Satellite navigation signal design method based on pseudo-random Chirp
A satellite navigation signal and design method technology, applied in satellite radio beacon positioning systems, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate carrier phase and long capture time of navigation signals, etc., to reduce multiple access interference, Shorter capture time and effects of Doppler tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
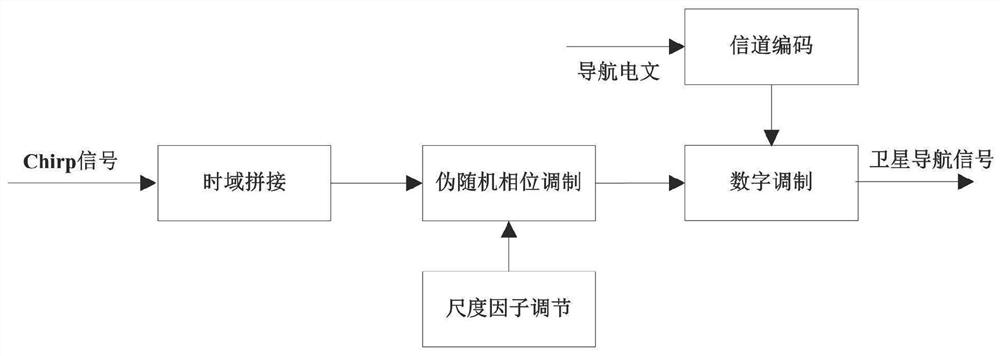
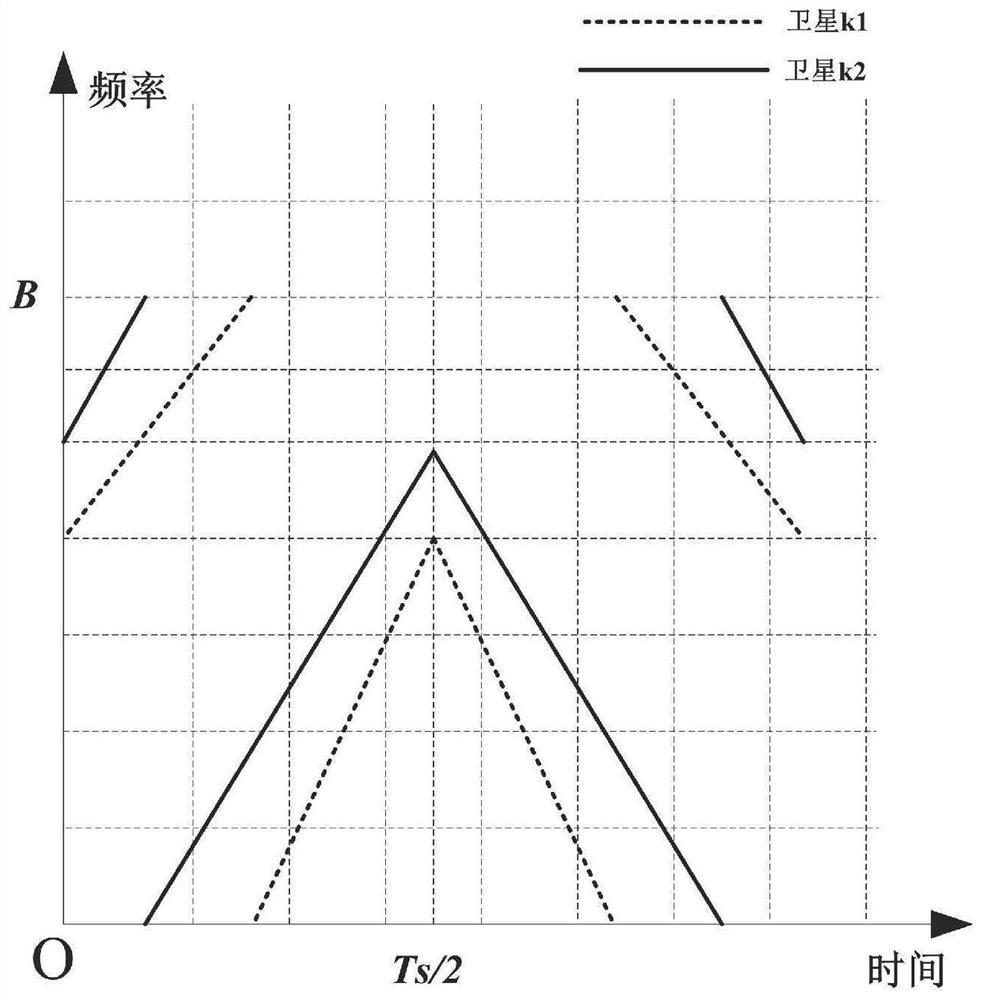
[0032] In order to meet the multiple access performance of satellite navigation signals in the present invention, the navigation signal reference signal of each satellite is spliced by two sections of Chirp signals with the same symbol duration and the same spectrum width but completely opposite modulation frequencies, wherein each section of the Chirp signal It is also spliced by two Chirp signals with the same modulation frequency but different starting frequencies. The spliced reference signals of different satellites all have the same symbol duration and symbol bandwidth, but have different starting frequencies or modulation frequencies. figure 2 A schematic diagram of the time-frequency characteristics of two satellite reference signals is given.
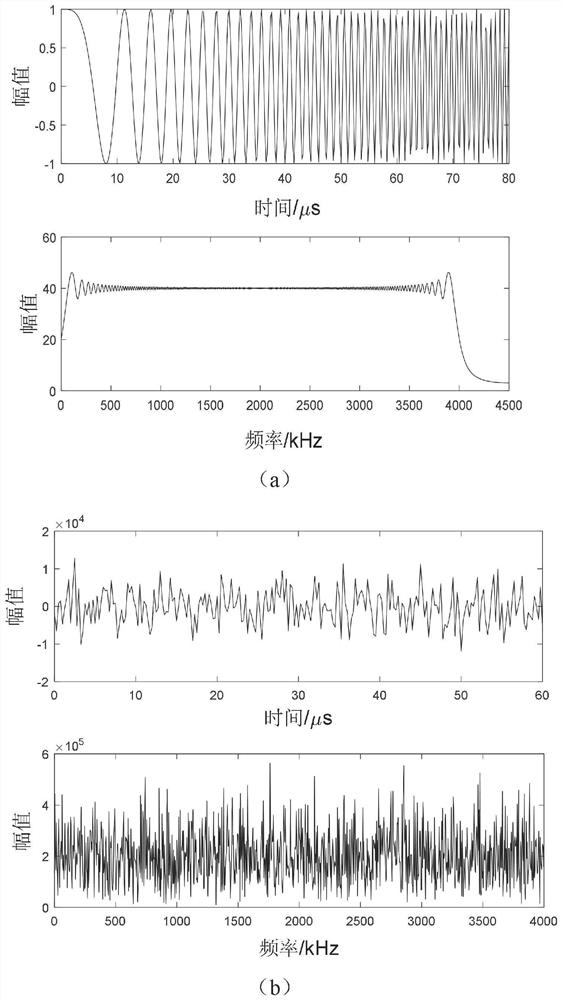
[0033] Secondly, in order to improve the security of the navigation signal and further redu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com