A Quantitative Calculation Method of Sea Surface Stress Induced by Rainfall
A quantitative calculation and stress technology, which is applied in design optimization/simulation, instrumentation, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as the quantitative calculation method of rainfall-induced sea surface stress that has not yet been researched, and achieve deepening cognition and understanding, physical well-defined effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
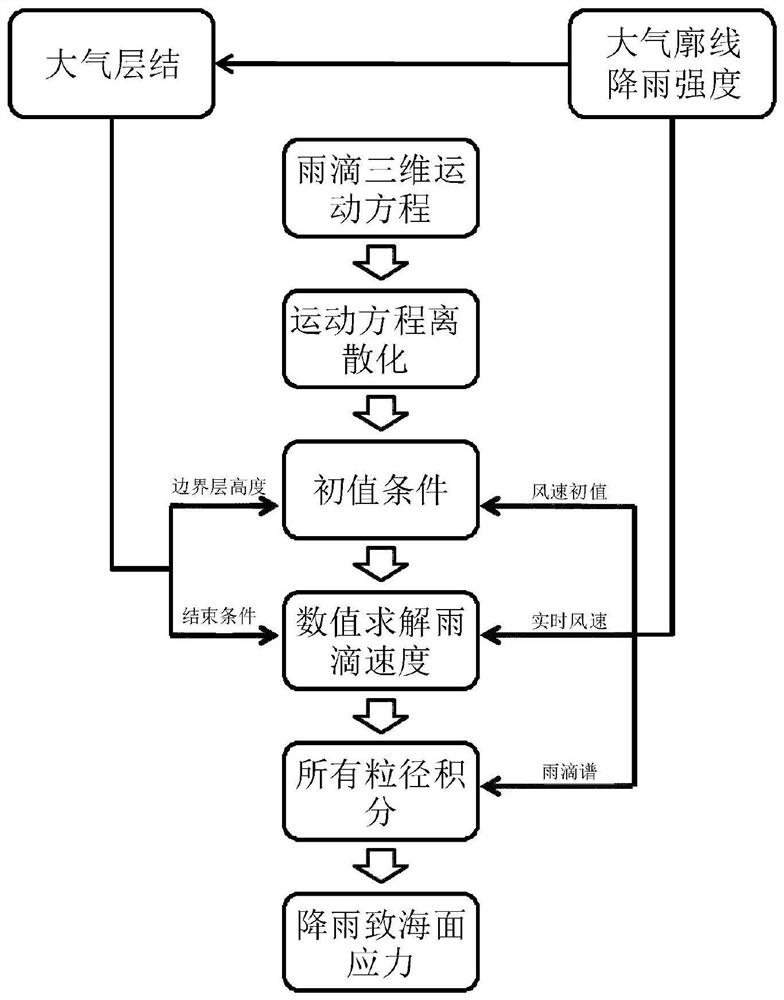
[0038] A method for quantitatively calculating rainfall-induced sea surface stress, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0039] (1) Collect observed or simulated wind speed data and rainfall rates;
[0040] (2) According to Calculate the boundary layer height h, and the height where the minimum value ε is located is the boundary layer height h;
[0041] (3) According to the force analysis of gravity and air resistance in the falling process of raindrops in the boundary layer, the three-dimensional motion model of raindrops with particle size D is established as follows:
[0042]
[0043] in,
[0044]
[0045] (4) Discretize the numerical value of the raindrop three-dimensional motion model equation, and obtain the numerical solution of the raindrop motion velocity:
[0046]
[0047] (5) Substituting the initial value condition in the discrete equation in the step (4), when t=0, satisfy following condition: z=h, u a = u R , v a =v R ,w T =w R ;
...
Embodiment 2
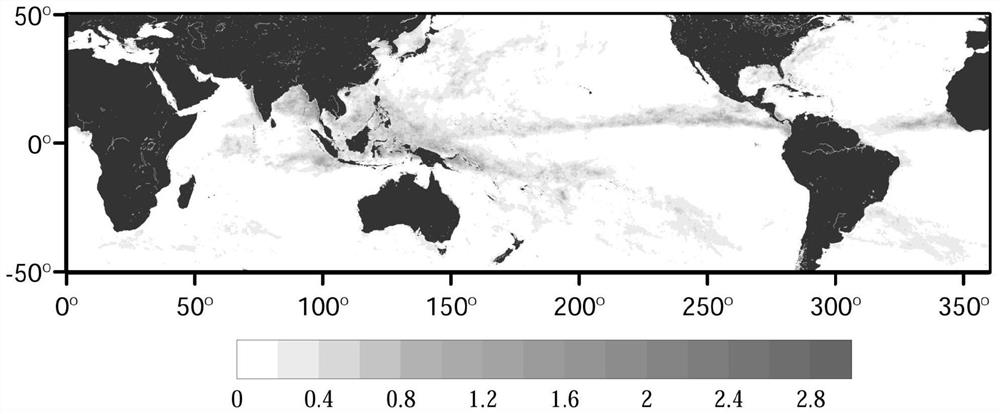
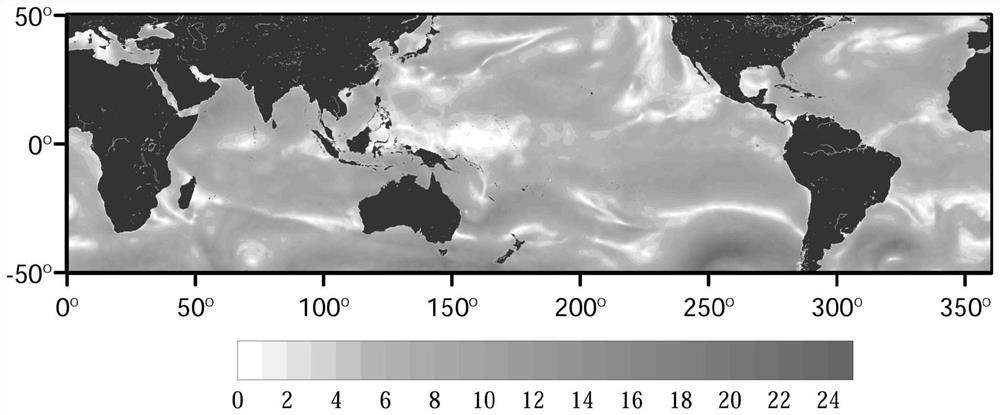
[0053] In this embodiment, the calculation method of the rainfall-induced sea surface stress value is the same as that of Embodiment 1: that is, the scheme provided in Embodiment 1 is used to calculate the rainfall-induced sea surface stress value through TRMM and ERA5 data;
[0054] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment also provides the global distribution of the ratio of rainfall-induced sea surface stress to wind stress. The ratio of rainfall-induced sea surface stress to wind stress is calculated according to the following formula:
[0055]
[0056] Among them, ρ a is the atmospheric density, C d is the sea surface drag coefficient, u 10 is the wind speed at a height of 10 meters.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com