Rock damage prediction method based on acoustic emission source dominant frequency uniqueness
A prediction method and acoustic emission technology, which is applied in the direction of using acoustic emission technology for material analysis, processing response signals of detection, etc., which can solve the problems of blurred emission source, main frequency bandwidth of acoustic emission, lack of established main frequency and acoustic emission source, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
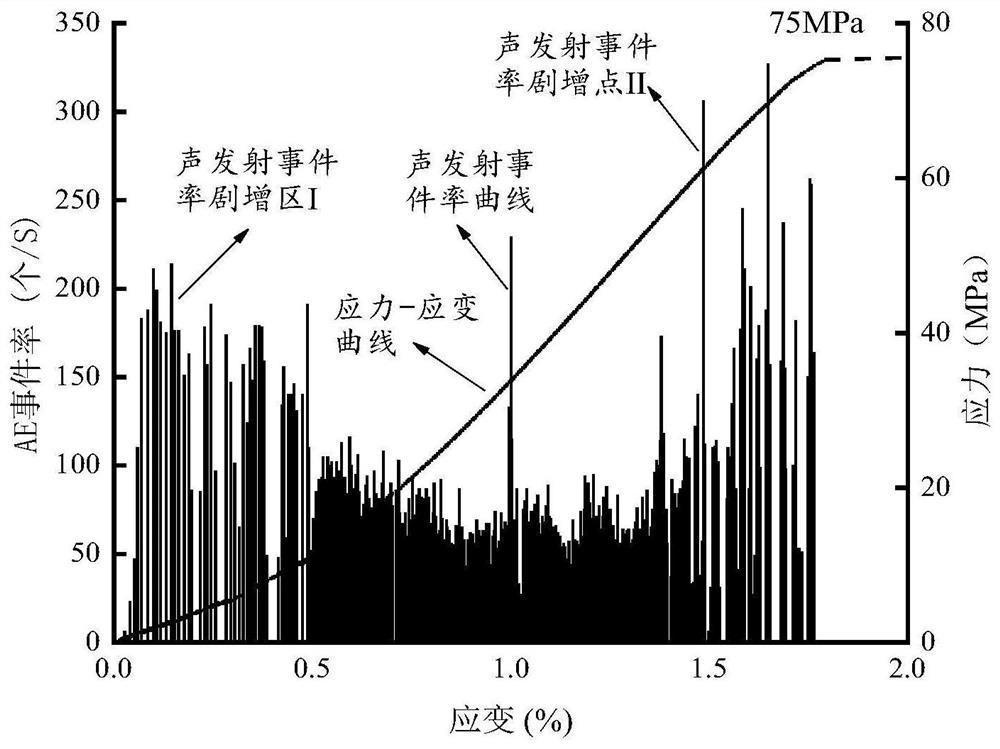
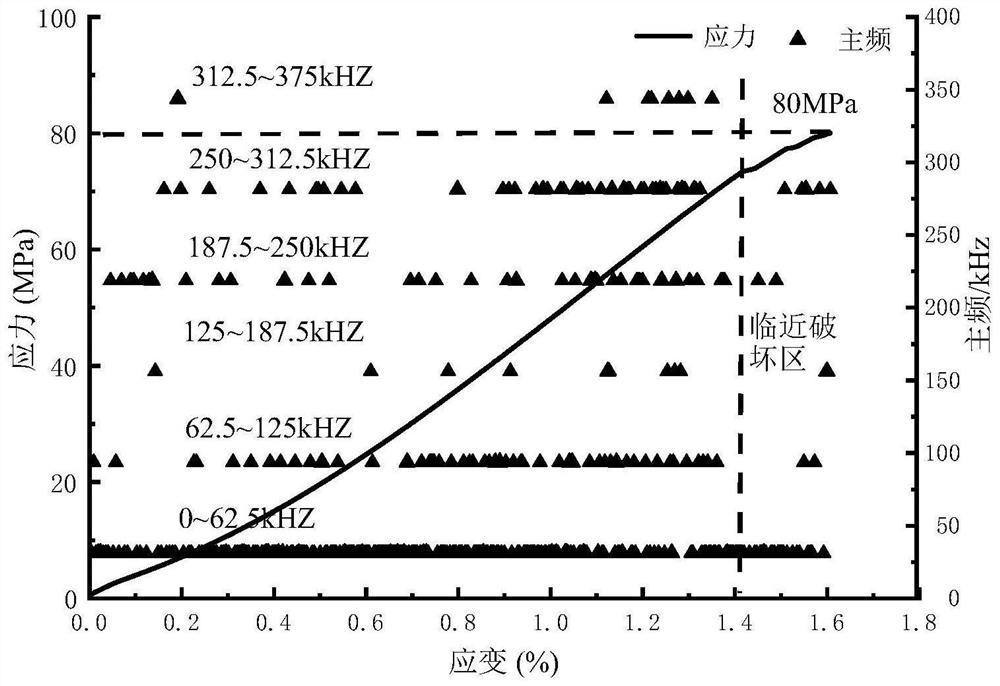
[0107] The specific technical solutions of the present invention are described in conjunction with the examples. This embodiment takes the uniaxial compressive strength test as an example.
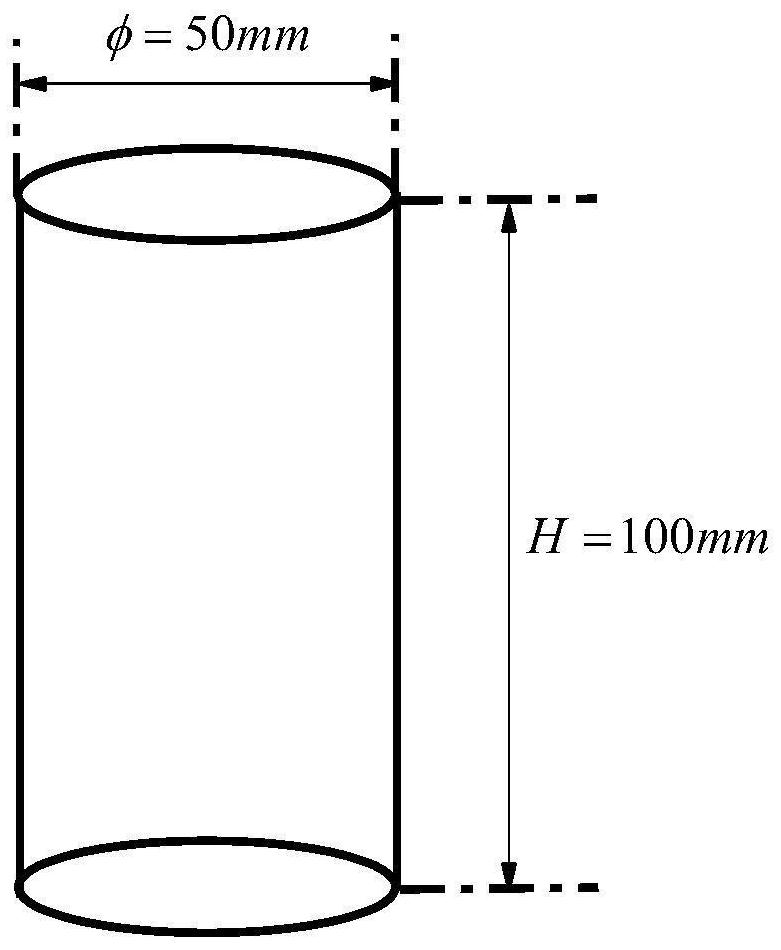
[0108] Preparation of S1 Standard Rock Specimen
[0109] Specimens were prepared according to the "Standards for Test Methods of Engineering Rock Mass" (GB / T50266-2013). Test specimens may be prepared from drilled core or rock blocks. Take a cylinder with a standard diameter of 50mm and a height of 100mm as an example. The instruments and equipment required for specimen preparation include: coring machine, cutting machine, grinding stone machine, etc. Among them, the coring machine is used to drill cores with a diameter of 50mm and a height greater than 100mm. The cutting machine is used to cut the drilled core to obtain a cylindrical core with a diameter of 50mm and a height slightly greater than 100mm. The stone grinding machine is used to grind the end face of the cut cylinder core...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com