Method for preparing bitter-free plant oligopeptide
A non-bitter, plant-based technology, applied in the preparation method of peptides, chemical instruments and methods, peptides, etc., to achieve the effects of high yield, sufficient raw materials, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
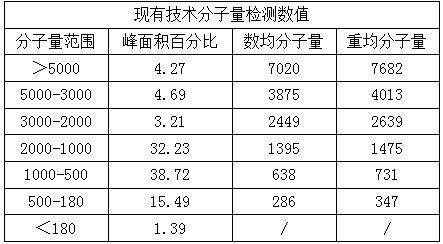
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Plant proteolytic enzyme Promatex, with an enzyme activity of 72,000 U / g, and Flavourzyme enzyme, with an enzyme activity of 500 LAPU / g, are industrial food and proteases.
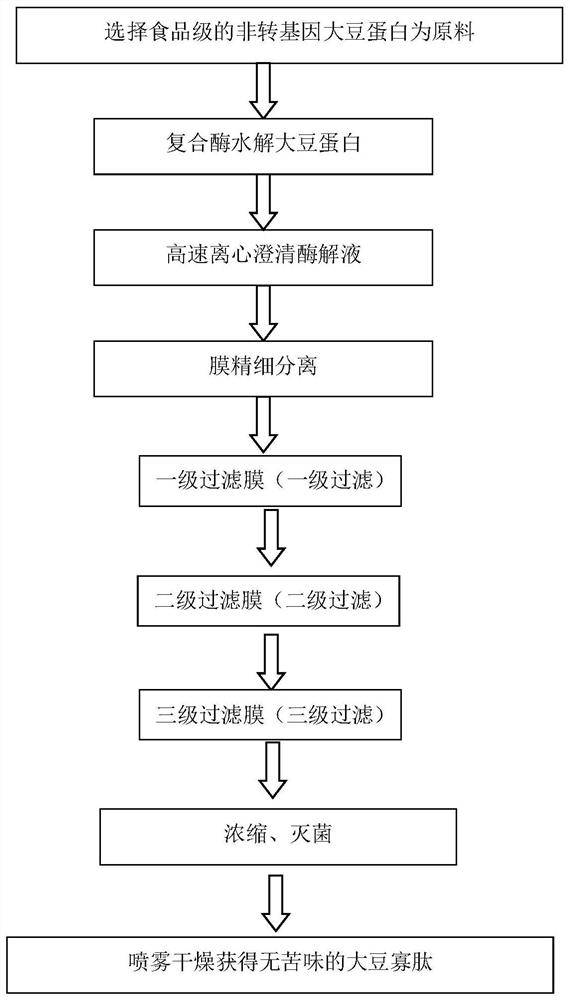
[0018] A method for preparing non-bitter plant oligopeptides: select food-grade vegetable protein as a raw material, add enzyme hydrolysis, wherein the enzyme is composed of plant proteolytic enzyme and flavor enzyme in a weight ratio of 5:3, and the dosage is 0.6% of the weight of vegetable protein , during the hydrolysis process, the pH of the hydrolyzate is maintained at 8.5 by adding acid and alkali, the degree of hydrolysis is 40%, the enzymolyzate is clarified by high-speed centrifugation, the enzymolysis time is 7 hours, the membrane is finely separated, concentrated, sterilized, and spray-dried to obtain no Bitter plant oligopeptide solid powder. Monitor the temperature at any time through the thermometer used in industrial production, and then add fuel at any time to keep the temperature co...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Plant proteolytic enzyme Promatex, with an enzyme activity of 72,000 U / g, and Flavourzyme enzyme, with an enzyme activity of 500 LAPU / g, are industrial food and proteases.
[0024] A method for preparing non-bitter plant oligopeptides: select food-grade vegetable protein as a raw material, add enzyme hydrolysis, wherein the enzyme is composed of plant proteolytic enzyme and flavor enzyme in a weight ratio of 4:3, and the dosage is 0.8% of the weight of vegetable protein During the hydrolysis process, the pH of the hydrolyzate is maintained at 9.0 by adding acid and alkali, the degree of hydrolysis is 60%, the enzymolyzate is clarified by high-speed centrifugation, and the enzymolysis time is 8 hours; the membrane is finely separated, concentrated and sterilized to obtain plant oligosaccharides without bitter taste Peptide liquid-like product. Monitor the temperature at any time through the thermometer used in industrial production, and then add fuel at any time to keep ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com