Error correction method based on raid information, computer-readable storage medium and processor
An error correction method and storage medium technology, applied in the field of data storage, can solve the problem of difficult to meet the error correction capability requirements of TLC and QLC flash memory, and achieve the effect of improving error correction capability and prolonging life cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
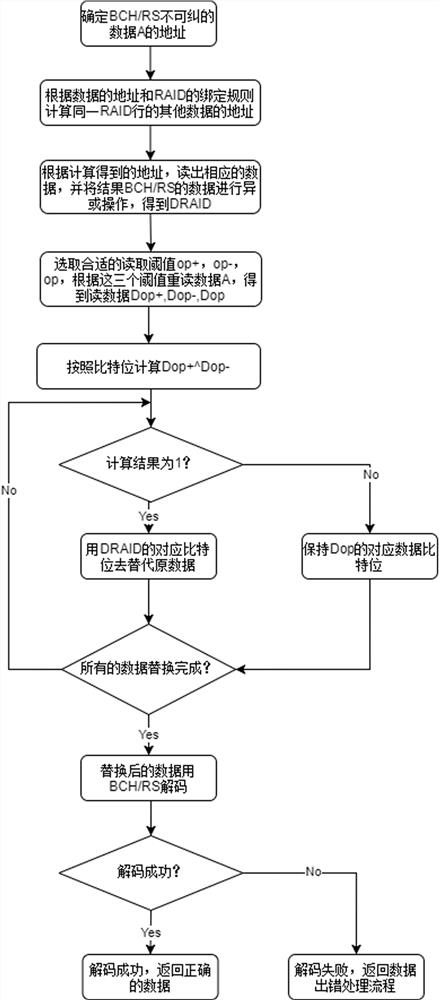
[0031] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides an error correction method based on RAID information. In this embodiment, there is no limitation on which level of RAID structure is used in the flash memory controller, as long as the constraints described below are met.
[0032] Let the check code data be XOR, said XOR=DATA1^DATA2^DATA3^...^DATAN, wherein the number of N is not limited.
[0033] Specifically, such as figure 1 As shown, the error correction method based on RAID information described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0034] Step 1. When a BCH or RS uncorrectable error occurs in the flash memory particle, record the address of the uncorrectable error data A. Among them, the uncorrectable error can be obtained by conventional methods, such as saving the error location by software, here No longer described in detail.
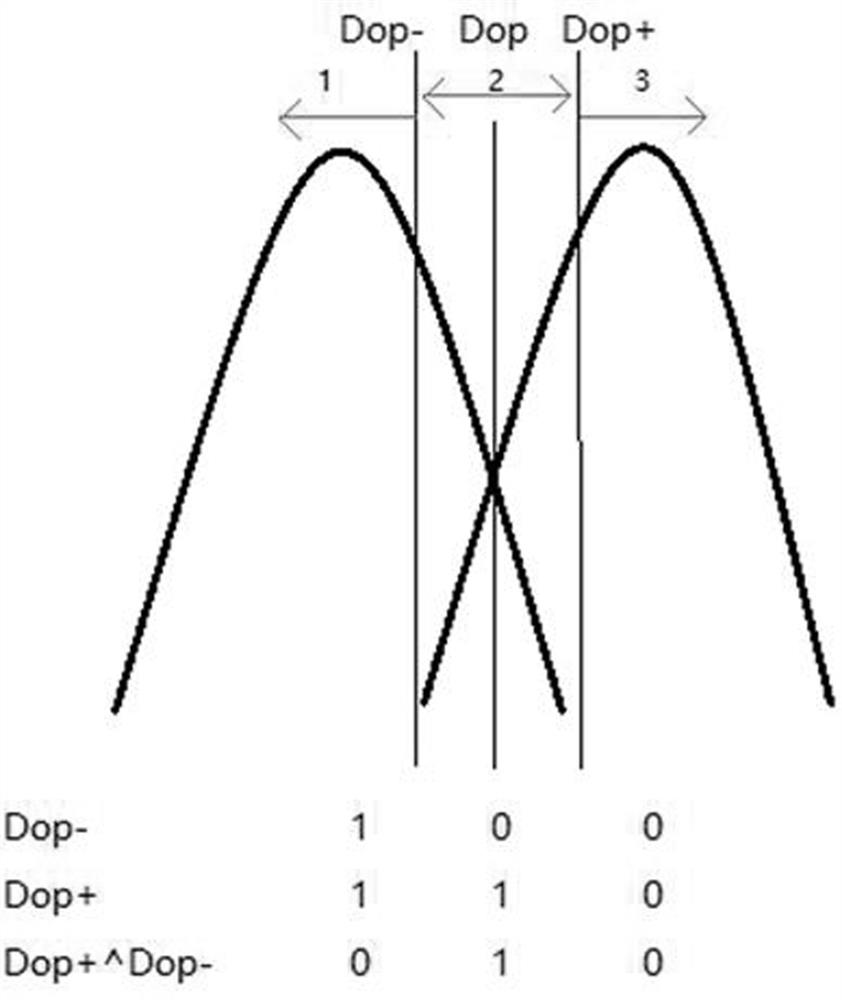
[0035] Step 2: Calculate the value DRAID obtained through RAID recovery.
[0036] In traditional RAID recovery, except for ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This embodiment provides a computer-readable storage medium, where the storage medium includes a stored program, wherein the error correction method based on RAID information described in Embodiment 1 is executed when the program is running.
Embodiment 3
[0053] This embodiment provides a processor, and the processor is configured to run a program, where the program executes the error correction method based on RAID information described in Embodiment 1 when running.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com