Multi-block fault monitoring method based on fault sensitive slow characteristics
A fault monitoring and slow feature technology, applied in electrical testing/monitoring, testing/monitoring control systems, instruments, etc., to solve the problems that fault monitoring methods cannot be dynamic and large-scale process monitoring.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
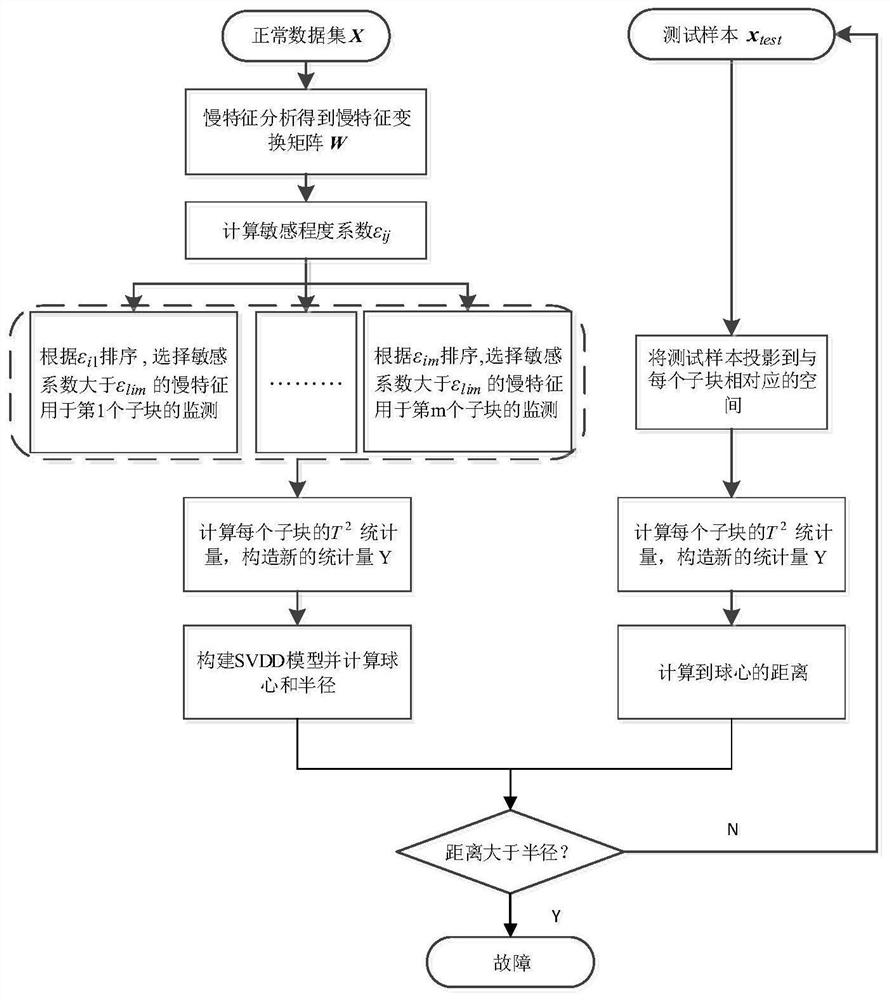
[0068] refer to figure 1 , provides a schematic diagram of the overall structure of a multi-block fault monitoring method based on fault-sensitive slow features, such as figure 1 , a multi-block fault monitoring method based on fault-sensitive slow features includes steps,
[0069] S1: collect data in the industrial production system, and divide the obtained data into training set and test set;
[0070] S2: Perform slow feature analysis on the training set, and calculate the slow feature transformation matrix;
[0071] S3: Define the fault sensitivity coefficient, and obtain the sensitivity of each slow feature to fault from the coefficient in the slow feature transformation matrix;
[0072] S4: Define the fault sensitivity threshold, select the fault-sensitive slow feature for each dimension variable of the training set, and use it as a training sub-block;
[0073] S5: Calculate the fault statistics for each training sub-block separately, and use the support vector data de...
Embodiment 2
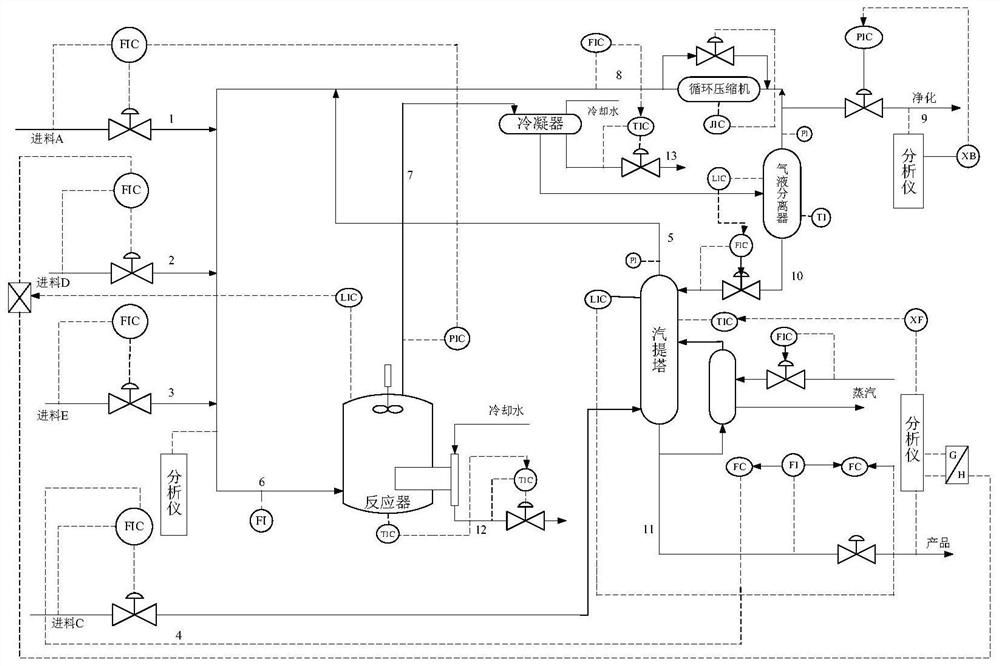
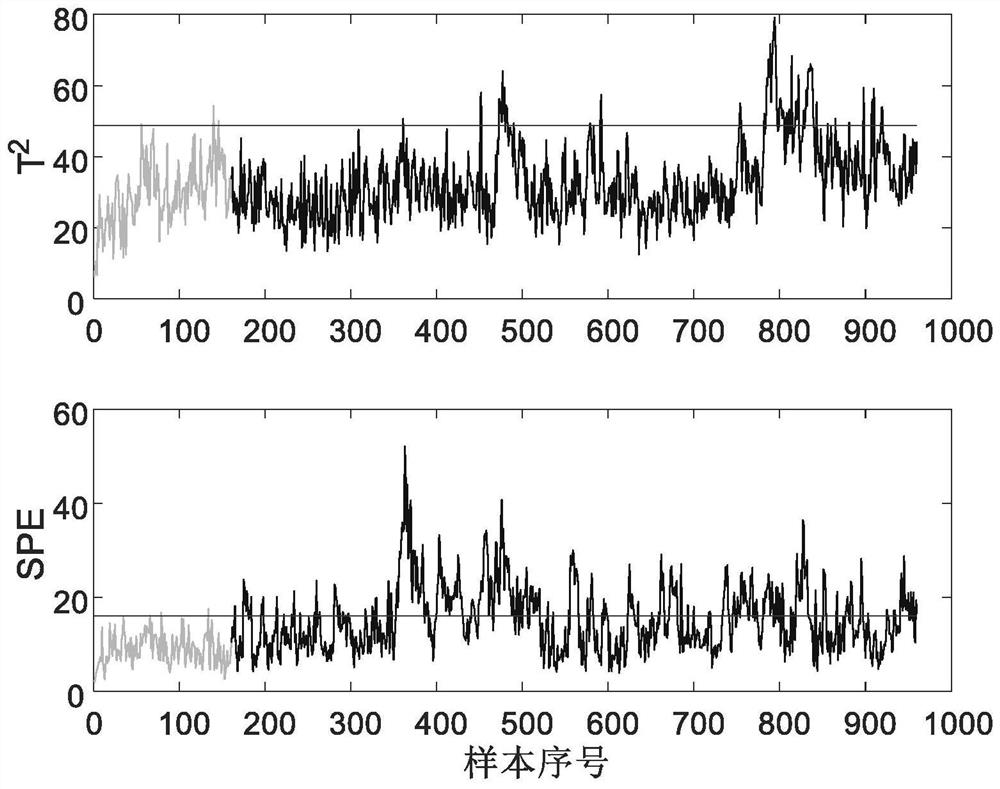
[0150] In order to verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method, five main units were built on the Tennessee-Eastman (TE) software platform: reactor, condenser, compressor, separator and stripper ,Such as figure 1 As shown, the simulation model contains 22 process measurement variables, 19 component measurement variables, and 12 operation variables. It should be noted that the TE process model is a realistic industrial process created by Eastman Chemical Company and used to evaluate process control and monitoring methods ;A total of 21 different types of faults were preset in the TE process, the types of faults include step change, random change, slow drift, and valve stickiness, of which 16 are known faults and 5 are unknown faults; normal The 960 samples under working conditions are used as the training data set, and the 960 samples under the fault condition are used as the fault test set. The faults are all introduced from the 161st sample point. Table...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com