Task scheduling method, device and equipment
A task scheduling and task technology, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, resources, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency of AGV, single processing method, and high complexity of production scene business, so as to improve operating efficiency, reduce distance reciprocation, and increase robustness Effects on performance and scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
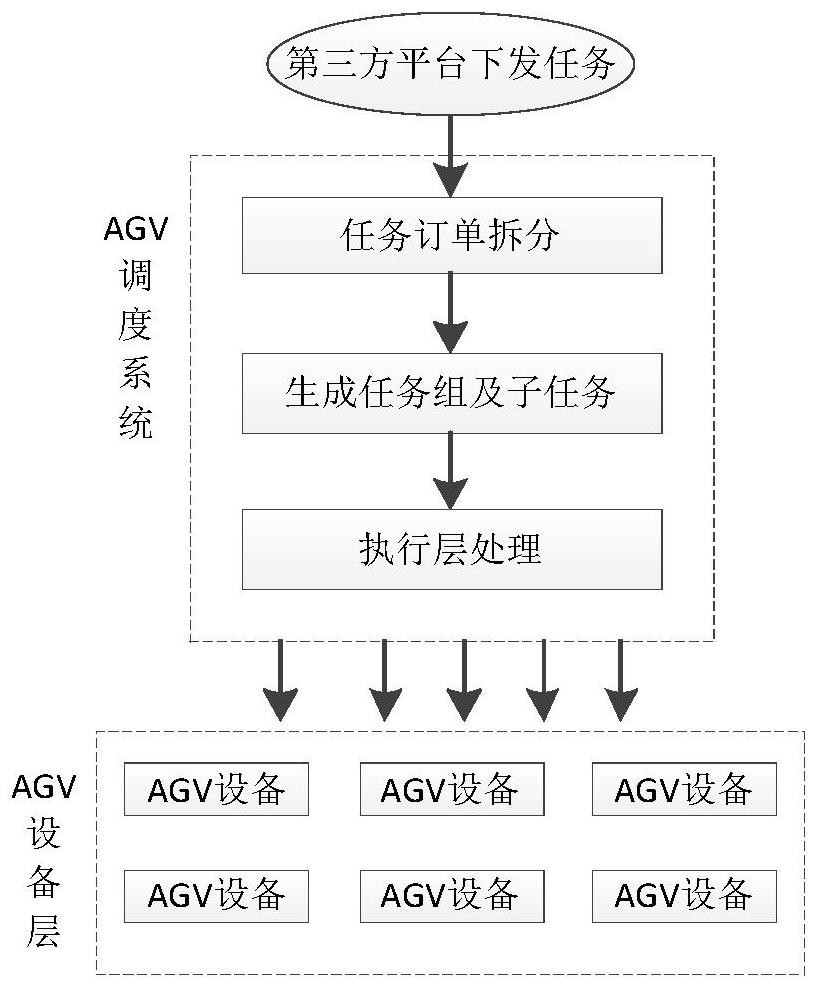
[0088] Embodiment 1. At present, the traditional AGV dispatching system puts the received tasks into the task pool without optimizing the processing, and passively waits for the sorting table to request tasks. This business scenario has high requirements on the functions of the AGV equipment, which leads to the excessive processing of the equipment itself. More involved in the specific task processing process, when the business requirements change, it may be necessary to adjust and upgrade the functional design of the AGV itself. It should be noted that the task that the general AGV needs to perform is the process of transporting the shelves carrying the goods to the sorting table, and finally manually pick the goods from the sorting table; in the prior art, the sorting table requests tasks and sends them to After the AGV equipment is installed, it is necessary to perform certain task optimization processing on the AGV equipment side, so there are two problems. First, there is ...
Embodiment 2
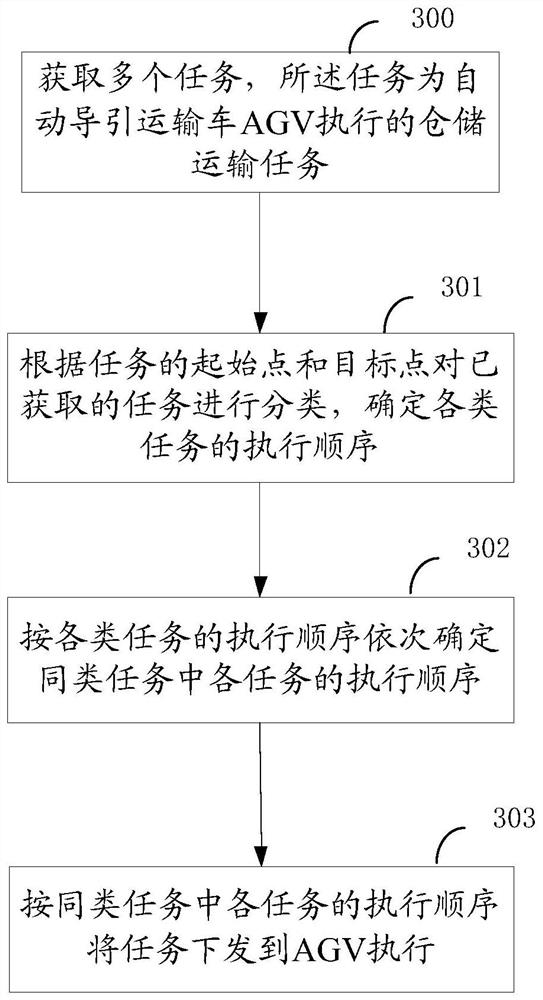
[0181] Embodiment 2. The embodiment of the present invention provides a task scheduling method, such as Figure 4 As shown, the specific implementation steps of the method are as follows:
[0182] Step 400, obtaining a plurality of tasks, the tasks being the storage and transportation tasks performed by the automatic guided transport vehicle AGV;
[0183] Step 401, judging whether the number of acquired tasks reaches a preset value, if so, execute step 402, otherwise return to step 400;
[0184] Step 402, judging whether the starting point and the target point of the task belong to the same area, if so, execute step 403, otherwise execute step 404;
[0185] Step 403, determining that the task type is the same area task;
[0186] Step 404, determining that the task type is a cross-regional task;
[0187] Step 405, according to the execution sequence of the same-region tasks being earlier than the execution sequence of the cross-region tasks, perform the operations of the fol...
Embodiment 3
[0195] Embodiment 3, based on the same inventive concept, the embodiment of the present invention also provides a device for task scheduling, because the device is the device in the method in the embodiment of the present invention, and the principle of solving the problem of the device is the same as that of the method Similar, therefore, the implementation of the device can refer to the implementation of the method, and the repetition will not be repeated.
[0196] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the device includes: a task acquisition module 500, a task classification module 501, a task execution module 502, and a task delivery module 503, wherein:
[0197]The task obtaining module 500 is used to obtain multiple tasks, and the tasks are storage and transportation tasks performed by the AGV;
[0198] The task classification module 501 is used to classify the acquired tasks according to the starting point and target point of the tasks, and determine the execution sequence of var...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com