Pressurizer for hydrogen fuel vehicle and braking gas taking and pressurizing system and method
A technology of supercharging system and hydrogen fuel, applied in machine/engine, transportation hydrogen technology, climate sustainability, etc., to achieve the effect of improving decompression efficiency, improving energy utilization efficiency, and reducing the impact of hydrogen pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
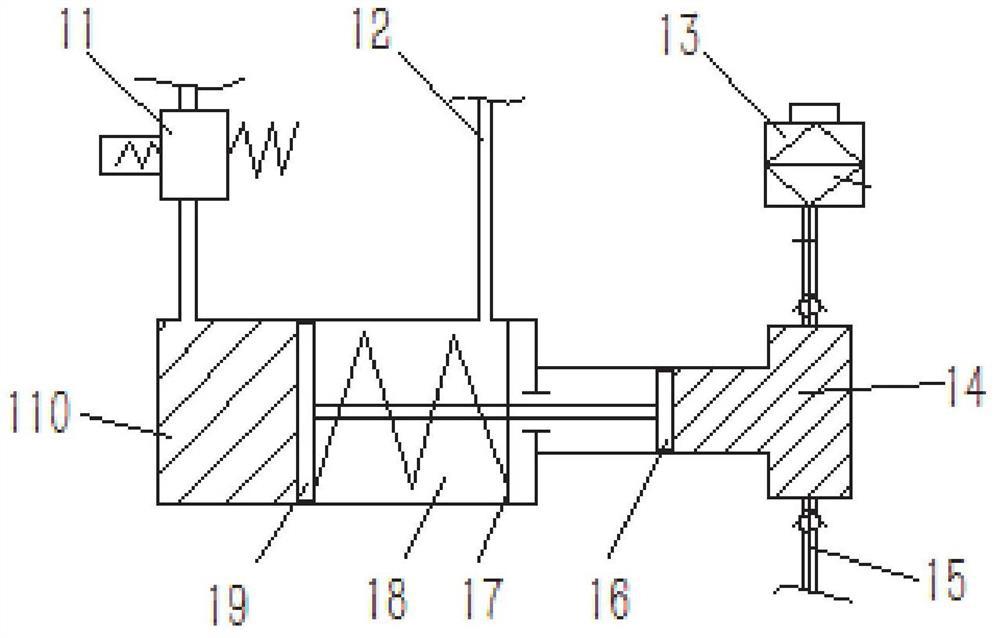
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a supercharger 1 for a hydrogen fuel vehicle, which includes a cylinder body with both ends blocked, a spring 18 and a piston plate group capable of moving along the axis of the cylinder body are arranged in the cylinder body, and the piston plate group will The inner cavity of the cylinder is divided into an isolated decompression chamber 110 and a pressurization chamber 14, and the spring 18 can provide the elastic force for the piston plate group to move toward the decompression chamber 110;
[0034] The end of the decompression chamber 110 away from the pressurization chamber 14 can be connected to the high-pressure gas supply end of the on-board hydrogen system 2, and the middle part of the cylinder is provided with a hydrogen outlet for connecting the inner cavity of the cylinder with the low-pressure return air end of the on-board hydrogen system 2; The end of the pressure chamber 14 away from the decompression ...
Embodiment 2
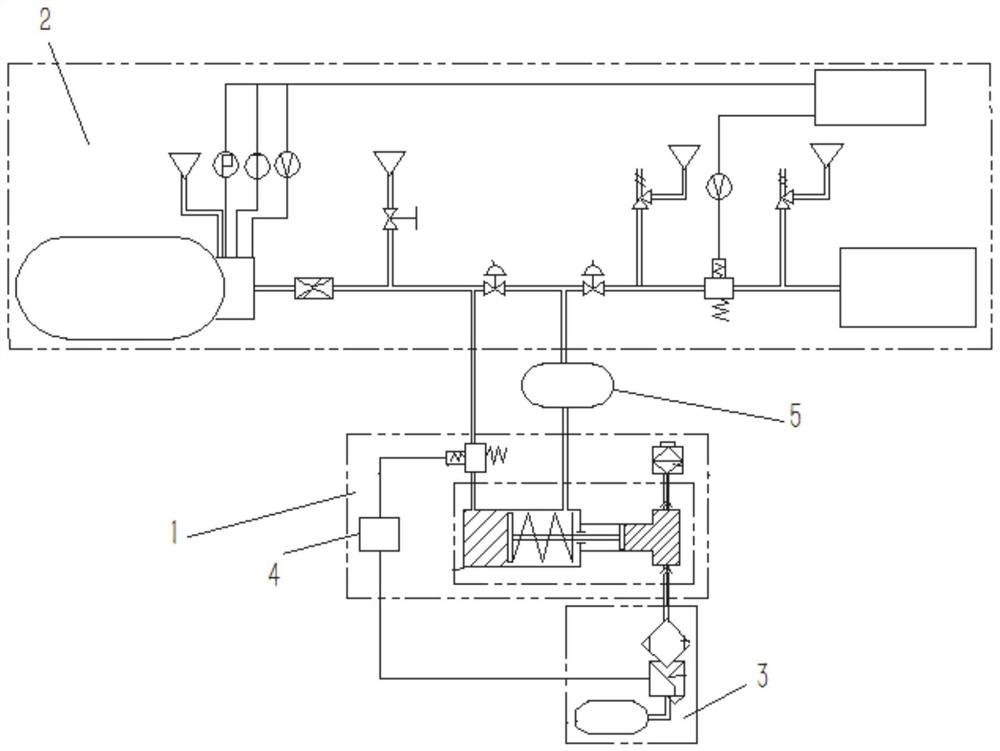
[0041] Such as Figure 2-Figure 4As shown, this embodiment provides a hydrogen-fueled vehicle braking air intake boosting system, the air boosting system includes the boost controller 24 described in Embodiment 1, and the boost controller 24 can control the decompression chamber 110 The hydrogen gas with relatively high pressure is obtained from the on-board hydrogen system 2, and the air filtered by the air filter 13 is boosted to a limited pressure through the supercharger 1. During the process, the hydrogen in the supercharger 1 is decompressed, and the air Get supercharged. The pressurized air enters the brake air intake system 3, is condensed by the condenser 31, and dried by the dryer 32. The pressurized air is stored in the gas storage cylinder group for use when the vehicle brakes; decompression The final hydrogen returns to the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system 2 through the hydrogen buffer tank 5 .
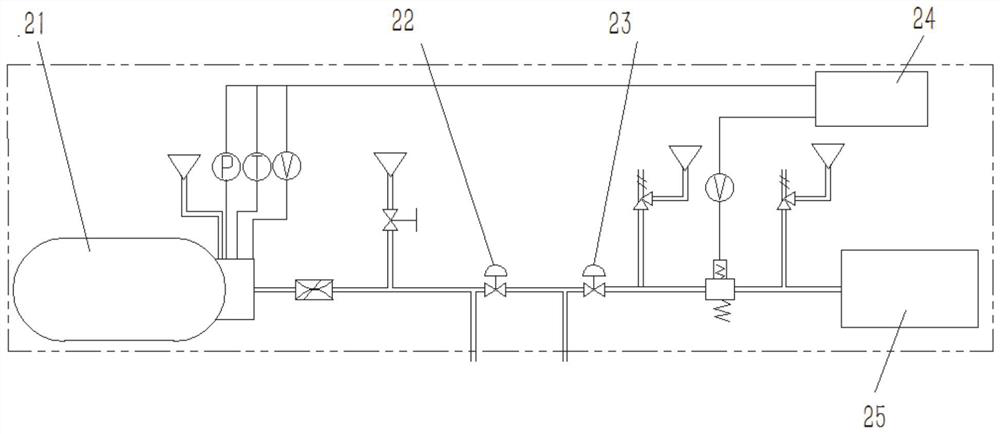
[0042] The on-board hydrogen system 2 is the hydrogen storage and s...
Embodiment 3
[0053] In this embodiment, a hydrogen-fueled vehicle brake intake boosting method is provided, which utilizes the hydrogen fuel vehicle brake intake booster system, including the following steps:
[0054] The solenoid valve 11 is opened, high-pressure hydrogen is charged into the decompression chamber 110, and the pressurization chamber 14 is filled with normal-pressure air; the high-pressure hydrogen pushes the piston plate group to move toward the pressurization chamber 14; before the hydrogen outlet communicates with the decompression chamber 110 , the solenoid valve 11 is closed; the air at normal pressure in the pressurization chamber 14 is compressed;
[0055] When the piston plate group moves to the limit position toward the pressurization chamber 14, the decompressed hydrogen in the decompression chamber 110 is discharged into the low-pressure return air end of the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system 2 through the hydrogen outlet; the air in the pressurization chamber 14 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com