Anticancer peptide recognition method based on fusion of random forests and related vector machine
A technology of correlation vector machine and random forest, which is applied in the field of anti-cancer peptide identification based on the fusion of random forest and correlation vector machine, can solve the problems of improving efficiency, time-consuming, expensive, etc., and achieve the effect of improving efficiency and reducing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
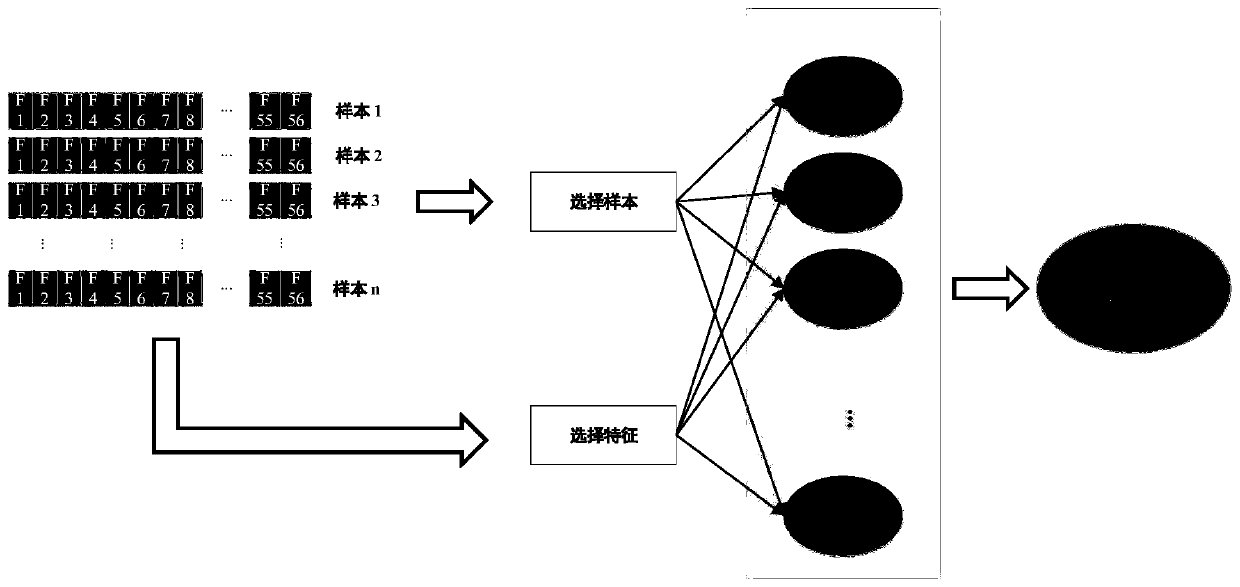
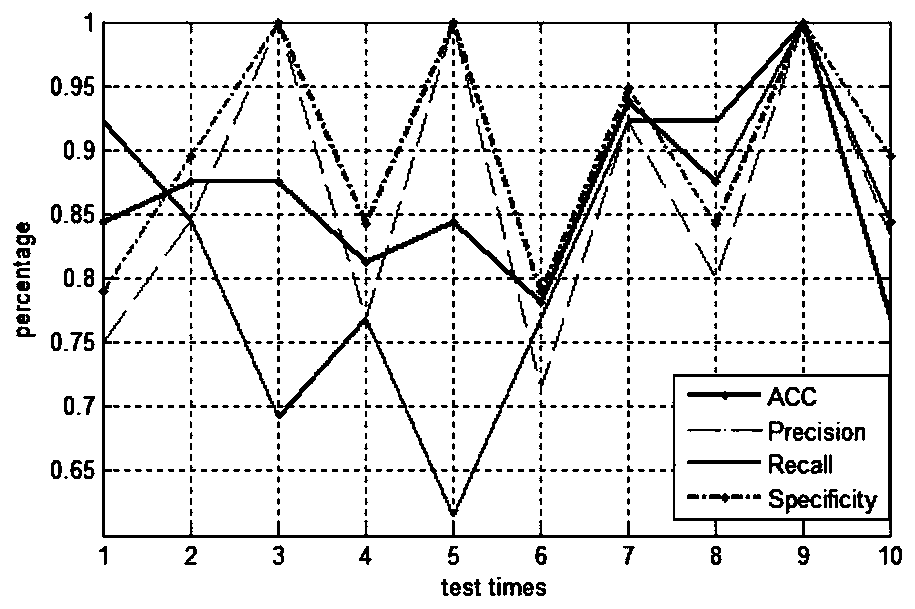
[0053] according to figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for identifying anticancer peptides based on random forest and correlation vector machine fusion, comprising the following steps:
[0054] Step 1: perform feature extraction on the composition of amino acids, determine the average percentage of each amino acid in ACP and non-ACP, and determine the sequence characteristics of ACP;
[0055] The step 1 is specifically:
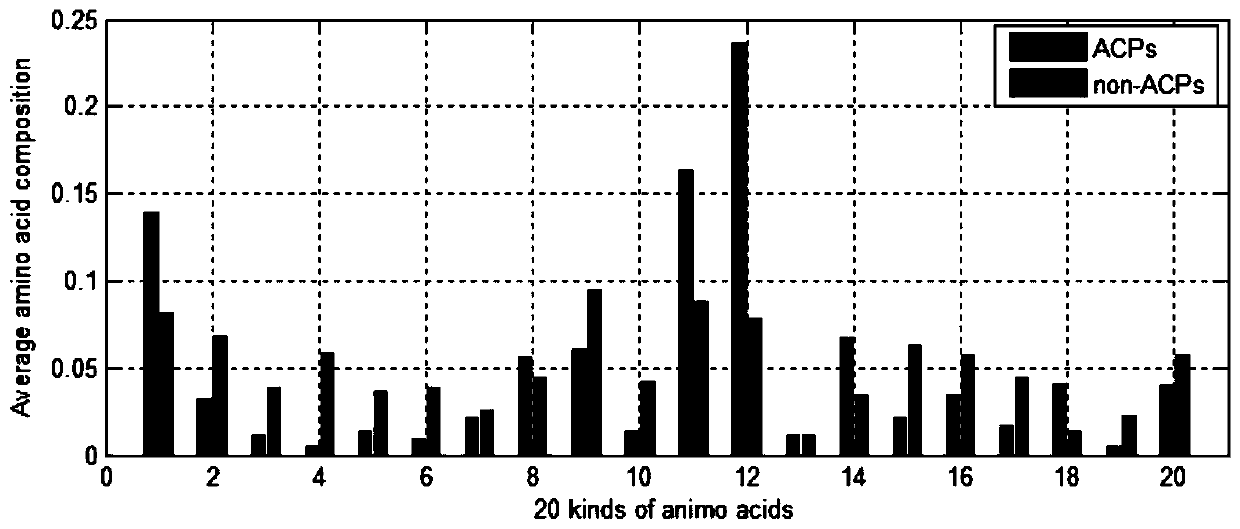
[0056] Step 1.1: Extract the features of the composition of amino acids. Since the composition of ACP and non-ACP is different, the frequency of occurrence of all 20 amino acids in the peptide will be complete. Differently draw the average amino acid composition map to distinguish the difference between ACP and non-ACP. Determine the average percentage of each amino acid in ACP and non-ACP;
[0057] Step 1.2: Amino acids are divided into 6 categories according to their hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity, which are strong hydrophilicit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com