User equipment information reporting and processing method, device and medium
A technology of user equipment and beam information, applied in connection management, wireless communication, advanced technology, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
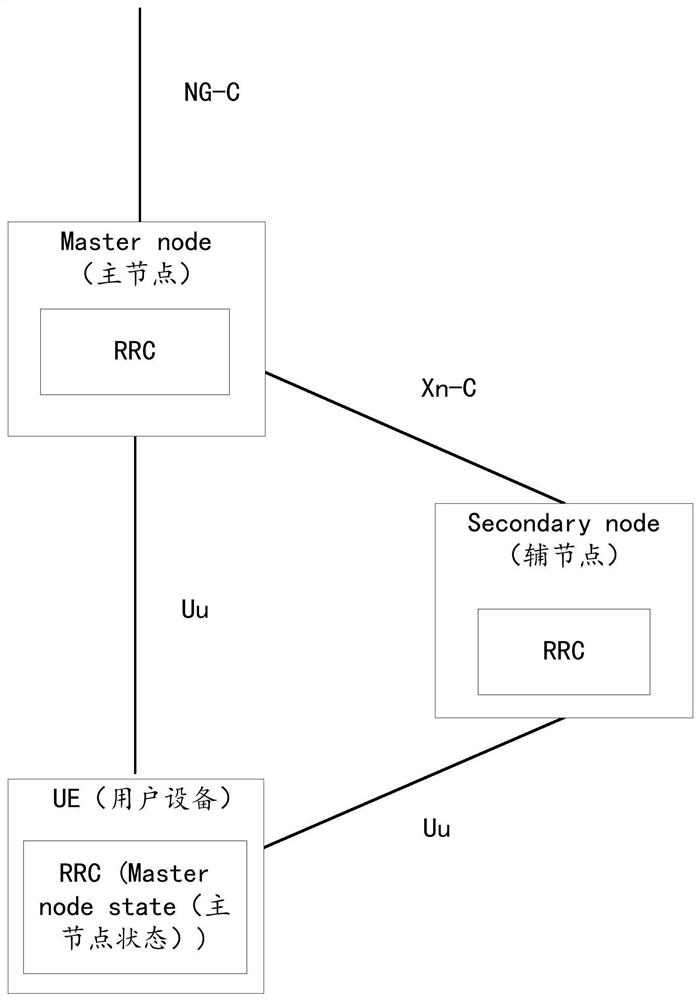
[0139] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of a UE in the multiple / dual connectivity architecture, as shown in the figure, the UE maintains connections with the MN and the SN in the multiple / dual connectivity architecture at the same time. As shown in the figure, it is assumed that both UE1 and UE2 use Cell1 as the primary cell. If UE1 is under the common coverage of Cell1 and Cell3, UE1 can establish a dual connection with Cell1 and Cell3 (the base station where it is located); and if UE2 is under the common coverage of Cell1 and Cell2, UE2 can establish dual connections with Cell1 and Cell2 (the base station where it is located). ) to establish a dual connection.
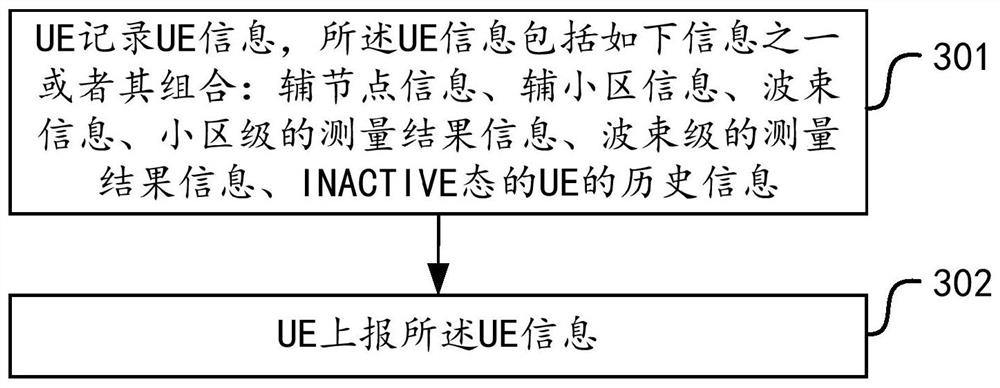
[0140] The UE history information of LTE only includes the information of the main serving cell, that is, for UE1 and UE2, the records in the current state are Cell1 cell ID and their respective access time. Secondary node information may include secondary node identifier, access time, etc. The secondary node i...
Embodiment 2
[0146] In the CA architecture, the UE can send and receive data from multiple cells. The cell that has a control plane signaling connection with the UE is the primary cell, and the other cells are only used to send and receive data to improve UE throughput and peak rate. They are called secondary cells.
[0147] The secondary cell and the primary cell may be located at the same node, or at different nodes. Even if the secondary cell and the primary cell belong to the same base station, the deployment of radio frequency units in the secondary cell may be geographically different from that of the primary cell, which is called remote radio.
[0148] Therefore, for the record of UE history information, the UE can also report records related to the secondary cell, including the cell identity and access time, etc., to assist the network side in determining UE path / speed and other information. The identifier of the secondary cell may be in the form of the frequency point + PCI access...
Embodiment 3
[0156] In the NR system, the beam (beam) is introduced on the basis of the cell. A cell can use different amounts of beam information according to different frequency locations and actual service conditions. The beam information is related to the direction, and the coverage areas of adjacent beams may partially overlap. On top of the cell-level records, the UE can also record information related to the beam direction, including the beam index, and the relevant access / dwell time of the UE in each beam.
[0157] For example, beam-related information can be recorded in the following manner:
[0158] 1) The UE enters the initial access / residence beam of the current cell, which may also include the time in the beam; or,
[0159] 2) All the beams that the UE has accessed / resided in after entering the current cell may also include the accumulated time in the respective beams; or,
[0160] 3) The UE records the information of all the beams that the UE passes through in chronologica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com