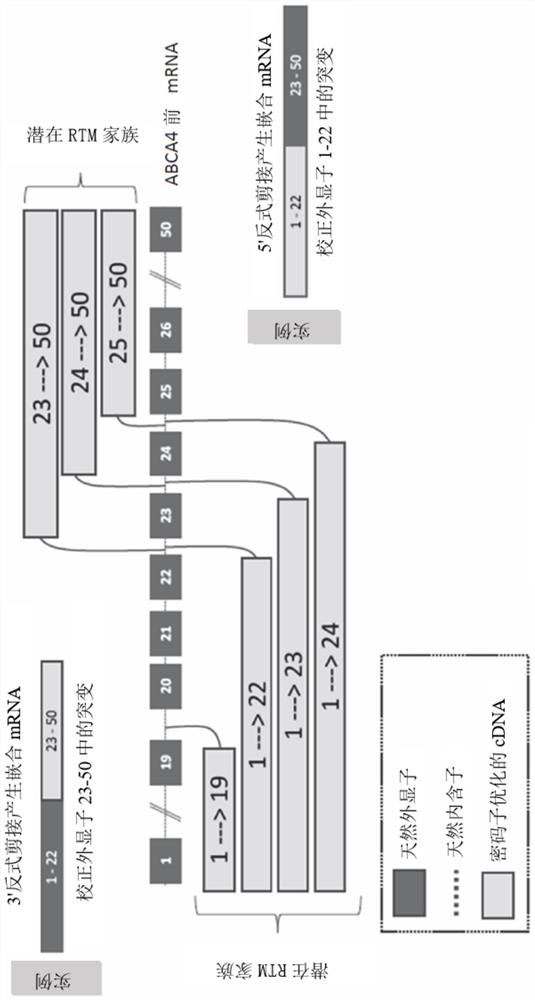
Trans-splicing molecules
A trans-splicing and molecular technology, applied in the direction of splicing changes, genetic material components, organic active components, etc., can solve problems such as hindering the delivery of large nucleic acid molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0283] Example 1. ABCA4
[0284] This example describes the development of ABCA4 trans-splicing molecules, for example, by screening for efficient binding sites within specific ABCA4 introns, the development of ABCA4 cell lines for testing trans-splicing molecules, and the testing of various ABCA4 trans-splicing Molecules to restore ABCA4 protein expression.
[0285] binding site screening
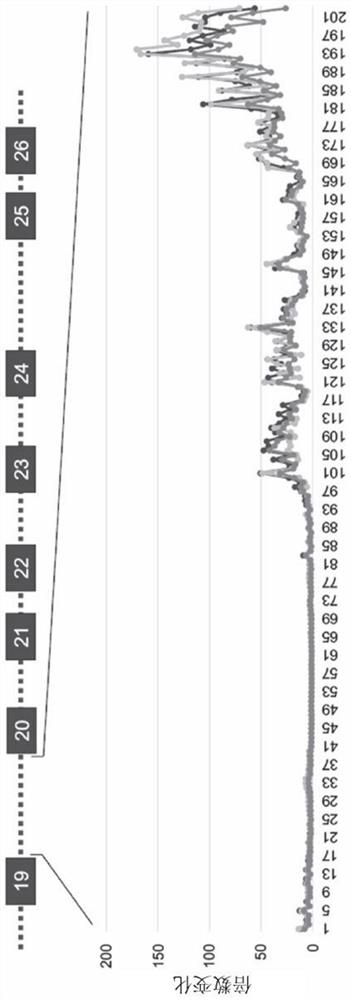
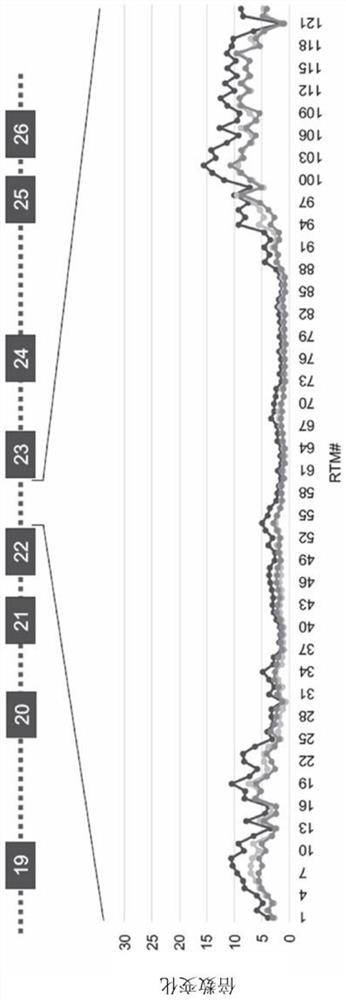
[0286] Screening of a series of binding domains configured to bind ABCA4 intron 19 (SEQ ID NO: 25) at sequential binding sites revealed a region of the 3' portion of ABCA4 intron 19 that is in 5' trans Preferentially effective in trans-splicing of splicing molecules—the region from nucleotides 990 to 2,174 of intron 19 ( figure 2 ). Binding sites ranging from 1,670 to 2,174, from 1,810 to 2,000, from 1,870 to 2,000, or from 1,920 to 2,000 nucleotides were revealed to be particularly efficient at mediating 5' trans-splicing of intron 19.
[0287] A suitable binding site for the 5' tran...
Embodiment 2
[0324] Example 2. CEP290
[0325] Screening of a series of binding domains configured to bind CEP290 intron 26 (SEQ ID NO: 85) at sequential binding sites revealed that the region of the 3' portion of CEP290 intron 26 is preferentially suited for 5' trans Trans-splicing of the splicing molecule - the region from nucleotides 4,980 to 5,838 of intron 26 ( Figure 22 ). Binding sites revealed to be in the range of nucleotides 5,348-5,838, 5,348-5,700, 5,400-5,600, 5,460-5,560, or 5,500 are particularly effective in mediating trans-splicing.
[0326] Figure 23Results of a similar screen for CEP290 intron 27 (SEQ ID NO: 86) are shown. Binding sites identified with nucleotides 120 to 680, 710 to 2,200, 2,670 to 2,910 are preferentially suitable for trans-splicing of 5' trans-splicing molecules. In particular, binding domains targeting binding sites in the range of nucleotides 790 to 2,100, nucleotides 1,020 to 1,630, or nucleotides 1,670 to 2,000 are efficient in trans-splicing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com