An Analytical Method for Subtracting the Matrix Effect in Determination of Cyclosporin in Whole Blood
An analytical method and technology of matrix effect, applied in the field of analysis, can solve the problems of inaccurate reduction effect, high cost, large consumption of organic solvents, etc., to reduce the analysis operation process and workload, reduce the absolute matrix effect of whole blood, and pre-treatment The effect of process simplification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
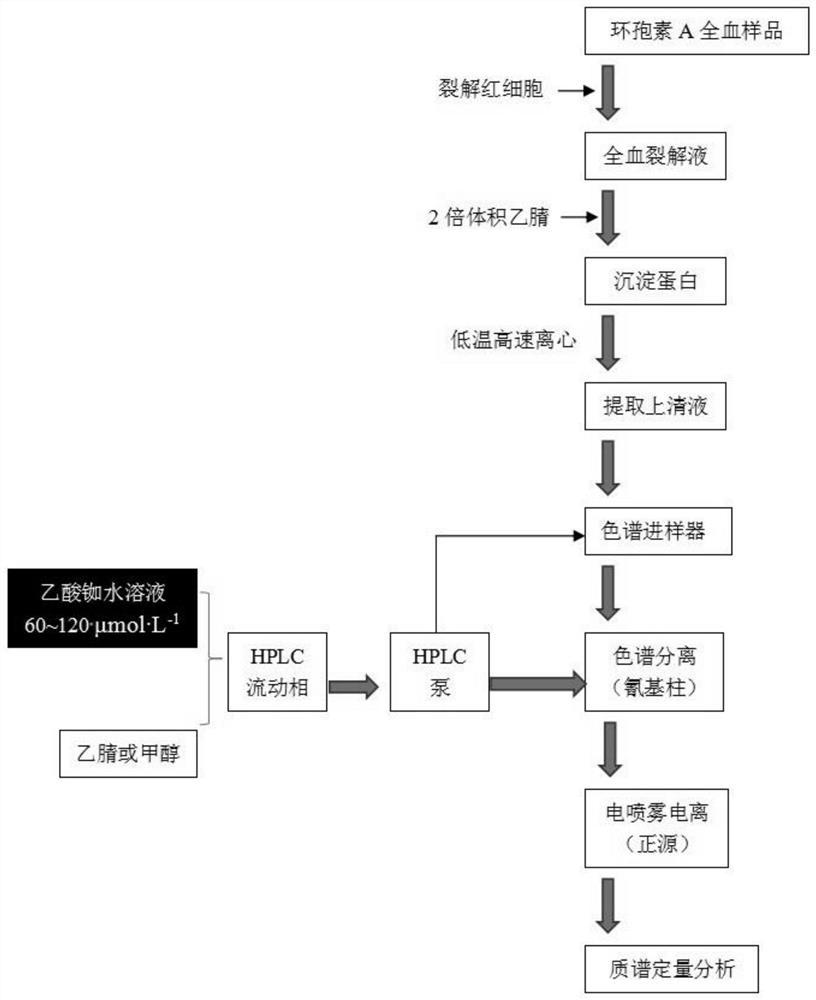
[0081] 1.1.2 Instruments
[0087] The column temperature of the chromatographic column: 40°C. Mobile phase: acetonitrile: rubidium acetate aqueous solution = 45:55 (V / V), flow rate: 0.4 ml·min
[0091] The mass spectrometry data acquisition mode is MRM, the Scan Time is 0.10s, and the Interscan Time is 0.005s. Span
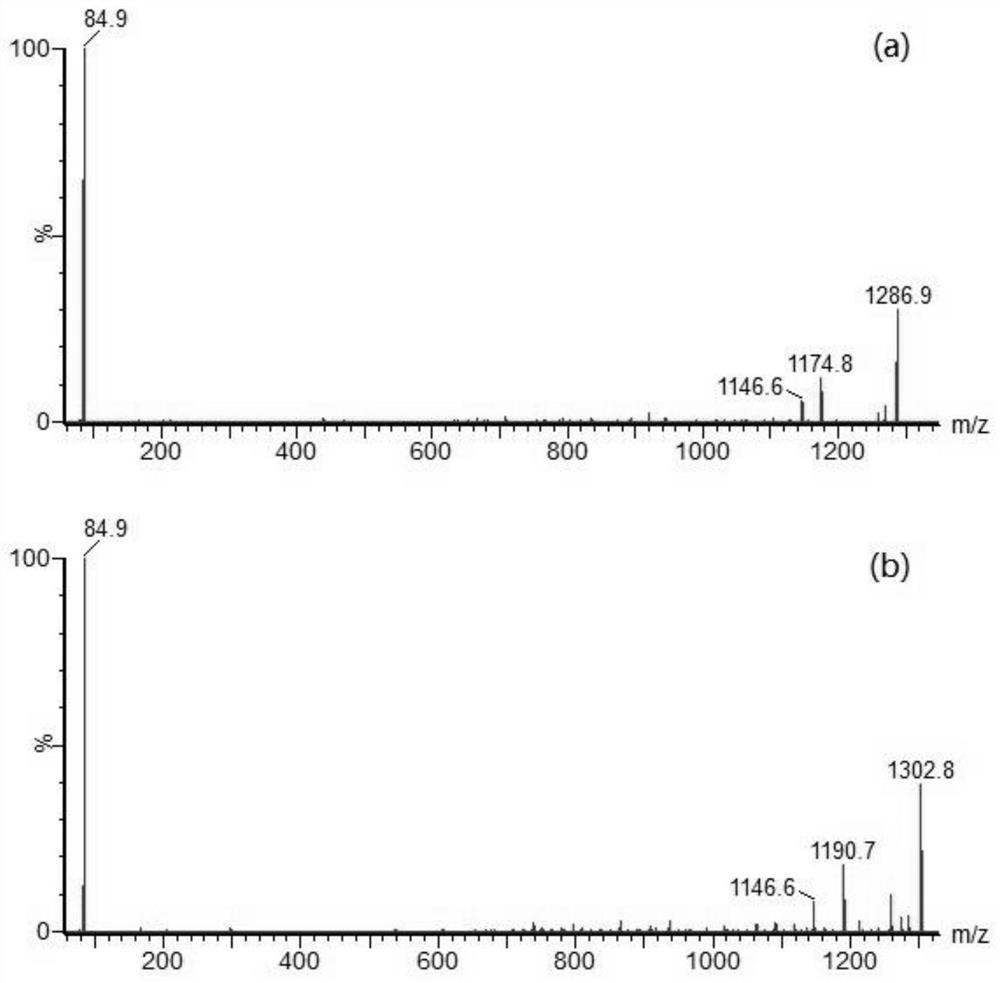
[0093]
[0102] MF=(Set2-Set1)÷S1×100%
[0104] RE=Set3÷Set2×100%
[0105] PE=Set3÷Set1×100%
[0106] According to industry consensus and relevant rules, when absolute MF≤±15%, it can be considered that there is no significant matrix effect. no
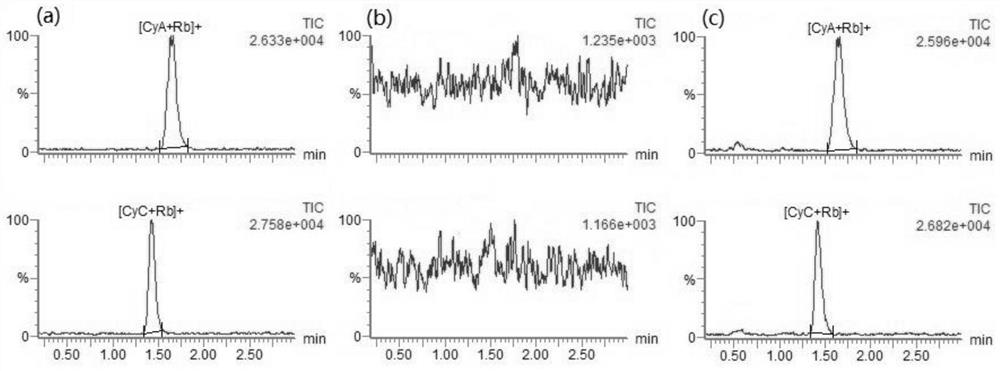
[0112] The matrix effect data of 10 different individual source whole blood sample extracts to CyA and CyC are shown in Table 1. Low,
[0114]
[0116] The average extraction recovery rate of CyA is between 76.0% and 81.6%, and the average extraction recovery rate of CyC is between 82.3% and 82.3%.
[0117] The average treatment efficiency of CyA is between 78.9% and 81.2%, and the average treatment efficiency of CyC is be...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| collision energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com