Slope type refractive index distribution multi-core optical fiber with low inter-core crosstalk
A refractive index distribution, multi-core fiber technology, applied in graded-index core/clad fibers, multi-core fibers, clad fibers, etc. Factors increase, information transmission capacity is reduced and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing crosstalk between cores, crosstalk between small cores, and improving communication quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
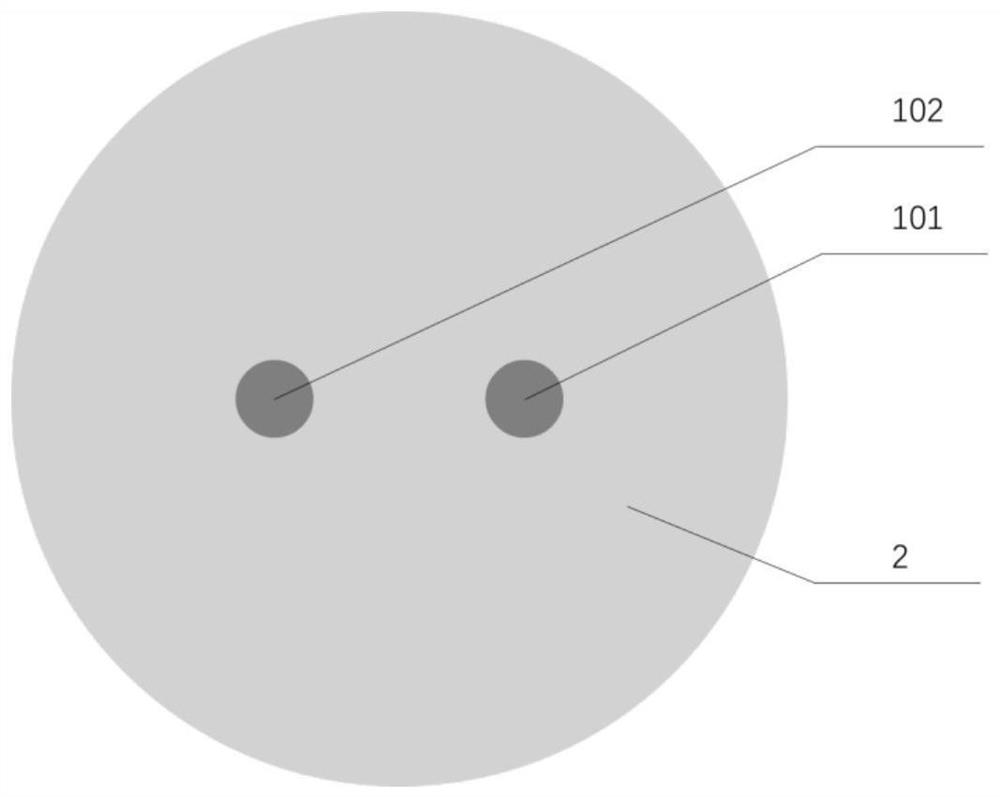
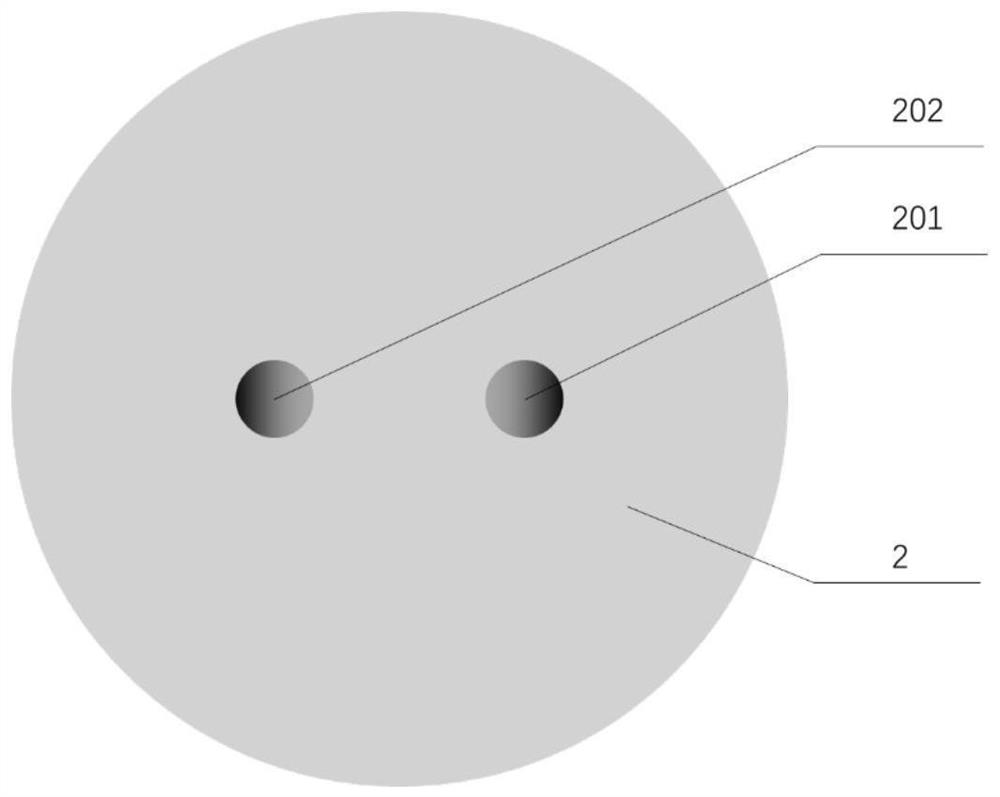
[0076] A slope-type refractive index distribution dual-core optical fiber with low inter-core crosstalk, its structural schematic diagram is shown in Figure 2(a), including a core area and a cladding area, and the core area includes the first core 201 of the slope-type dual-core optical fiber and the second core 202 of the ramp-type dual-core fiber.
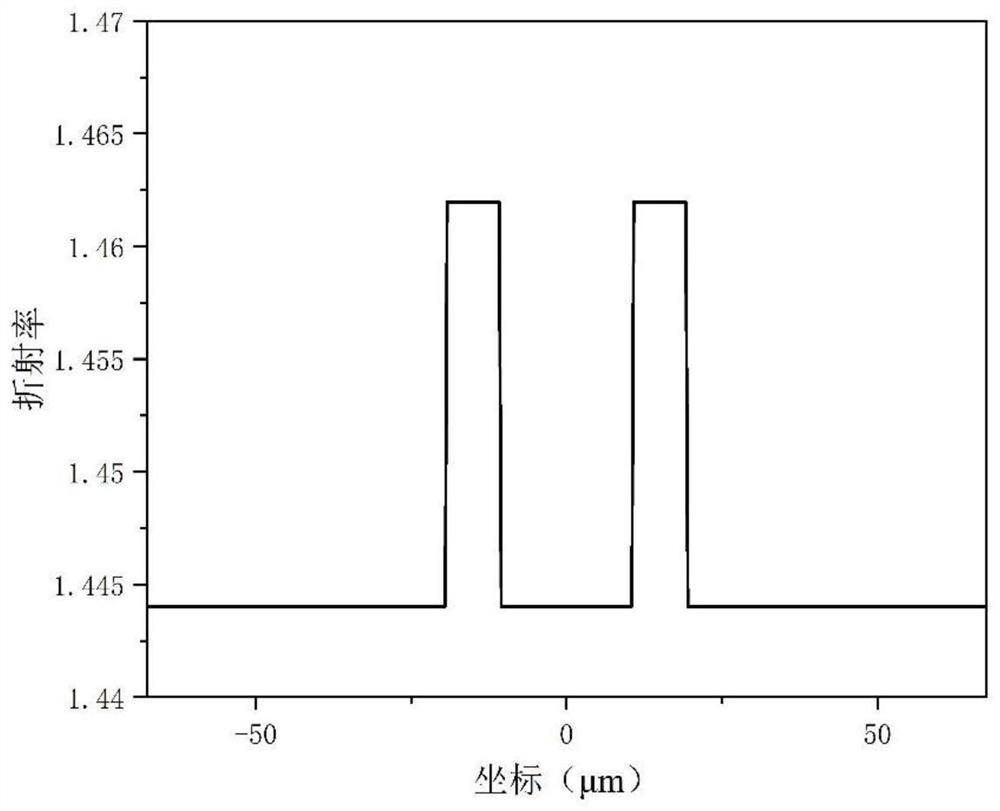
[0077] Both the first core 201 of the ramp-type dual-core fiber and the second core 202 of the ramp-type dual-core fiber are made of highly doped silica glass rods, the cladding 2 is pure silica glass, and the maximum refractive index of the core is n 1 and cladding index n 0 The relative refractive index difference is (n 1 -n 0 ) / n 0 =1.54%, the core diameter is 9 μm, the core spacing is 30 μm, and the refractive index n of the conventional step dual-core fiber core is compared 2 and cladding index n 0 The relative refractive index difference is (n 1 -n 0 ) / n 0 =1.24%, and the cladding diameters are all 125 μm.
[0078]...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Extend dual-core fiber to more cores to Figure 5 The shown hexagonal distributed six-core optical fiber is taken as an example. The structural parameters are consistent with the double-core optical fiber structure in Embodiment 1 except for the number and arrangement of the cores. Figure 6 As an example, the mode field is biased towards the high refractive index portion of each fiber core.
[0099] Using the power coupling equation in Embodiment 1 and the definition of each parameter can also obtain the crosstalk between adjacent cores in the six-core optical fiber:
[0100]
[0101] and crosstalk between spaced cores:
[0102]
[0103] The crosstalk between the two cores in the six-core optical fiber with hexagonal distribution is so small that it can be ignored for the above two kinds of crosstalk, so only the above two kinds of crosstalk are considered. The crosstalk comparison curves at the working wavelength of 1.55 μm are shown in Figure 7(a) and Figure ...
Embodiment 3
[0105] On the basis of the dual-core structure in Example 1, an auxiliary groove structure is added around the fiber core, such as Figure 8 shown. Among them, the inner diameter of the trench is 7 μm, the outer diameter is 13 μm, and the refractive index at the working wavelength of 1.55 μm is 1.44. The simulation shows that the crosstalk with the unassisted structure is reduced by 9.26 dB after the transmission of 1 km at the working wavelength of 1.55 μm, and the crosstalk with the unassisted structure see comparison Figure 10 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com