Vehicle cooling apparatus
A technology for cooling devices and vehicles, which is applied in the direction of power devices, liquid cooling, and vehicle components, and can solve problems such as increased compressor power and increased power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0027] Hereinafter, a first embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. The vehicle cooling device of the present embodiment is applied to an electric vehicle equipped with a rechargeable secondary battery. In addition, the vehicle cooling device performs air-conditioning control in the vehicle interior by a heat pump cycle, and cools a heating element by a cooling cycle.
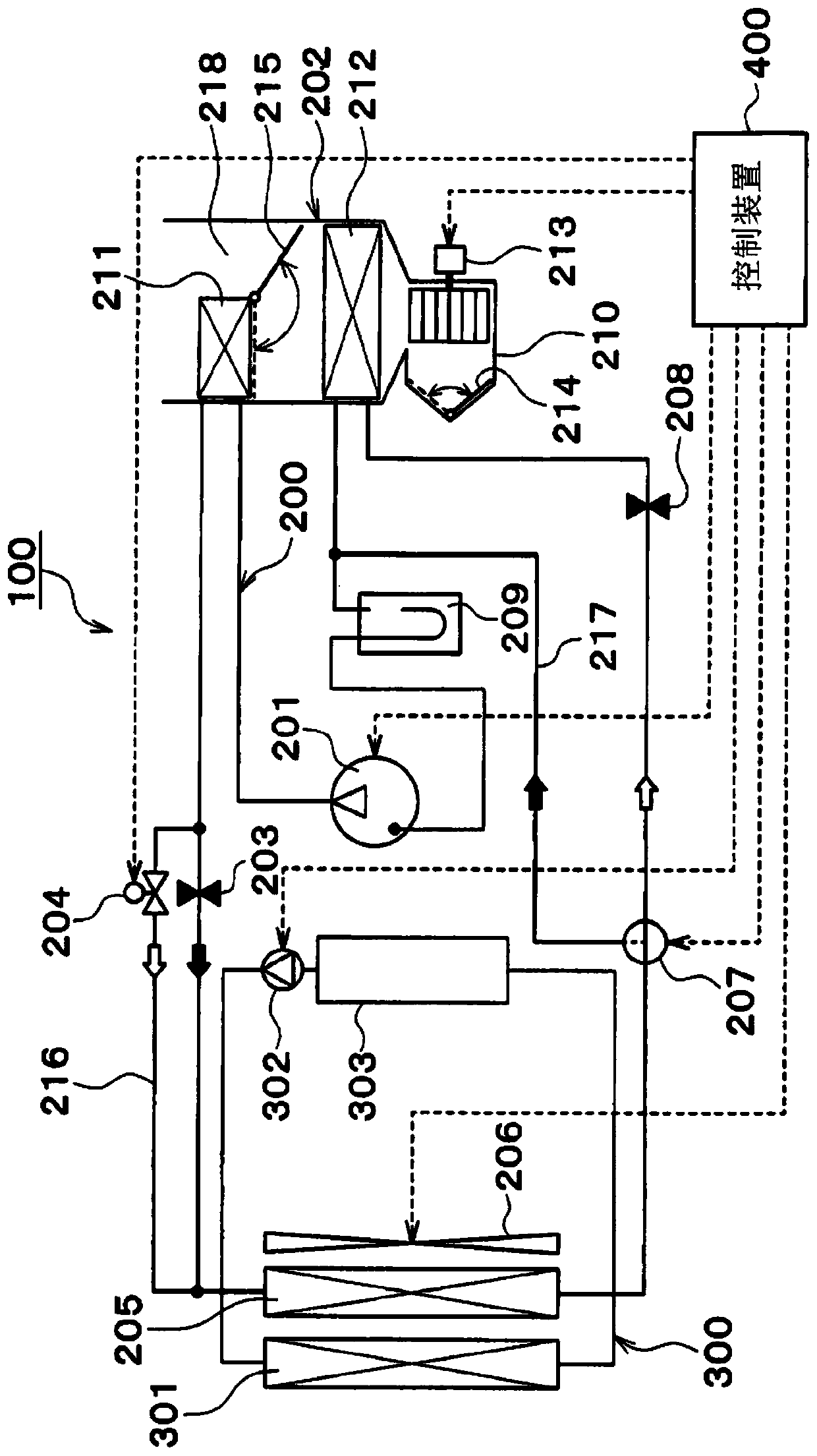
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, the vehicle cooling device 100 includes a heat pump cycle 200 , a cooling cycle 300 , and a control device 400 .
[0029] The heat pump cycle 200 is a refrigeration cycle that heats or cools the vehicle interior supply air that is blown into the vehicle interior, which is a space to be air-conditioned. The heat pump cycle 200 performs a heating operation and a cooling operation by switching the refrigerant flow path. The operation in which the air supplied to the vehicle interior is cooled to cool the interior of the vehicle.
[0030] Specifically, the ...
no. 2 approach
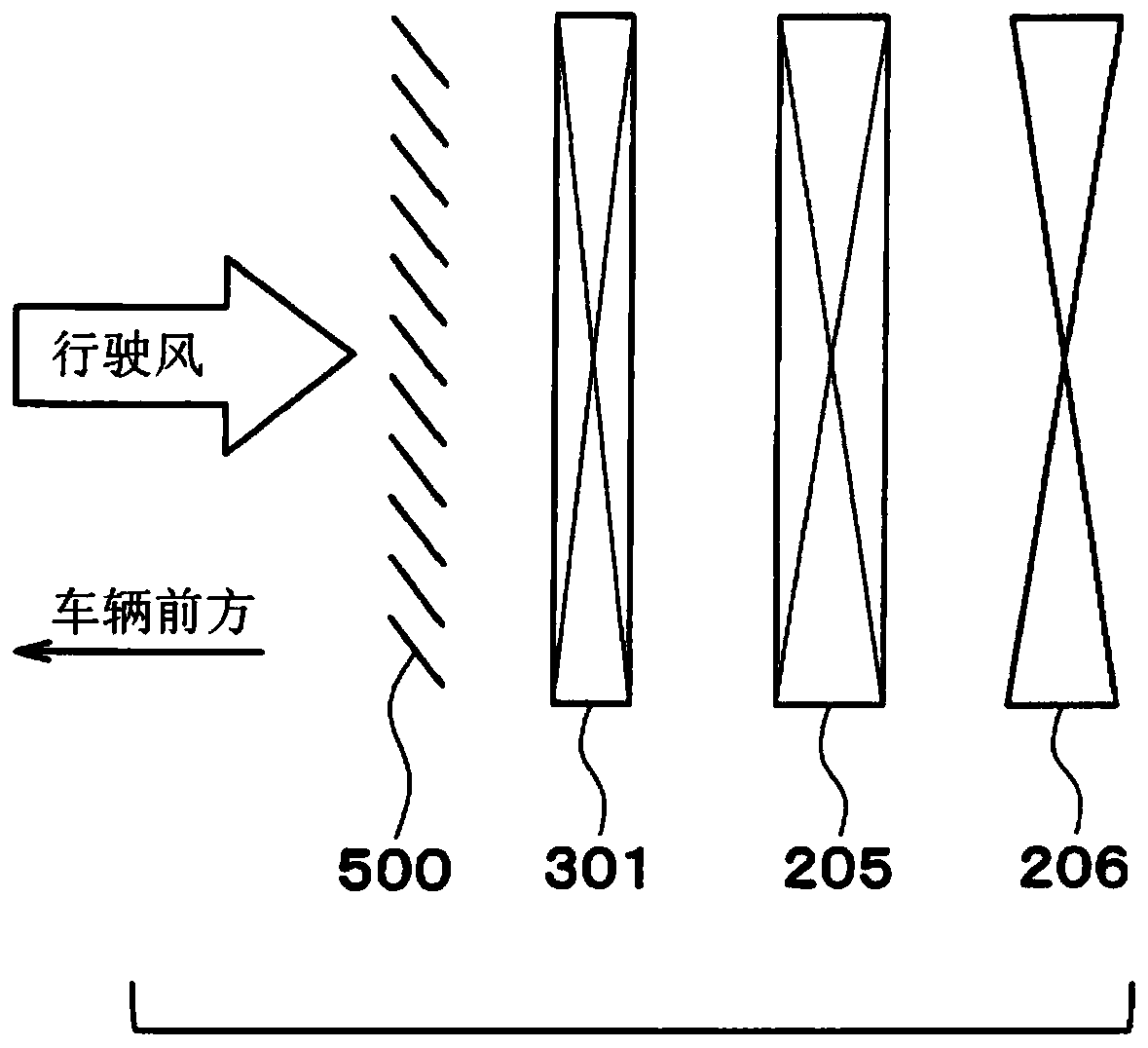
[0081] In this embodiment, differences from the first embodiment will be described. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the cooling cycle 300 includes a first cooling cycle 304 and a second cooling cycle 305 . In addition, in Figure 5 Devices other than the outdoor heat exchanger 205 in the heat pump cycle 200 are omitted here. In addition, the control device 400 is omitted.
[0082] The first cooling cycle 304 is a circuit for circulating cooling water through the first flow path 306 and the second flow path 307 . The first flow path 306 and the second flow path 307 are connected by a first connection part 308 and a second connection part 309 .
[0083] The first flow path 306 has a first radiator 310 and a first supply machine 311 . The first supply machine 311 makes cooling water flow from the first connection part 308 to the second connection part 309 through the first radiator 310 . The first feeder 311 is controlled by the control device 400 .
[0084] The second flow pa...
no. 3 approach
[0103] In this embodiment, differences from the second embodiment will be described. Such as Figure 8 As shown, the first cooling cycle 304 has a detour flow path 330 and a solenoid valve 331 .
[0104] The detour channel 330 is provided in parallel with the first radiator 310 and bypasses the first radiator 310 . That is, the detour flow path 330 is a flow path connecting the inflow side of the first radiator 310 and the inflow side of the first supply machine 311 .
[0105] The solenoid valve 331 is provided in the bypass flow path 330 . The solenoid valve 331 is controlled by the control device 400 to adjust the flow rate of the cooling water flowing to the bypass flow path 330 .
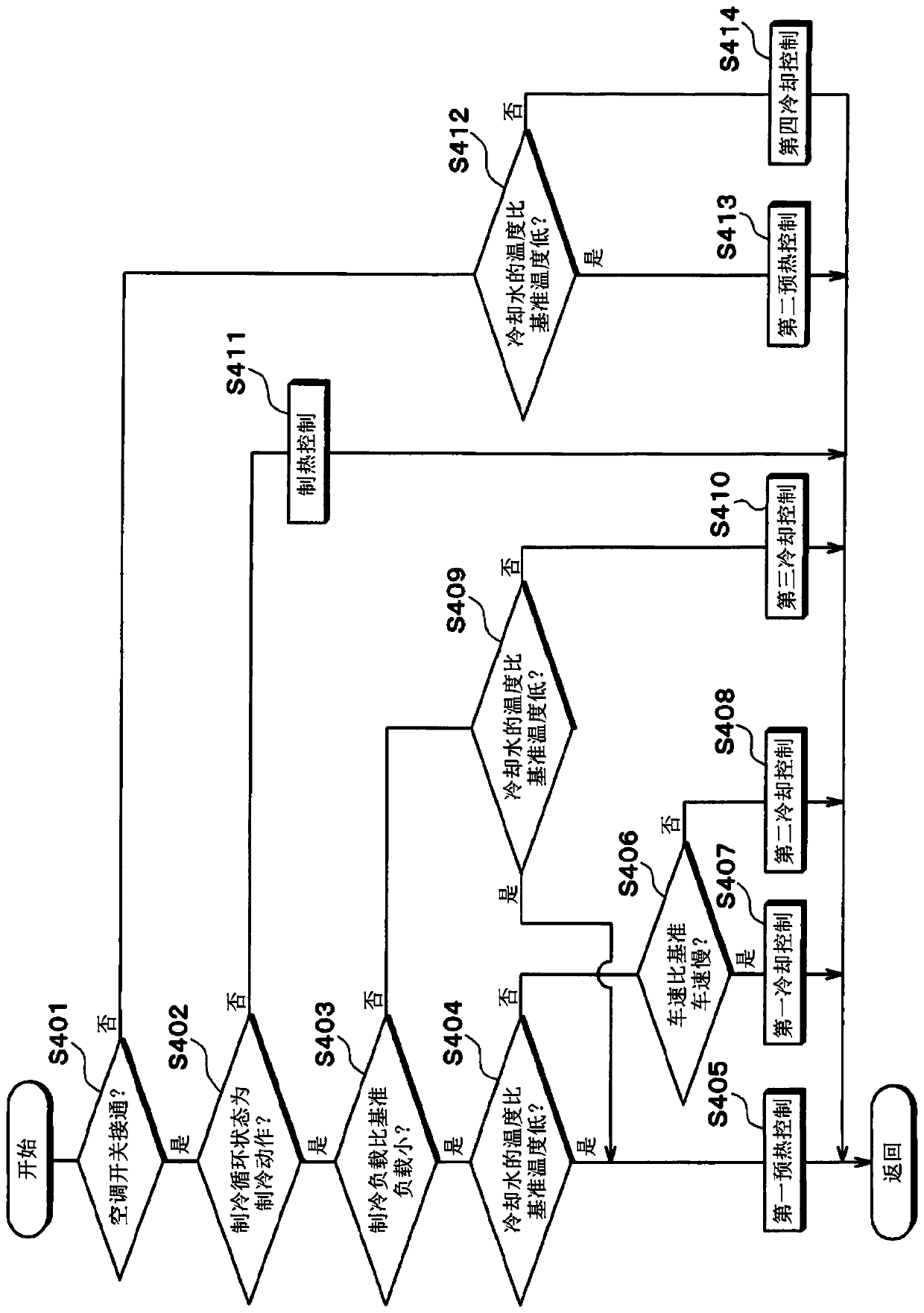
[0106]In the cooling cycle 300 described above, when the outdoor heat exchanger 205 is made to function as a condenser according to the air conditioner request, the control device 400 obtains the temperature of the cooling water, and repeatedly executes the preheating mode and the cooling mod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com