Mechanical arm and surgery robot
A robotic arm and medical device technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of heavy mechanical arm structure, low stability, and poor flexibility, and achieve the effects of reducing difficulty, small overall size, and easy installation and use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
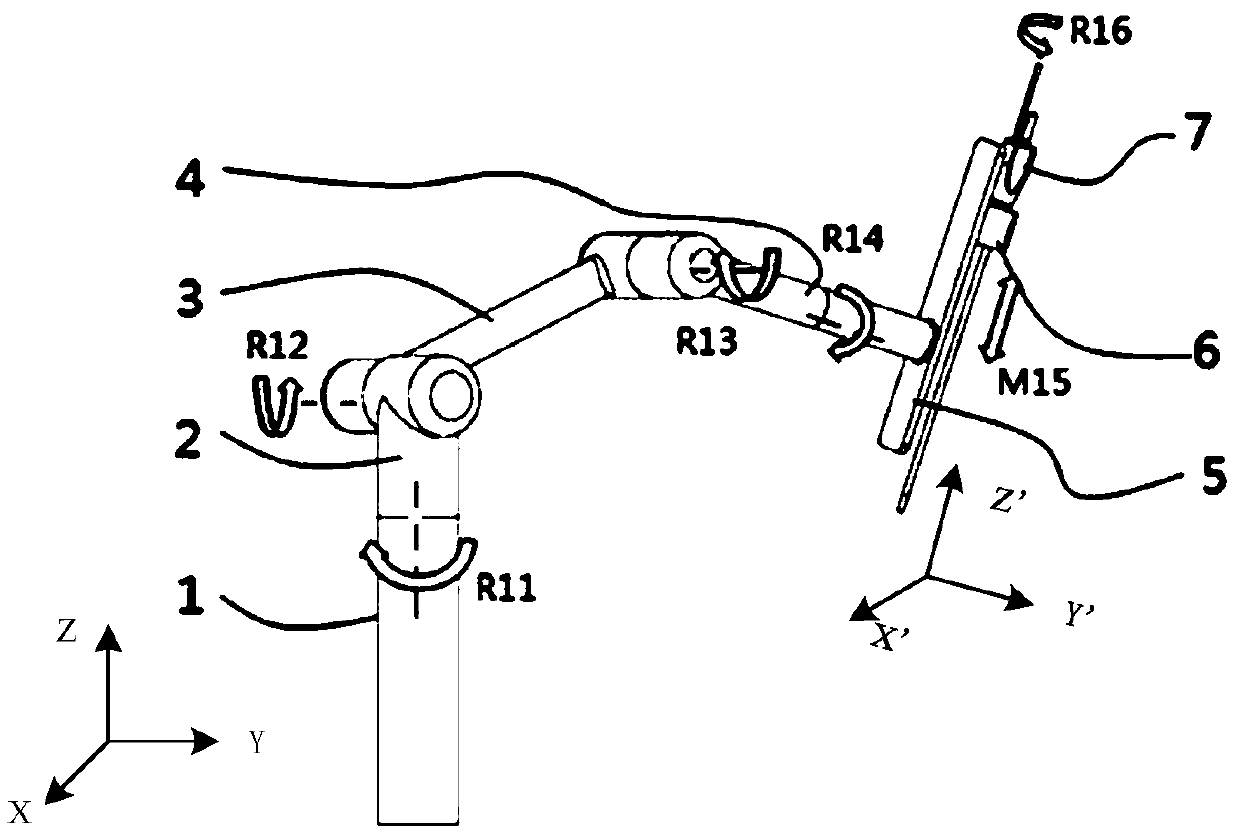
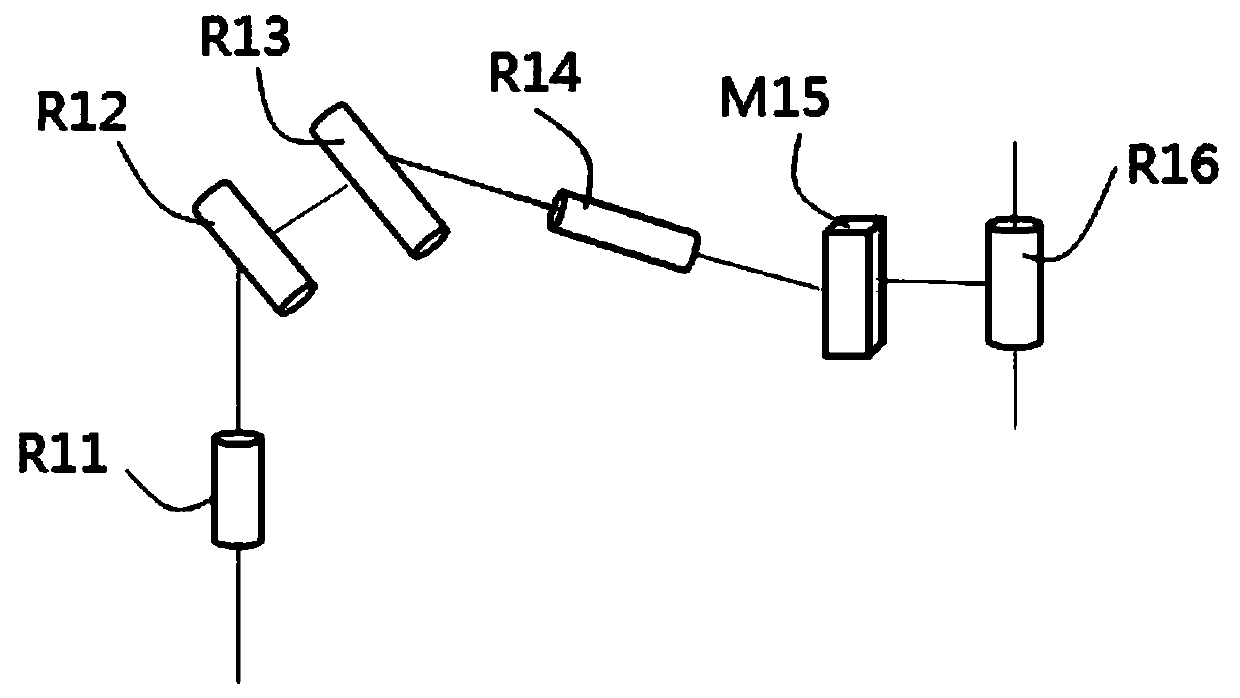
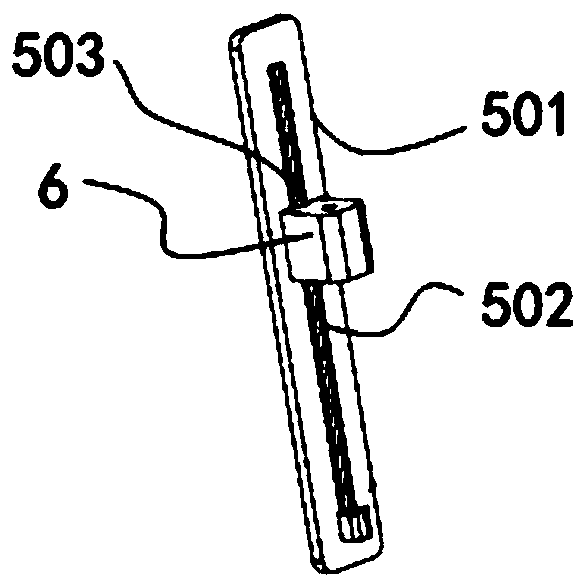
[0059] Please refer to Figure 1 to Figure 5 ,in, figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of the robotic arm provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 2 yes figure 1 The schematic diagram of the degrees of freedom of the manipulator shown, image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the connection between the telescopic structure and the endoscope clamping structure provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention, Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the surgical robot adjusting the endoscope in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the endoscope driven by the surgical robot to swing in the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0060] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the first embodiment provides a mechanical arm for clamping medical instruments, the end of which is connected to the endoscope 7, specifically connected to the endoscope 7 in a detachable manner, so as to adjust the space of the end...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Please refer to Figure 6 to Figure 8 ,in, Figure 6 It is a schematic structural diagram of the mechanical arm provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, Figure 7 yes Figure 6 A schematic diagram of the joints of the robotic arm shown, Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of the endoscope driven by the surgical robot to swing in the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0075] The mechanical arm of the second embodiment of the present invention is basically the same as that of the first embodiment, the same parts will not be described, and only the differences will be described below.
[0076] Such as Figure 6 and Figure 7 As shown, the mechanical arm also includes a fourth connecting rod 8, the distal end of the fourth connecting rod 8 is connected to the telescopic structure 5 through the third swing joint R17, the proximal end is connected to the second rotating joint R14, and the second rotating joint R14 is connected with the far end of th...
Embodiment 3
[0083] This embodiment provides an exemplary method for controlling the movement of the endoscope connected to the end of the above-mentioned robotic arm around a remote center of motion (Remote Center of Motion). Based on the configuration of the robotic arm in the first embodiment, the robotic arm includes a control module, a position acquisition module, and a drive module (not shown). The position acquiring module, the driving module are connected in communication with the control module. The position acquiring module is used to acquire each joint (that is, the first rotational joint R11, the first swing joint R12, the second swing joint R13, the second rotational joint R14, the moving joint M15 and the rotation joint R16 in the first embodiment) the current location of . The driving module is used to drive the above-mentioned joints to move. The control module includes an active mode and a passive mode. In this active mode, the control module controls the movement of ea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com