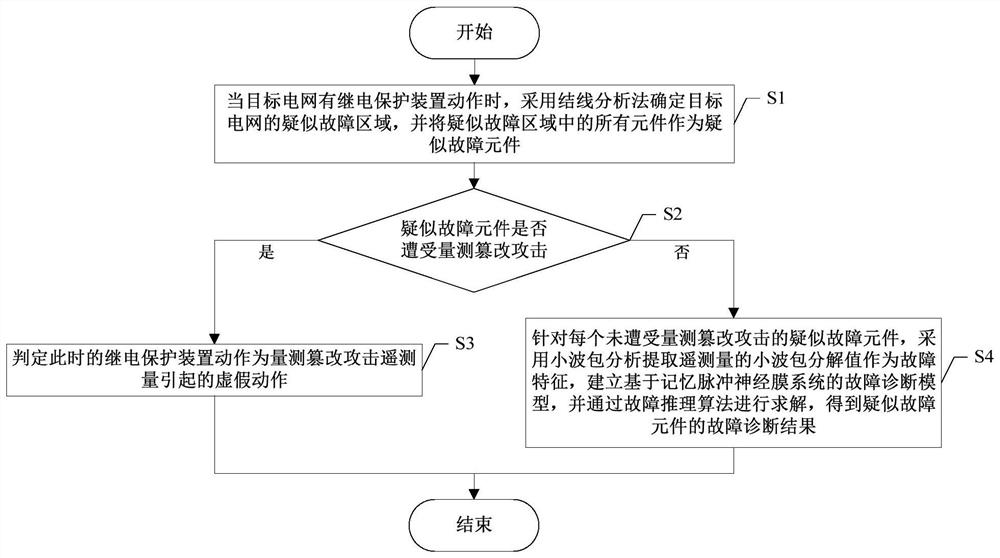
A power grid fault diagnosis method considering false faults caused by measurement tampering attacks
A power grid fault and measurement technology, which is applied in the direction of detecting faults according to conductor types, measuring electricity, and fault locations, etc., can solve problems such as auxiliary decision-making for wrong faults, ignoring the cause of faults, and false start-up of the diagnostic system, etc., to achieve a simple model structure, The effect of improving the accurate identification rate of attacks and reducing the scope of diagnosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0221] Experimental example 1 is a preset failure scenario of a single component failure under the condition of no measurement tampering attack, and its relevant information is shown in Table 1:
[0222] Table 1
[0223]
[0224] First, step S1 of the method of the present invention is executed, and the suspected fault area is determined in the L3 component; then, step S2 is executed to identify the measurement tampering attack on the L3 component, wherein the measurement tampering result of the line L3 is shown in Figure 11 shown. It should be noted that in this experimental example, the normal characteristic root of the random matrix is marked as a star point, and the attack characteristic root is marked as a square.
[0225] Depend on Figure 11 It can be seen that the characteristic roots of the measurement tampering attack identification random matrix are almost completely distributed between the rings, and all of them are marked as star points, which shows that t...
experiment example 2
[0227] Experimental example 2 is a preset failure scenario of a single component failure when the single component is subjected to a measurement tampering attack. The relevant information is shown in Table 2:
[0228] Table 2
[0229]
[0230] In Experimental Example 2, the target power grid did not actually fail, but the attacker maliciously tampered with the voltage value of line L3, which led to successive actions of the relay protection devices of the L3 element, and finally caused false faults caused by measurement tampering attacks.
[0231] Executing step S1 of the present invention, it is determined that the suspected faulty component is L3. Execute step S2 to obtain the characteristic root distribution of measurement and tampering identification of L3, such as Figure 12 shown.
[0232] Depend on Figure 12 It can be seen that the distribution of the characteristic roots of the measurement tampering attack identification random matrix is relatively scattered, ...
experiment example 3
[0234] Experimental example 3 uses Table 3 to compare the power grid fault diagnosis method provided by the present invention with four existing fault diagnosis methods.
[0235] table 3
[0236]
[0237] It can be seen from Table 3 that the five methods can achieve correct diagnosis without attack, but when a measurement tampering attack occurs, ANN, SVM, and IFSNPS cannot identify false alarm information, resulting in misdiagnosis. However, the method of the present invention can effectively identify the false fault information caused by the attack of measurement tampering, thereby avoiding false startup and false diagnosis of the diagnostic module. In addition, from the point of view of modeling method and modeling time, the method of the present invention is an inference model without complicated learning and training process, so it is obviously better than ANN and SVM in terms of modeling time. From the diagnosis results, since the method of the present invention, ANN...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com