are evenly distribut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com