Self-learning speed control method based on active observation of load change rate
A load change and control method technology, applied in engine control, electrical control, fuel injection control, etc., can solve problems such as poor quality of speed control, improve robustness, reduce calibration workload, and avoid control performance degradation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
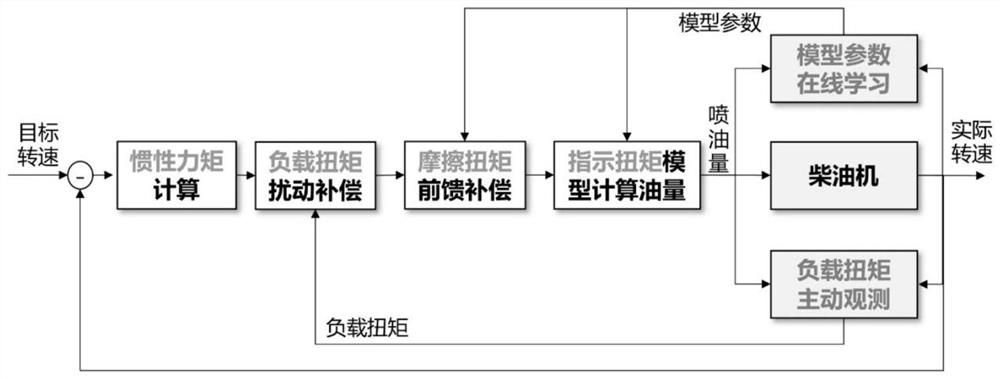
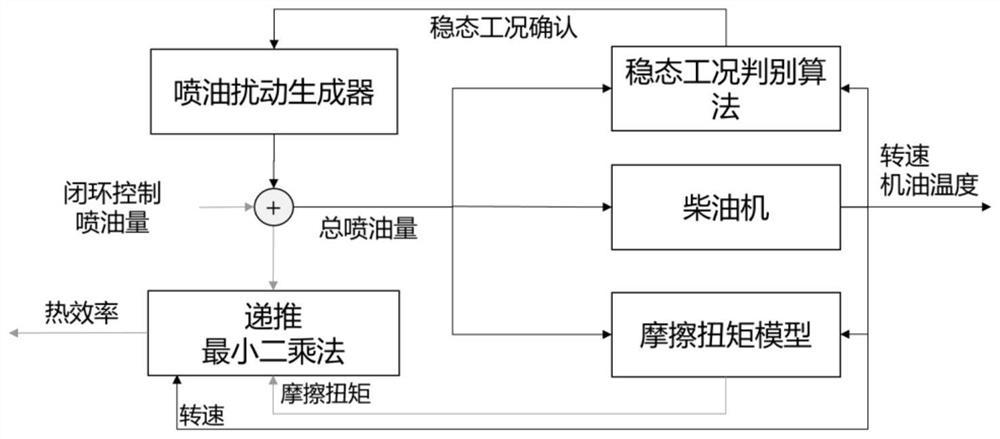
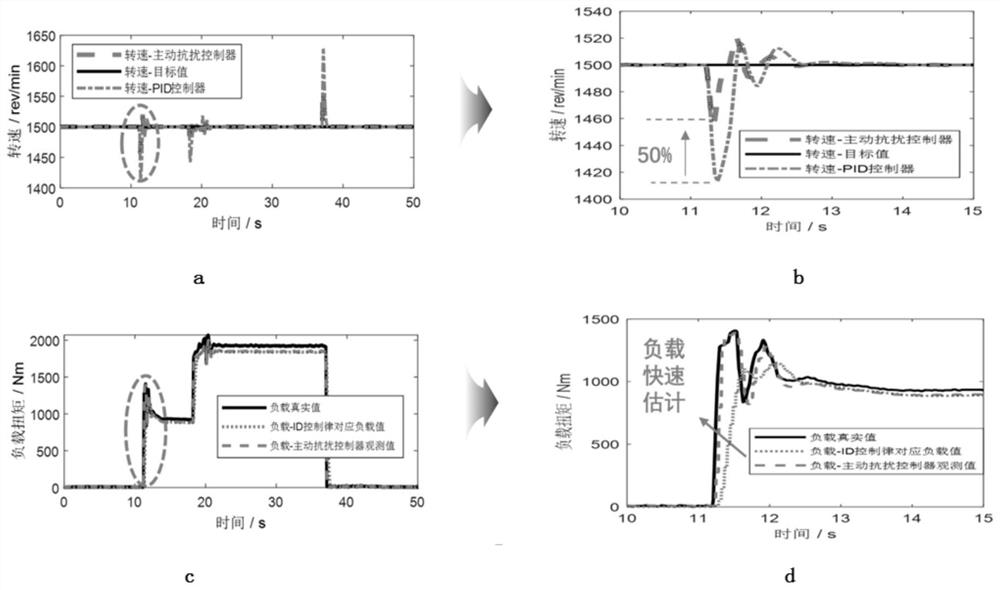
[0045] Based on the engine rotation speed variation rate active load observed self-learning control method, comprising the steps of:
[0046] Step 1, according to the engine rotational speed and the target engine rotation speed deviation of the actual rotation moment of inertia calculations required by feedback control; friction torque is estimated using the current model friction torque, and a friction torque;
[0047] Step 2, the rotational speed of the engine for the dynamic process, based on the dynamic speed, the load torque increases and the load torque variation rate two "expanded state";
[0048] Step 3, using the method of reduced-order extended state observer, in combination with the friction torque, rotation speed, load torque and load torque variation rate online observations to obtain an estimated value of load torque;
[0049] Step 4, step 1 to give the rotational moment of inertia based on the estimated value observed using a 3 step do load torque compensation, to g...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Further, the step 1, the rotational moment of inertia u 0 The calculation method is:
[0057] U 0 = K p (Ω ref -ω) (1)
[0058] Where: ω ref Target engine rotational speed (unit: rpm), ω is the actual engine speed (unit: rpm), the engine may be a diesel engine, k p Is a proportional coefficient, the rotational speed may be adjusted in response to the required speed.
[0059] Further, the differential equation model in Step 2, the engine speed is increased two "expanded state", the rotational speed to obtain a dynamic model with an expanded state:
[0060] Rewrite the equation (2):
[0061]
[0062] Where, ω is the actual engine speed (unit: rpm), Representative derivative of the actual engine speed, J is the moment of inertia of crankshaft rotation system (unit: kg · m 2 ), M i Is indicated torque (unit: Nm), M Fri Is the friction torque (unit: Nm), M load A load torque (unit: Nm).
[0063] To simplify the expression (2), so that As an equivalent load torque, the load...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com