Compositions and methods for treating retinal disorders
A technology of cone photoreceptor cells and sequences, which is applied in the field of treatment and/or prevention of retinal diseases, and can solve problems such as residual vision and loss of central vision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0145] Preparation of vector
[0146] The vectors of the invention can be prepared by standard methods known in the art for providing vectors for therapeutic use. Accordingly, established common domain transfection, packaging and purification methods can be used to prepare suitable vector formulations.
[0147] As described above, the vector of the present invention may contain the entire genome of a naturally occurring AAV virus in addition to the promoter of the present invention or a variant thereof. Typically, however, a derivatized genome will be used, for example with at least one inverted terminal repeat (ITR), but may lack derivatives of AAV genes such as rep or cap.
[0148] In such embodiments, in order to assemble the derived genome into an AAV virion, an additional genetic construct providing AAV and / or helper virus function may be provided in the host cell in combination with the derived genome. These additional constructs will generally contain genes encoding t...
Embodiment 1
[0208] Example 1: Optimizing Cone-Specific Transcriptional Control Units (TCUs)
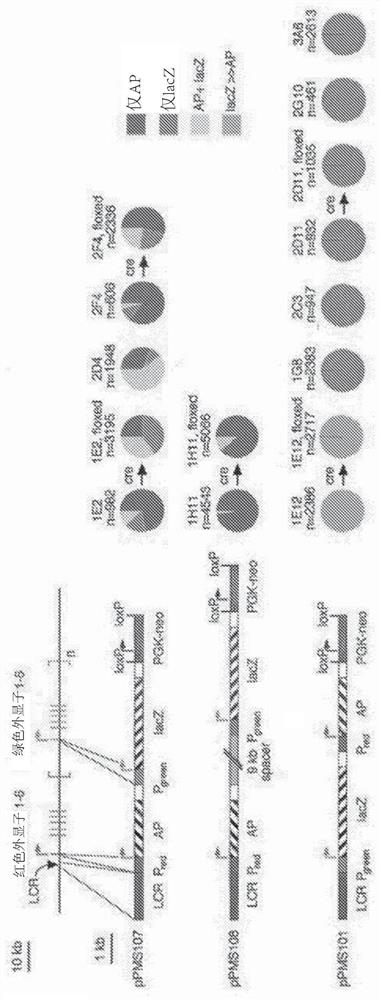
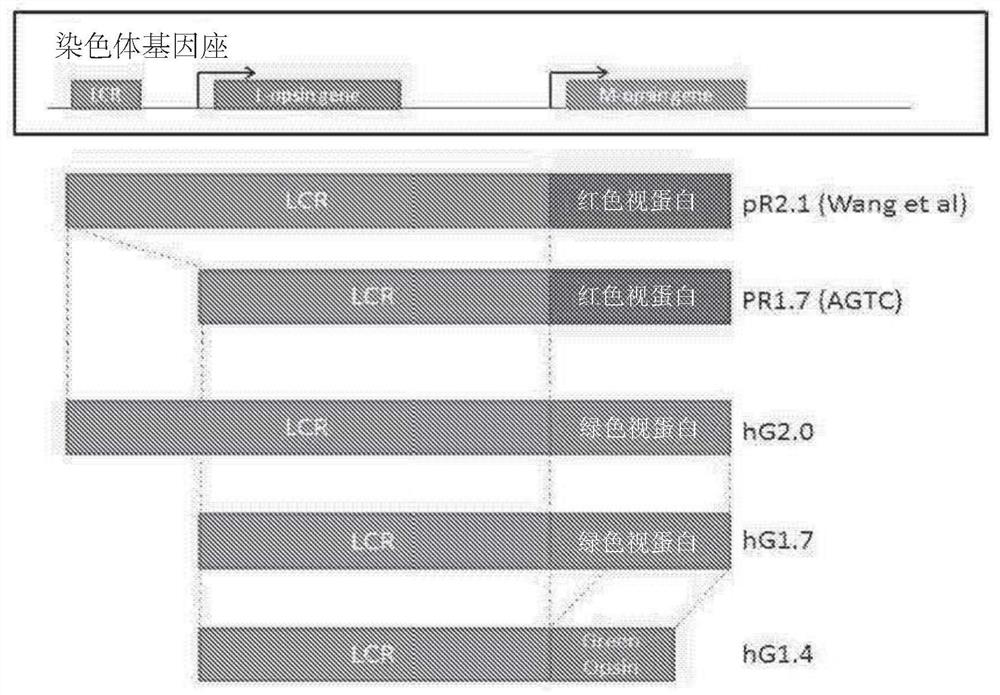
[0209] The human locus control region (LCR) located upstream of the red opsin gene enhances expression of the red opsin (L opsin) and green opsin (M opsin) genes arranged in tandem (see figure 1 , top left). Strong cone-specific promoters have previously utilized the LCR and red opsin promoters, as they are physically adjacent elements. In the in vivo reporter gene expression studies performed on transgenic mice by Smallwood et al., different expression levels from the red or green opsin promoter based on their physical proximity to the LCR were investigated. Smallwood et al. constructed several derivatives of the human red and green arrays to demonstrate different expression levels of the red or green opsin promoters based on their physical proximity to the LCR (see figure 1 , lower left). Each derivative consists of an alkaline phosphatase (AP) reporter gene under the control of the red opsi...
Embodiment 2
[0214] Example 2 - Optimized TCU Provides Strong Expression of Reporter Genes in All Cone Subtypes
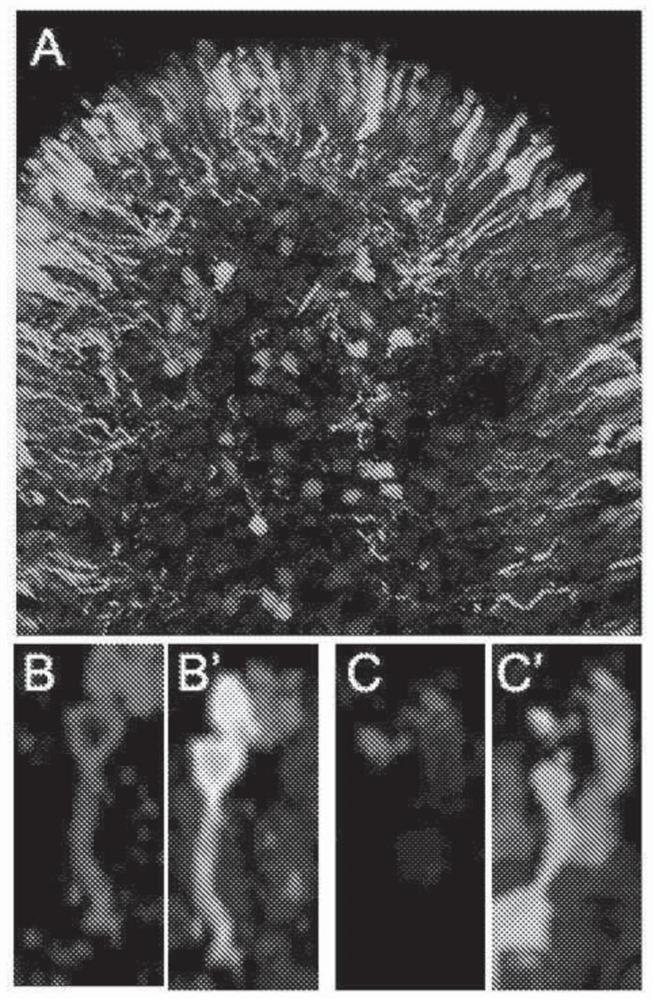
[0215] To test the ability of the optimized TCU disclosed herein to promote reporter protein expression in cones, human ES-derived retinas were transduced with AAVshh10-hG1.4.GFP. observed in all cone subtypes ( image 3 B', C') Strong expression of the reporter gene ( image 3 A).
[0216] Compared to the previously characterized human cone arrestin (CAR) promoter, hG1.4 provided higher expression levels in human cones and no ectopic expression in rods or retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells. In mice, the cone promoter based on the human red opsin promoter is not cone-specific and mediates expression in rods (Ye et al., 2016).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com