Mask non-woven fabric and process
A technology of non-woven fabrics and masks, which is applied in the field of mask non-woven fabrics and technology, which can solve the problems of poor antibacterial properties and antistatic properties of mask non-woven fabrics, and discomfort in the softness of mask non-woven fabrics, so as to increase the anti-static effect and hand feeling Smooth, Complexity-Reduced Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
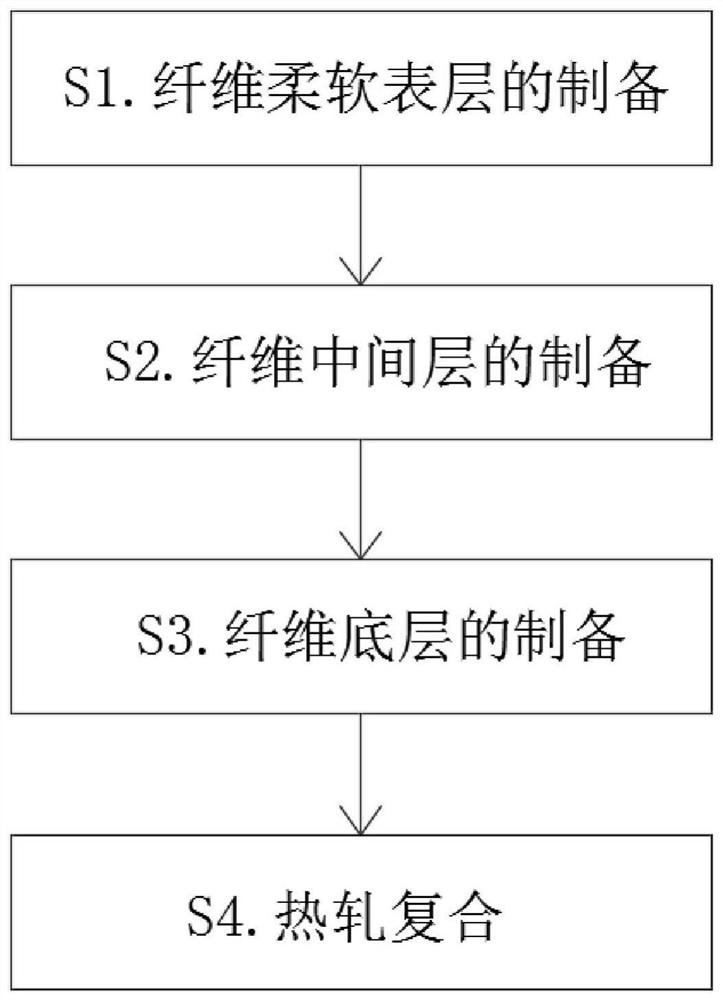
[0024] A nonwoven fabric for a mask, comprising a soft surface layer of fibers, a middle layer of fibers and a bottom layer of fibers, the components of the soft surface layer of fibers are calculated in the following mass percentages: 46% of polypropylene and 54% of soft masterbatches, the middle layer of fibers The components of the fiber base layer are calculated by the following mass percentages: 44% polypropylene and 56% of auxiliary materials, and the components of the fiber bottom layer are calculated by the following mass percentages: 48% polypropylene and 52% color masterbatch.
[0025] In this embodiment, preferably, the preparation process of the soft masterbatch is to take polypropylene raw material, carry out melt treatment to polypropylene raw material, then add cationic softener, stearic acid, paraffin and emulsifier, and cationic softener and The addition ratio of stearic acid, paraffin and emulsifier is 1:4:2:4, and stir evenly after mixing.
[0026] In this e...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A mask nonwoven fabric, comprising a fiber soft surface layer, a fiber middle layer and a fiber bottom layer, the components of the fiber soft surface layer are calculated in the following mass percentages: polypropylene 54% and soft masterbatch 46%, the fiber middle layer The components of the fiber bottom layer are calculated by the following mass percentages: 56% of polypropylene and 44% of auxiliary materials, and the components of the fiber bottom layer are calculated by the following mass percentages: 52% of polypropylene and 48% of color masterbatch.
[0029] In this embodiment, preferably, the preparation process of the soft masterbatch is to take polypropylene raw material, carry out melt treatment to polypropylene raw material, then add cationic softener, stearic acid, paraffin and emulsifier, and cationic softener and The addition ratio of stearic acid, paraffin and emulsifier is 1:4:2:4, and stir evenly after mixing.
[0030] In this embodiment, preferably, ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] A nonwoven fabric for a mask, comprising a soft surface layer of fibers, a middle layer of fibers and a bottom layer of fibers, the components of the soft surface layer of fibers are calculated in the following mass percentages: 50% of polypropylene and 50% of soft masterbatches, and the middle layer of fibers The components of the fiber bottom layer are calculated by the following mass percentages: 50% polypropylene and 50% of auxiliary materials, and the components of the fiber bottom layer are calculated by the following mass percentages: 50% polypropylene and 50% color masterbatch.
[0033] In this embodiment, preferably, the preparation process of the soft masterbatch is to take polypropylene raw material, carry out melt treatment to polypropylene raw material, then add cationic softener, stearic acid, paraffin and emulsifier, and cationic softener and The addition ratio of stearic acid, paraffin and emulsifier is 1:4:2:4, and stir evenly after mixing.
[0034] In ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com