Transmission type image slicer device and working system thereof
A working system and transmissive technology, applied in the fields of astronomical optics, optics, and spectroscopy, it can solve the problems of optical performance defects, different optical paths of segmented images, and difficulty in processing segmented image data.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
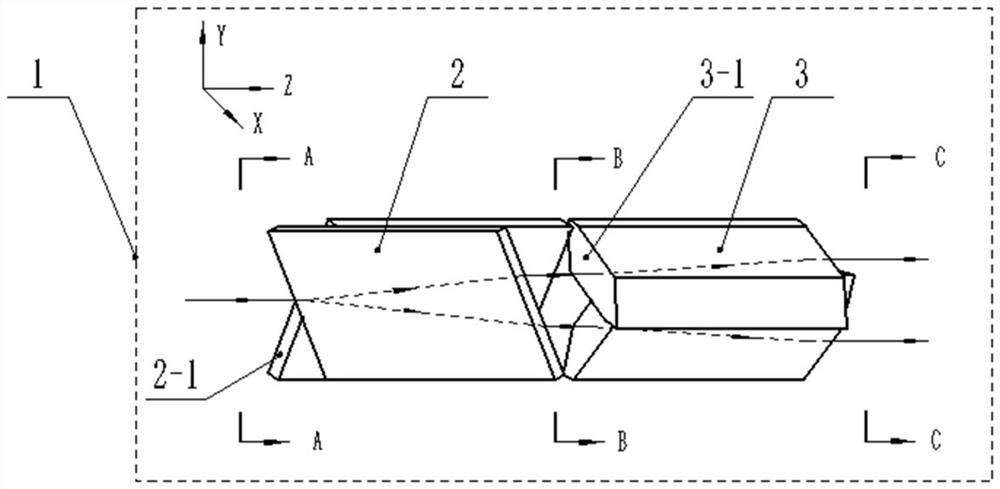
[0028] This embodiment provides a figure 1 The transmissive image splitter device 1 shown includes a front optical unit 2 and a rear optical unit 3 arranged in series along the optical axis direction (Z). in:
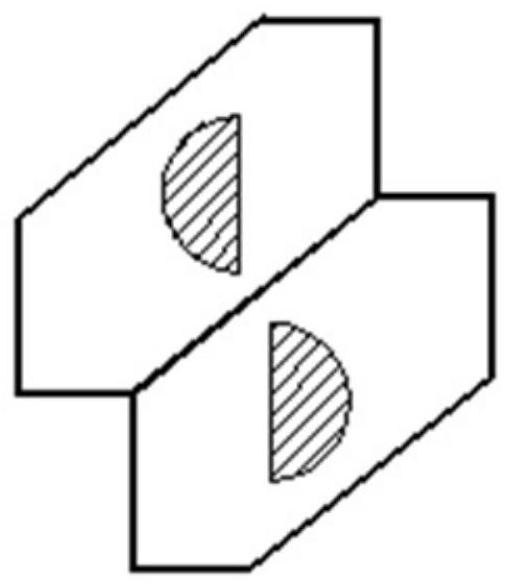
[0029] The front optical unit 2 includes a front first optical element and a front second optical element connected sideways. In this embodiment, the front first optical element and the front second optical element are preferably two identical rhombic prisms , the front side optical unit is set opposite to each other by two rhombic prisms. The front ends of the two rhombic prisms are all inclined first surfaces 2-1, the light beam is incident from the first surface 2-1, and the normal directions of the first surfaces 2-1 of the two rhombic prisms are opposite, forming a certain The included angle, the edges of the connected sides of the rhombic prism are used as a tool for segmenting the image spot. The function of the front optical unit 2 is to segment the image spo...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This embodiment provides a Figure 5 The transmissive image slicer array device shown includes several transmissive image slicer devices 1 sequentially connected along the spatial direction (Y), and several transmissive image slicer devices 1 are neatly stacked to form an array along this direction . In this way, the purpose of separately segmenting and rearranging several linearly arranged image spots is achieved.
[0041] Here, the names of each surface of the transmissive image slicer device 1 can be firstly defined, which are divided into front surface, rear surface, upper surface, lower surface, left side, and right side. The front surface is the slope on which the beam is incident, and the back surface is the slope on which the beam exits; the normal directions of the upper and lower surfaces are parallel to the spatial direction; the normal directions of the left and right sides are parallel to the splitting direction. When multiple transmissive image splitter ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] This embodiment provides a Figure 5 The transmission-type image splitter array working system shown includes a front optical system 4, a turning mirror system 5, and a transmission-type image splitter device 1 (when a single transmission-type image splitter device 1 is used) arranged in sequence along the optical axis direction (Z). During splitter device 1, correspondingly, front optical system 4 only needs to comprise a front optical unit, and turning mirror system 5 also only needs to comprise a turning mirror) or comprise a plurality of transmissive image splitter devices 1 Transmissive image slicer array device (this embodiment specifically uses such as Figure 5 The transmissive image slicer array device shown is taken as an example for illustration), the follow-up optical system 6 . in:
[0045] The front optical system 4 includes several front optical units, these front optical units are sequentially connected along the spatial direction (Y), and are used to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com