Patents
Literature
95 results about "Trans-splicing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
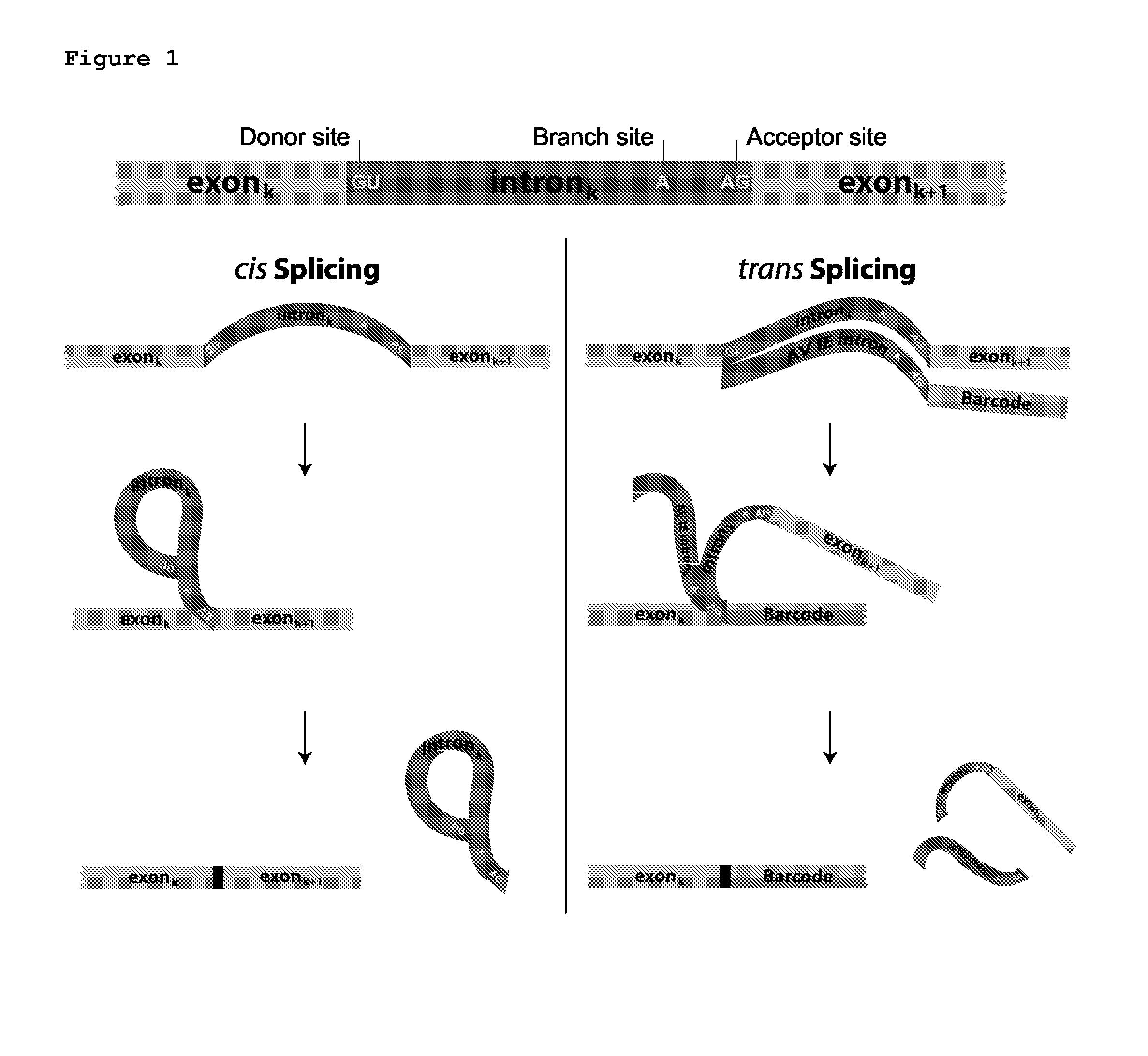
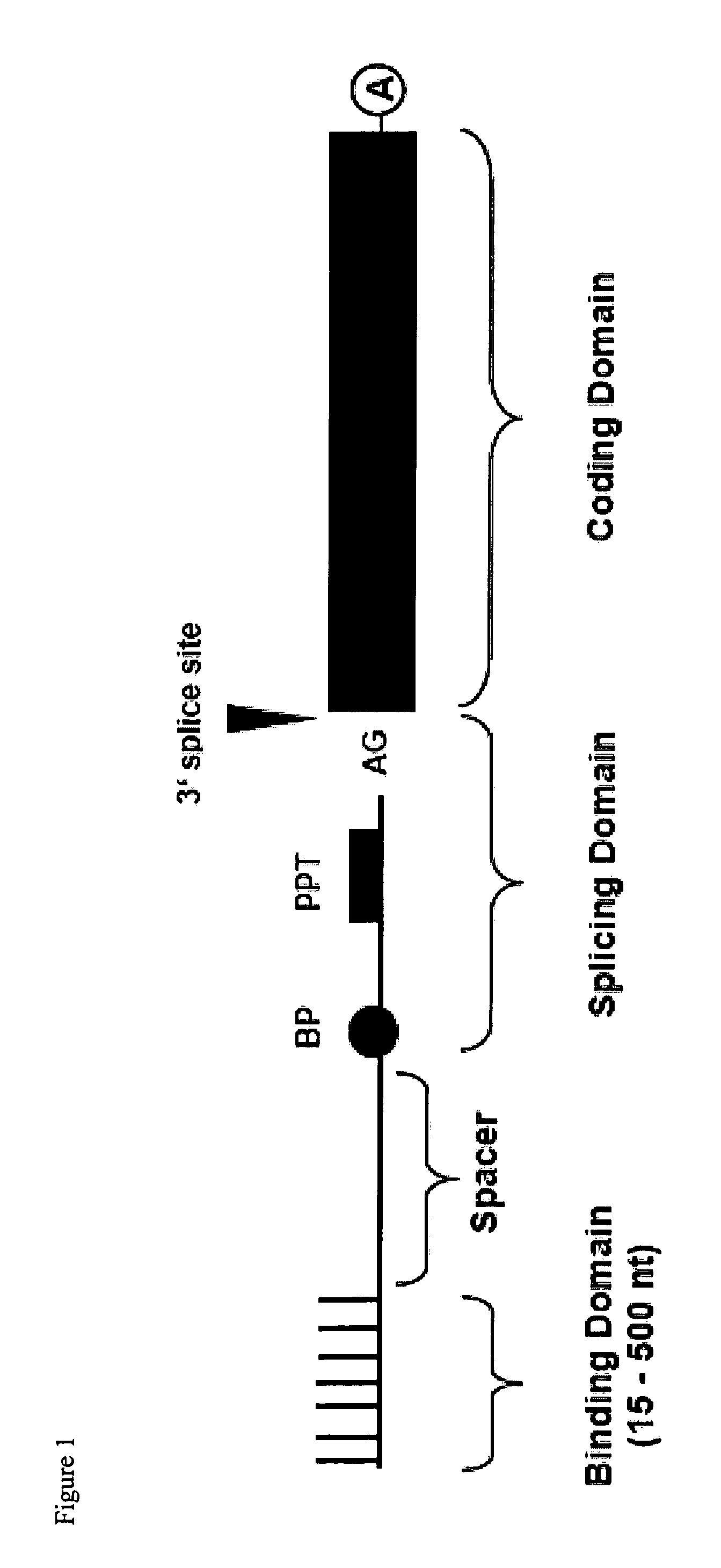
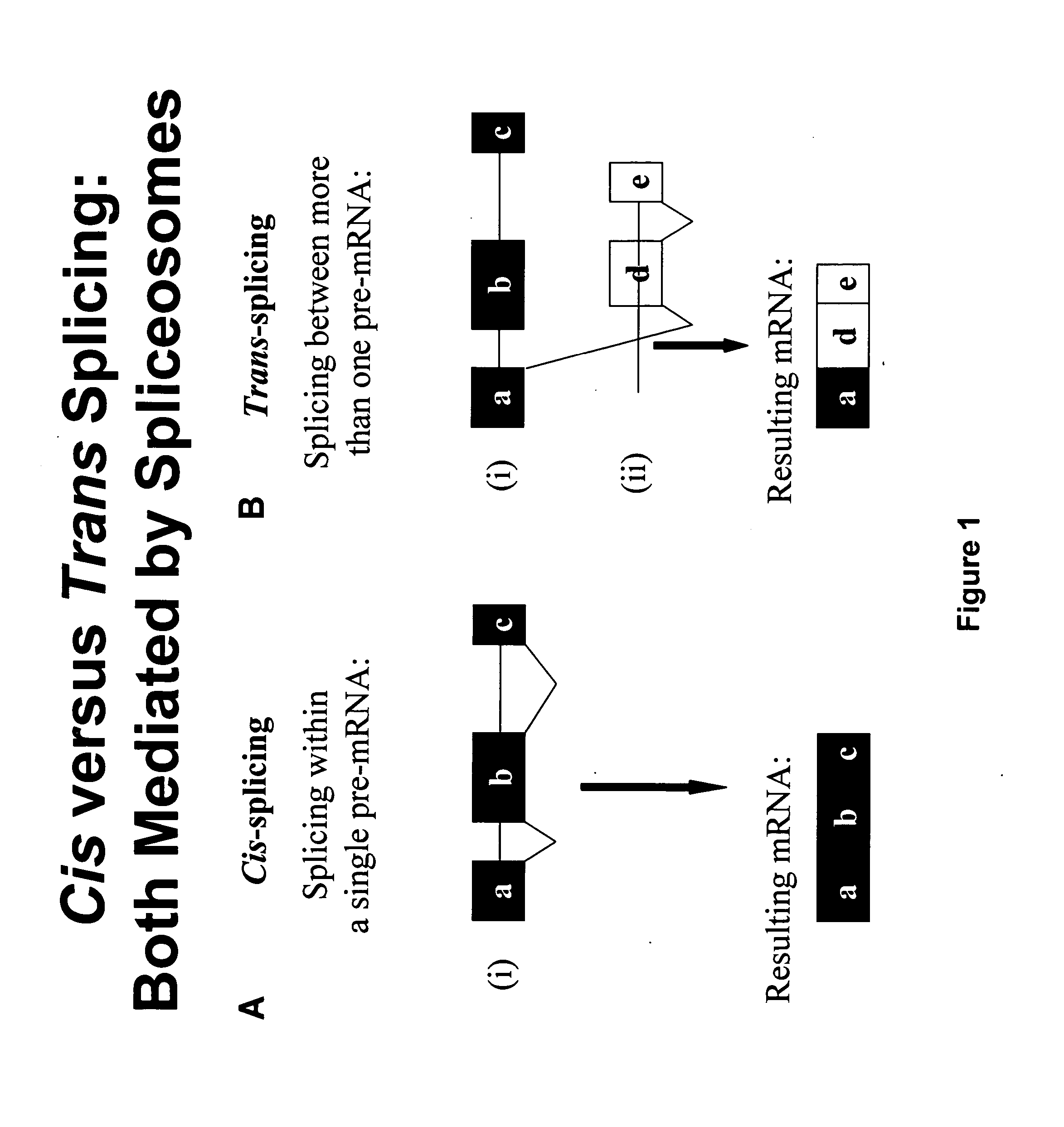
Trans-splicing is a special form of RNA processing where exons from two different primary RNA transcripts are joined end to end and ligated. It is usually found in eukaryotes and mediated by the spliceosome, although some bacteria and archaea also have "half-genes" for tRNAs.
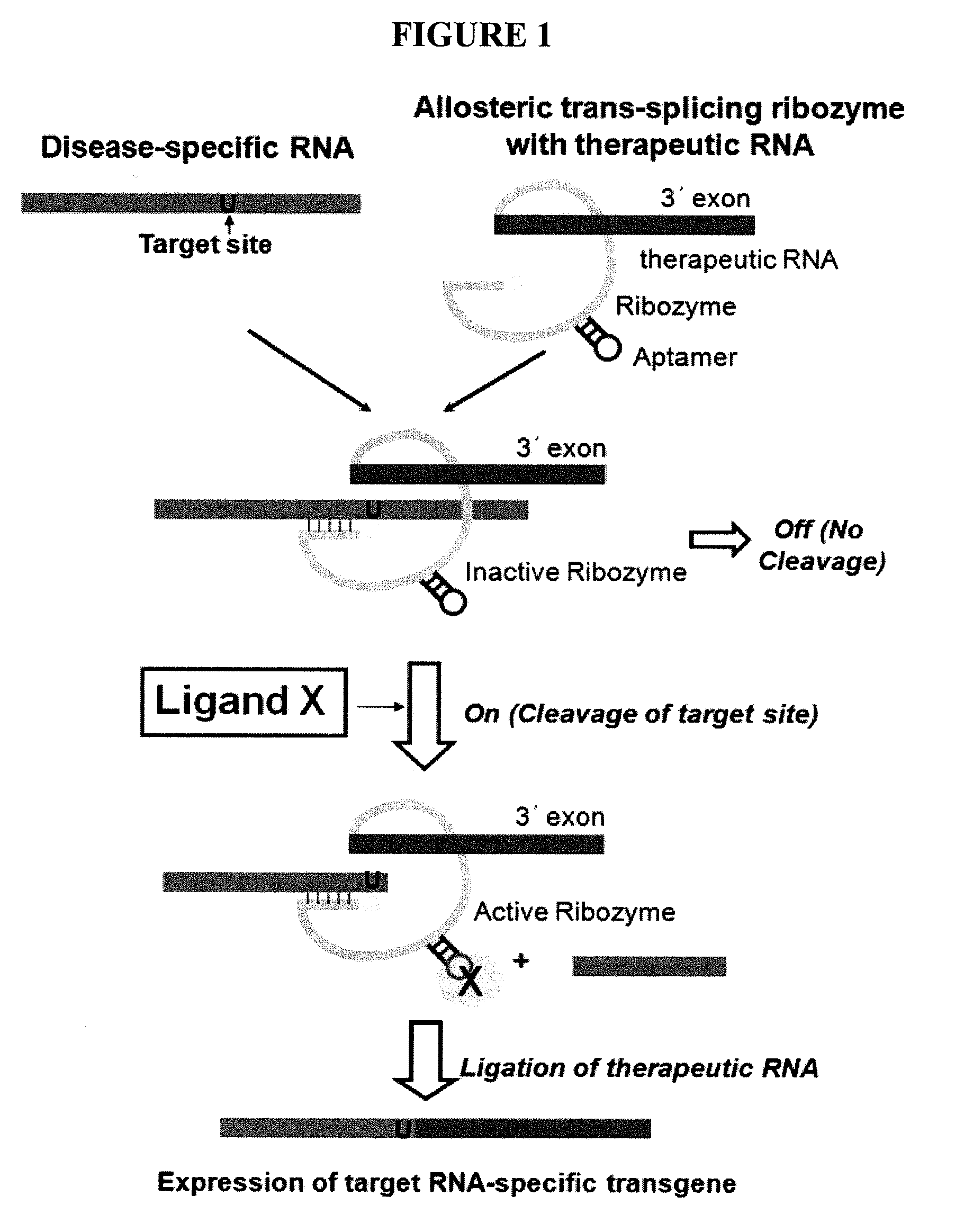
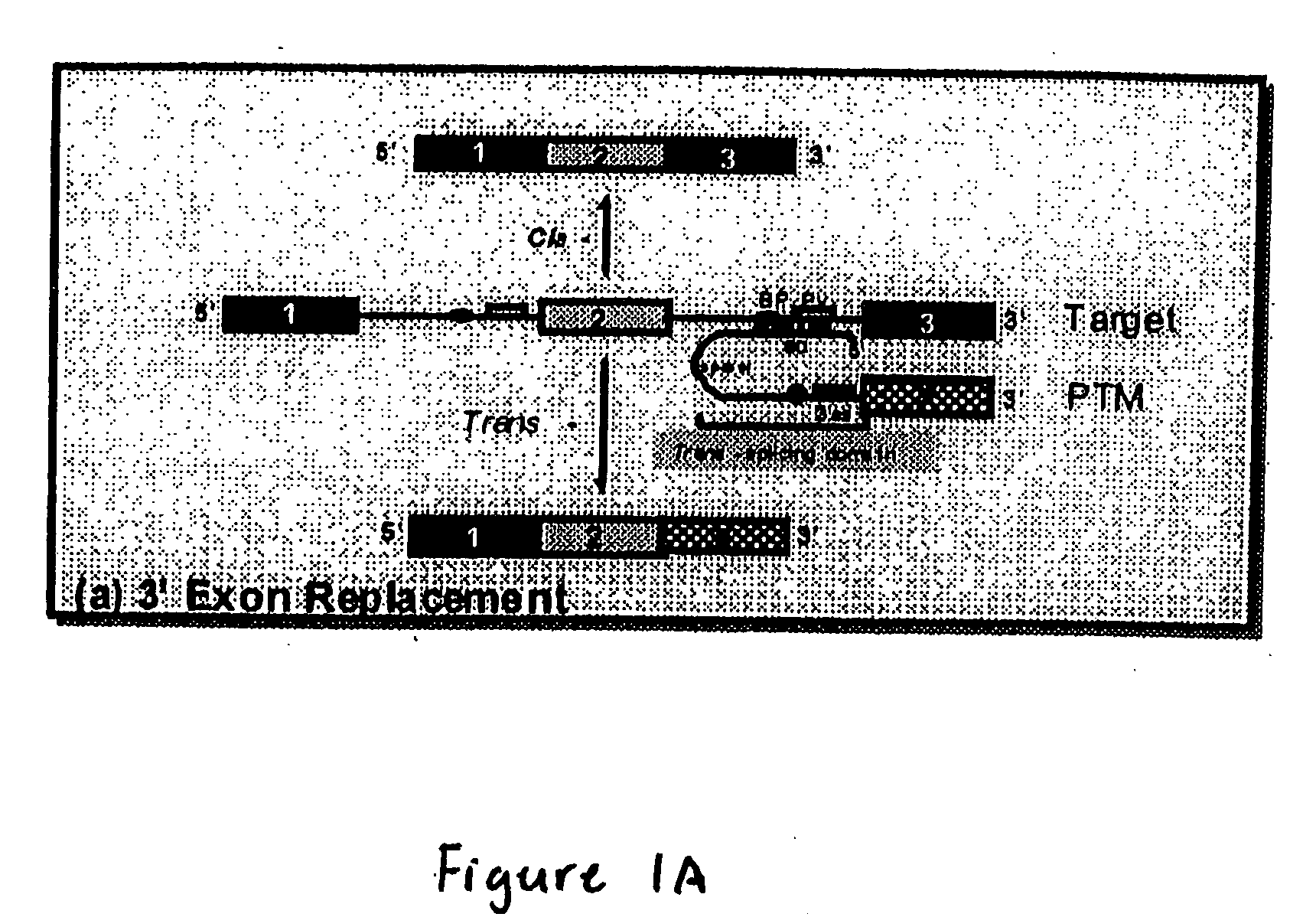
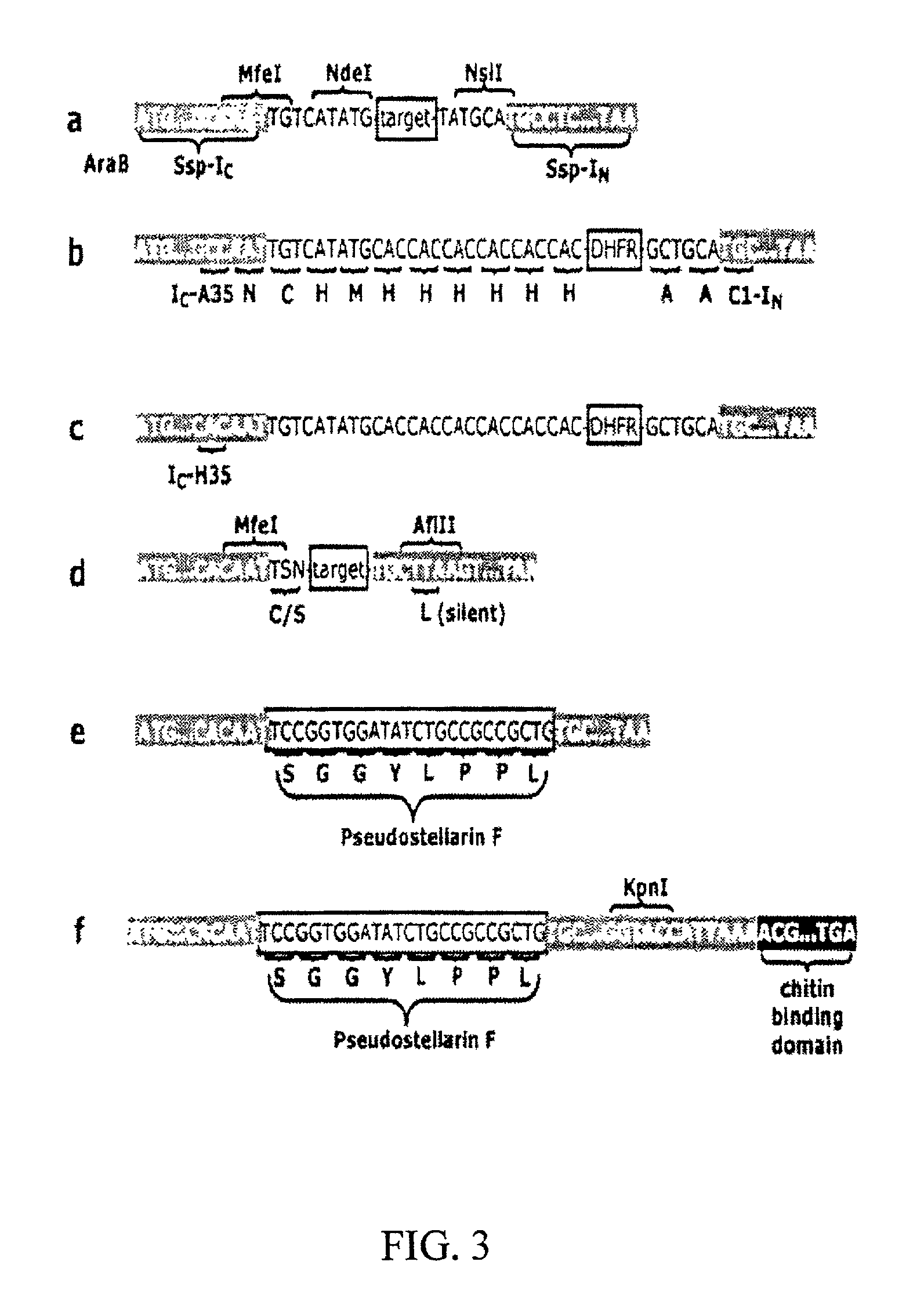
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
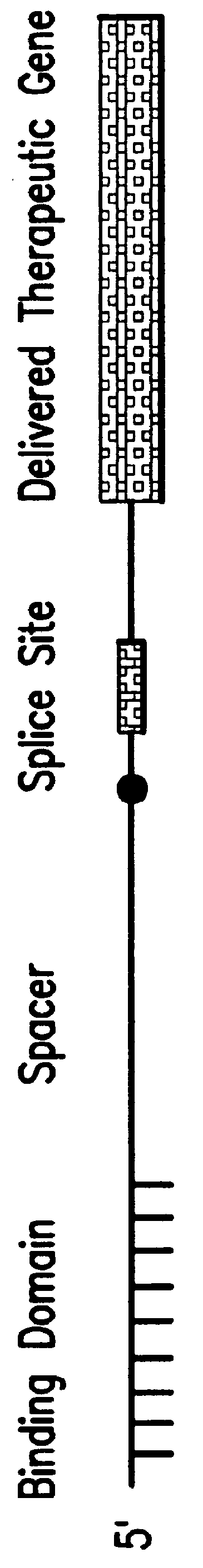
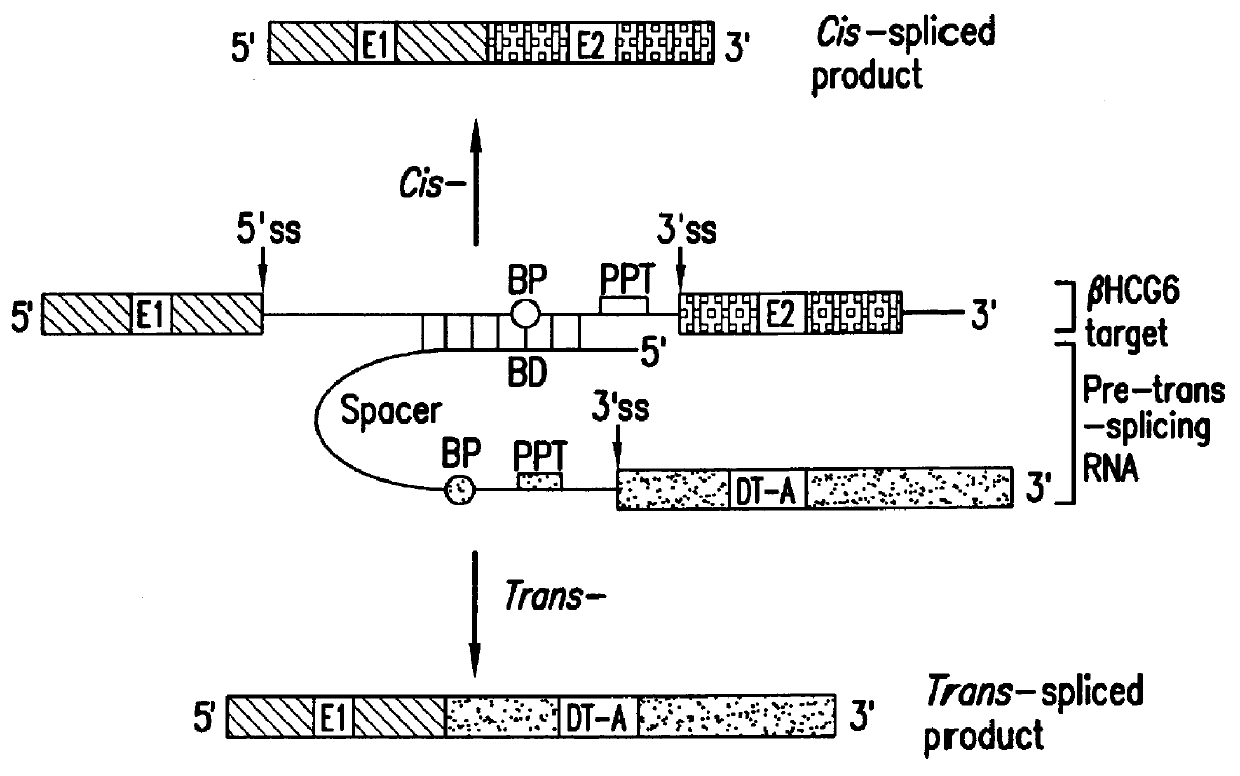
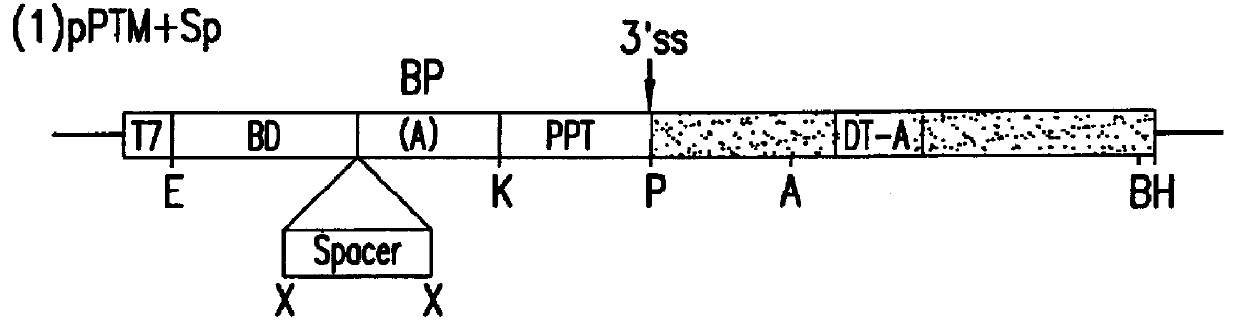
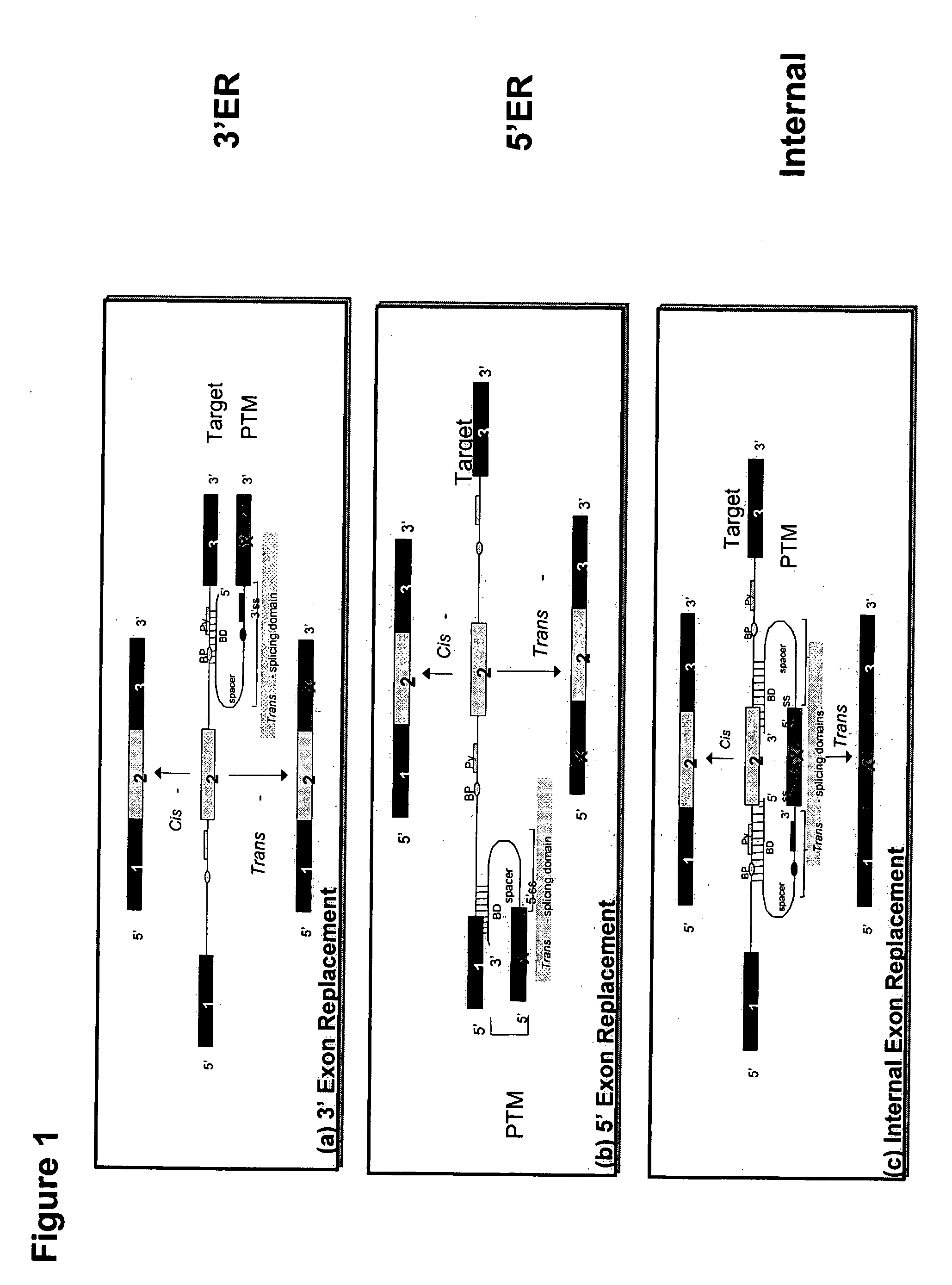
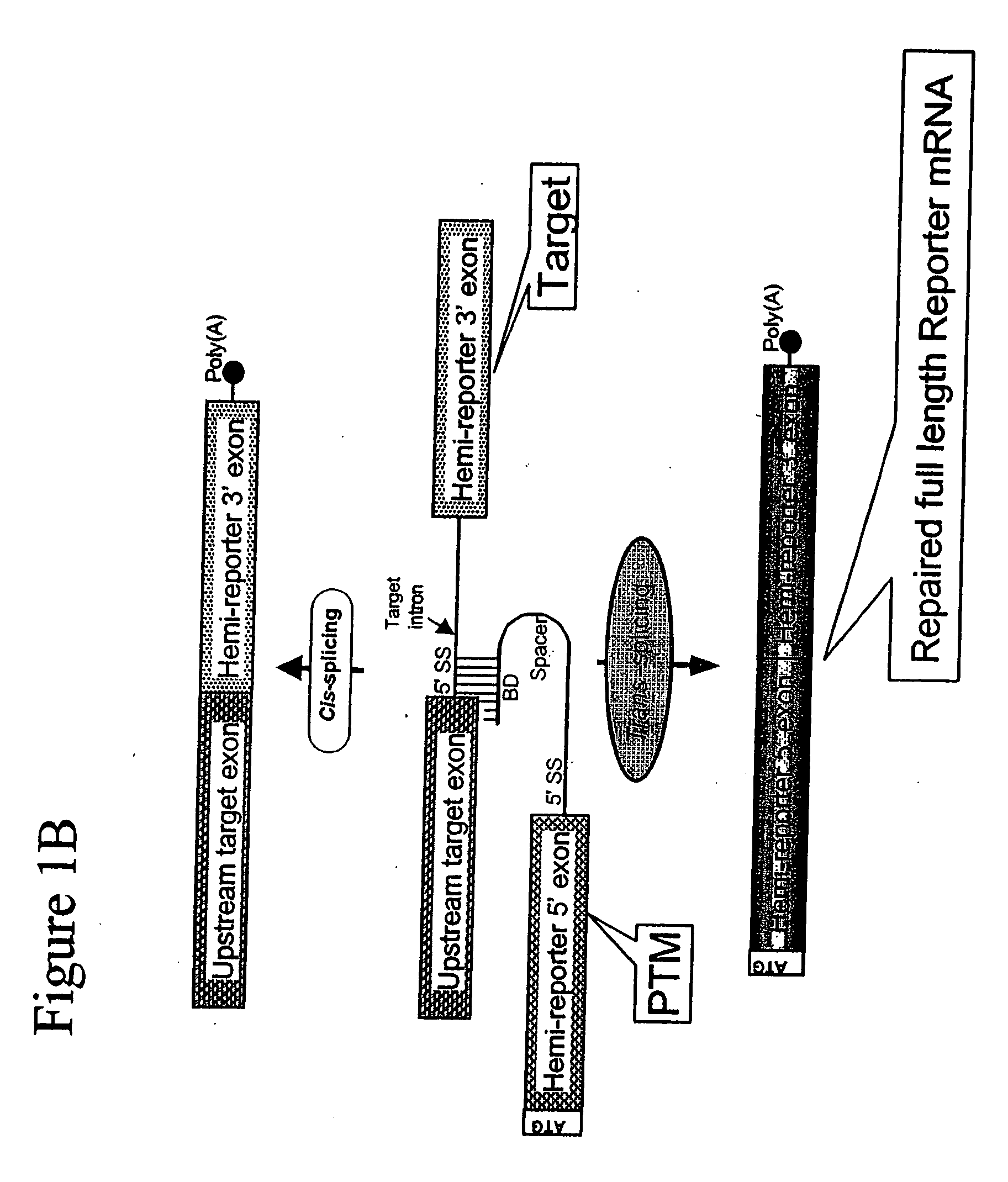
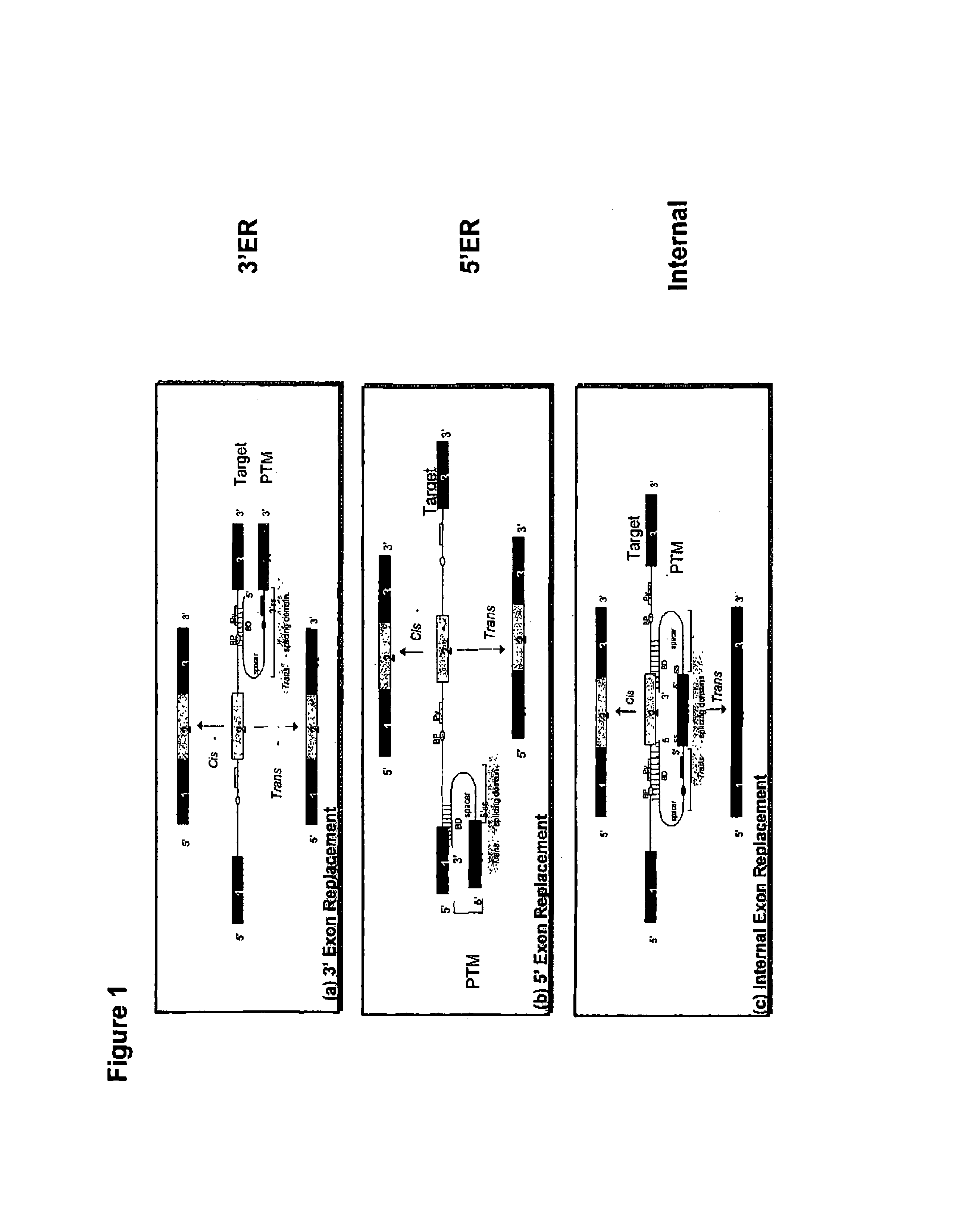
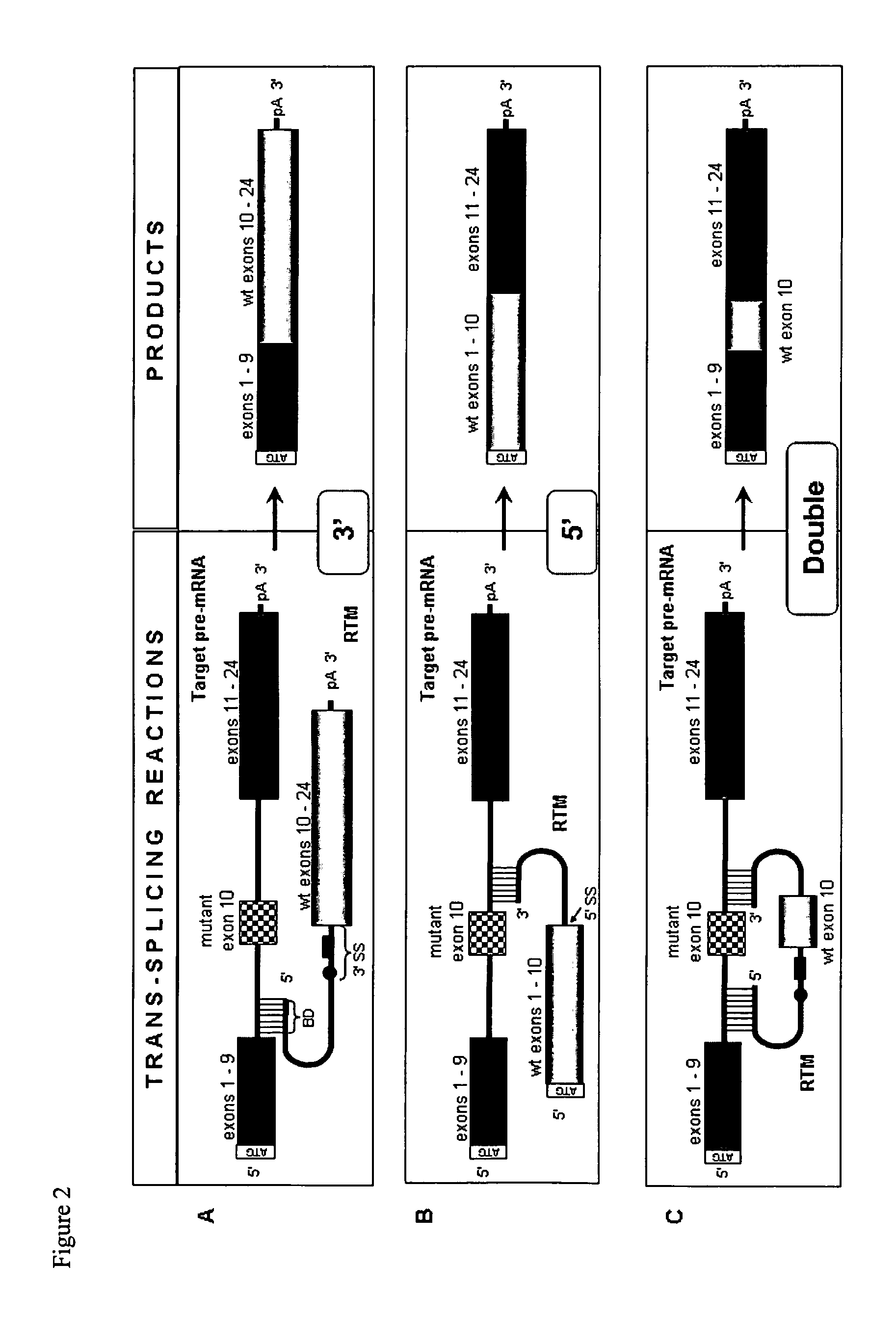
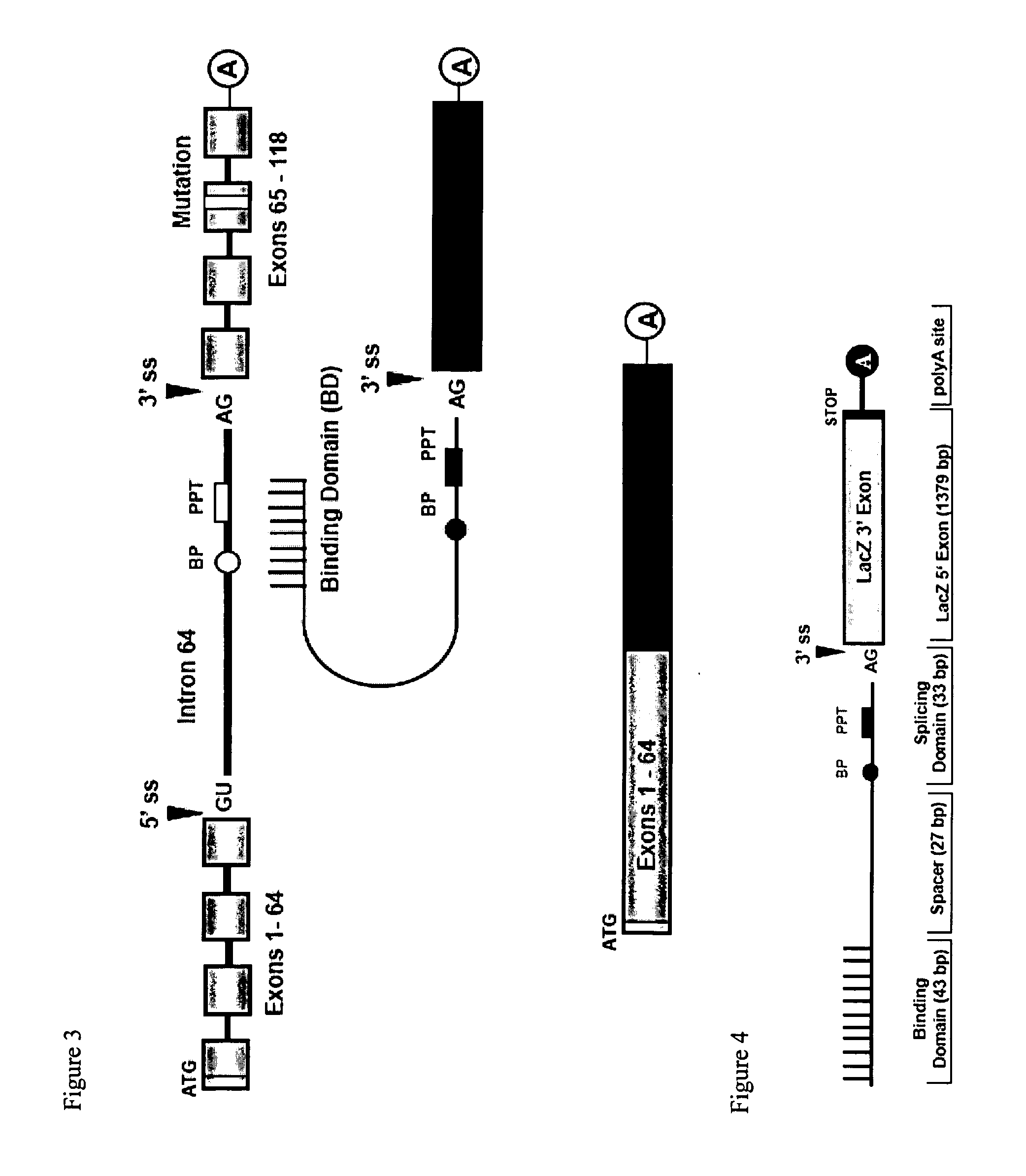
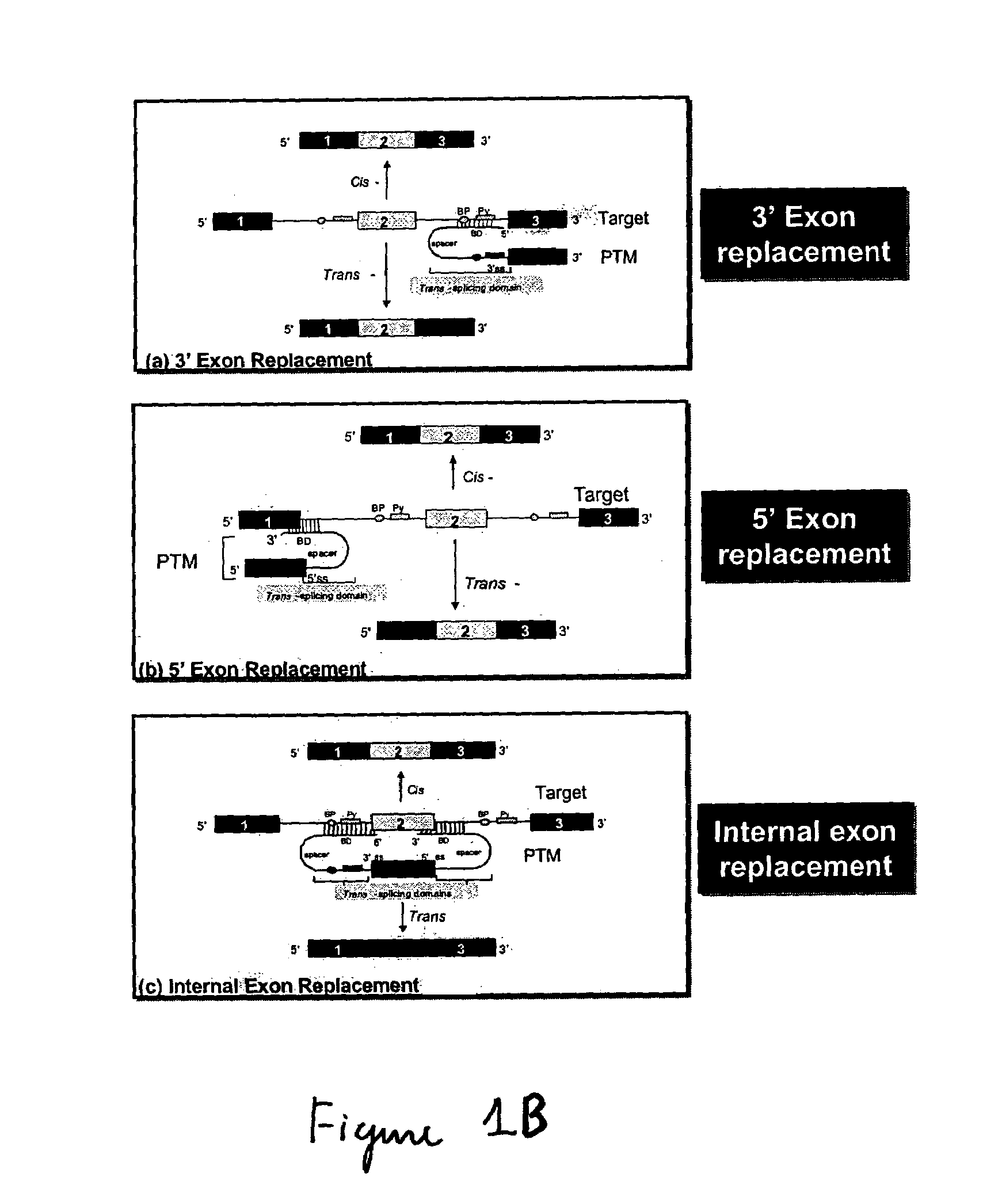
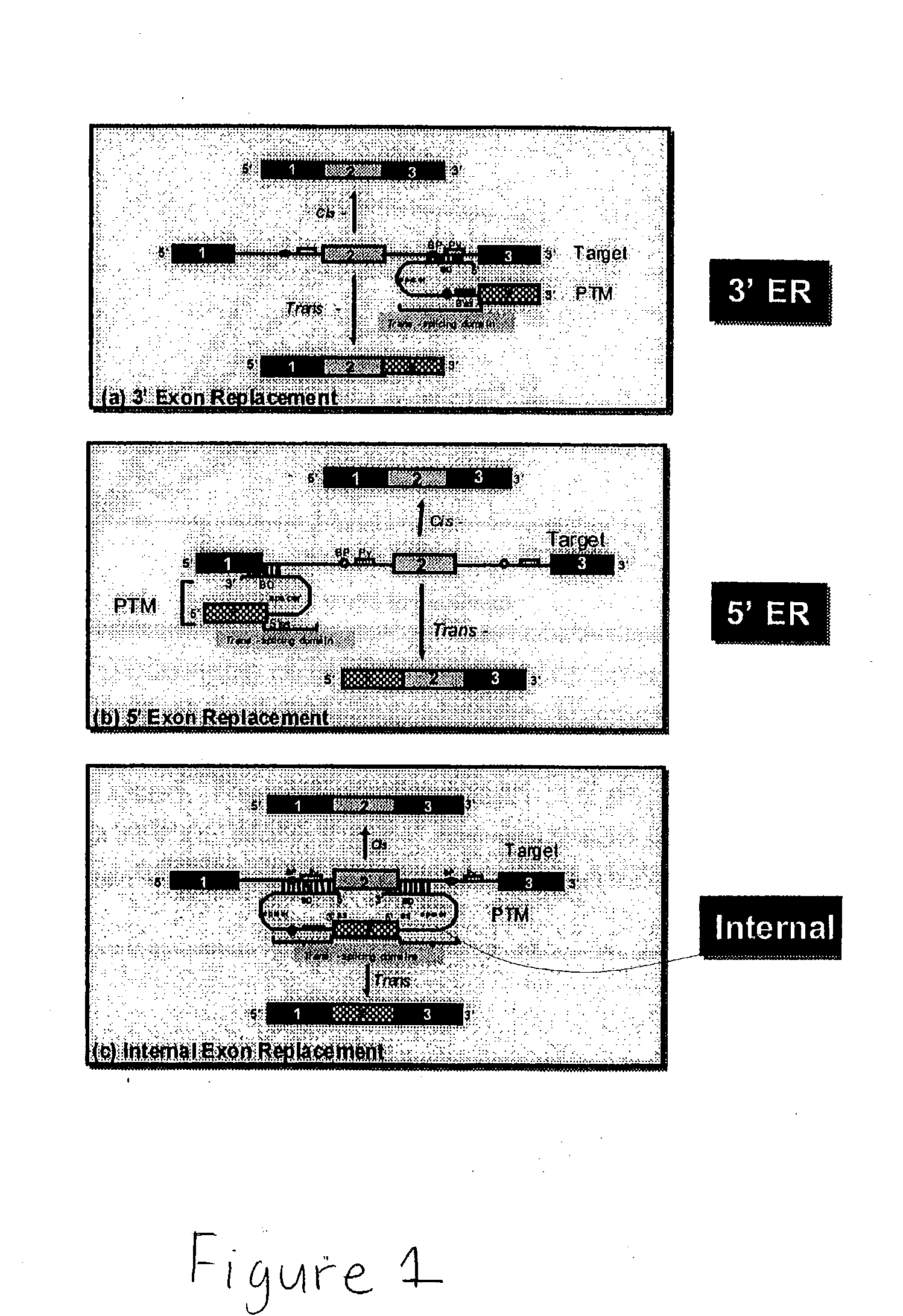
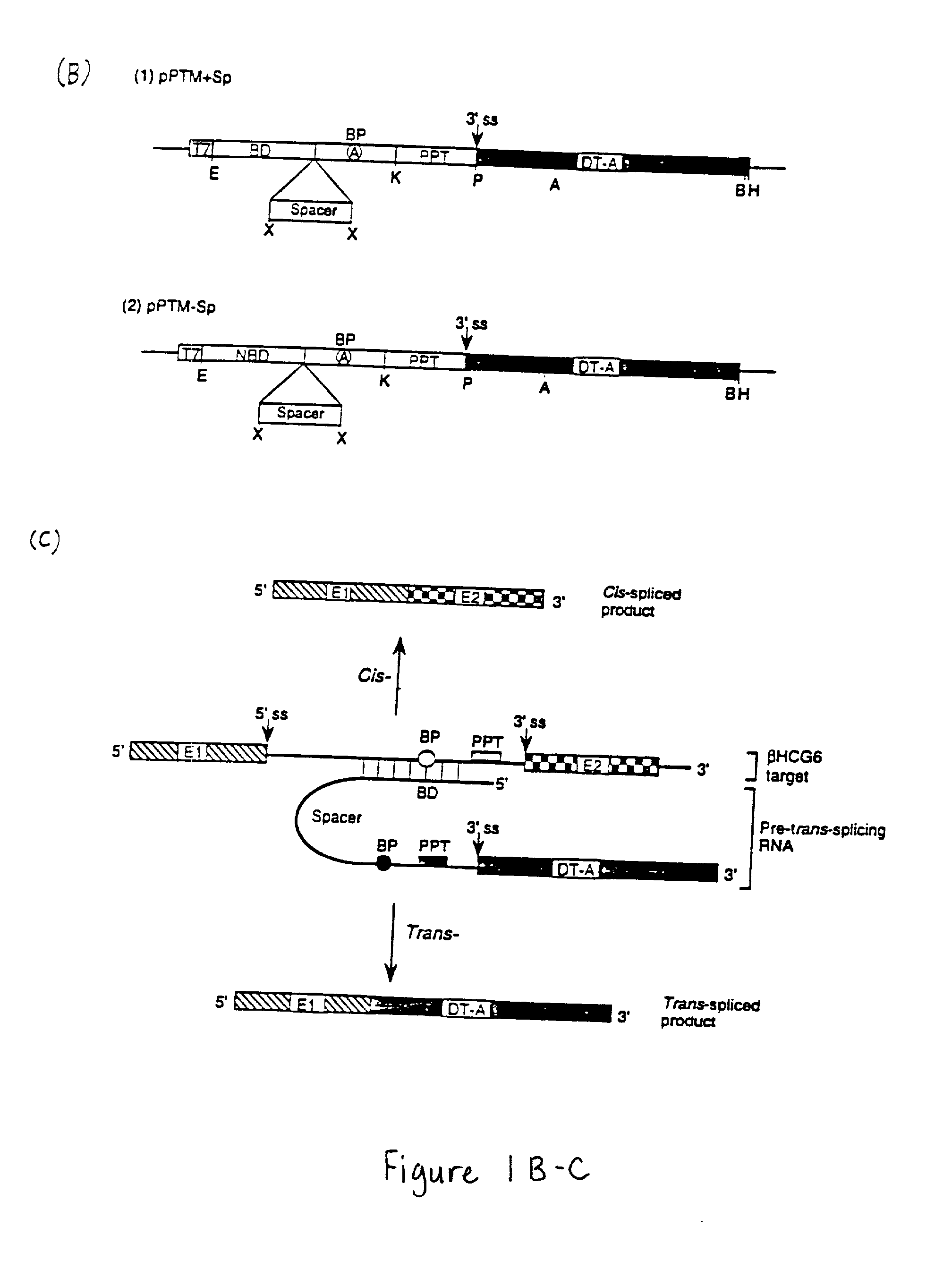
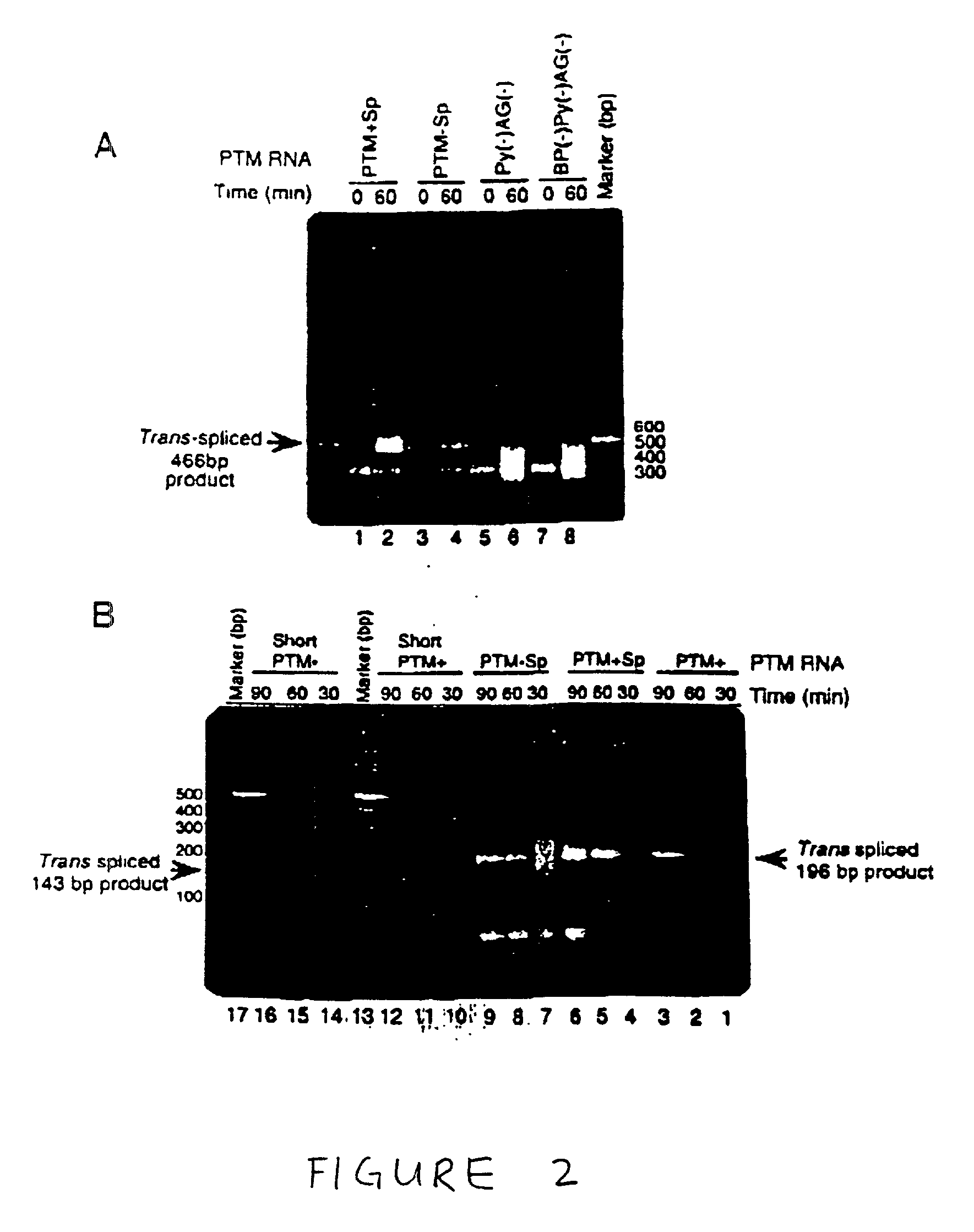
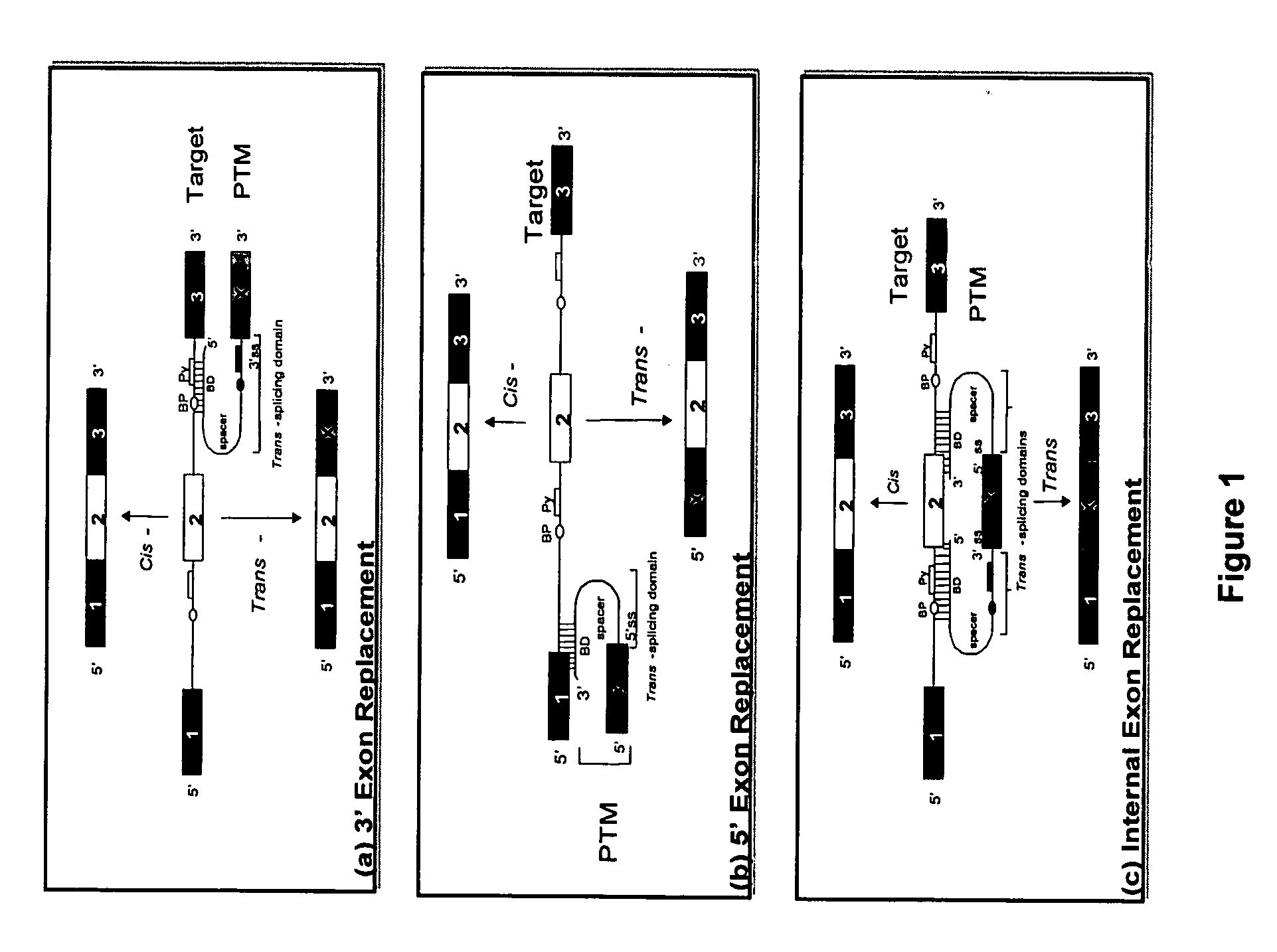
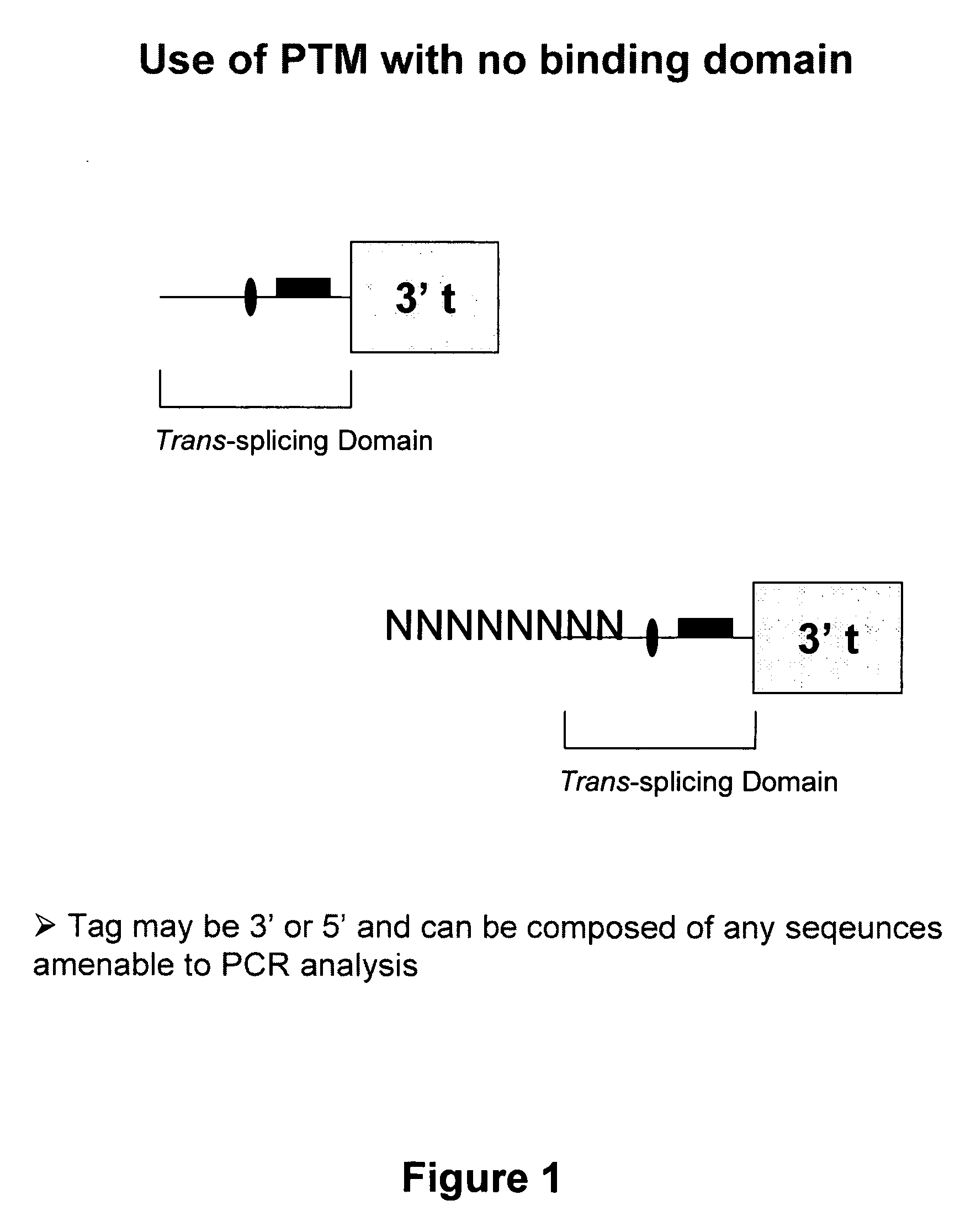
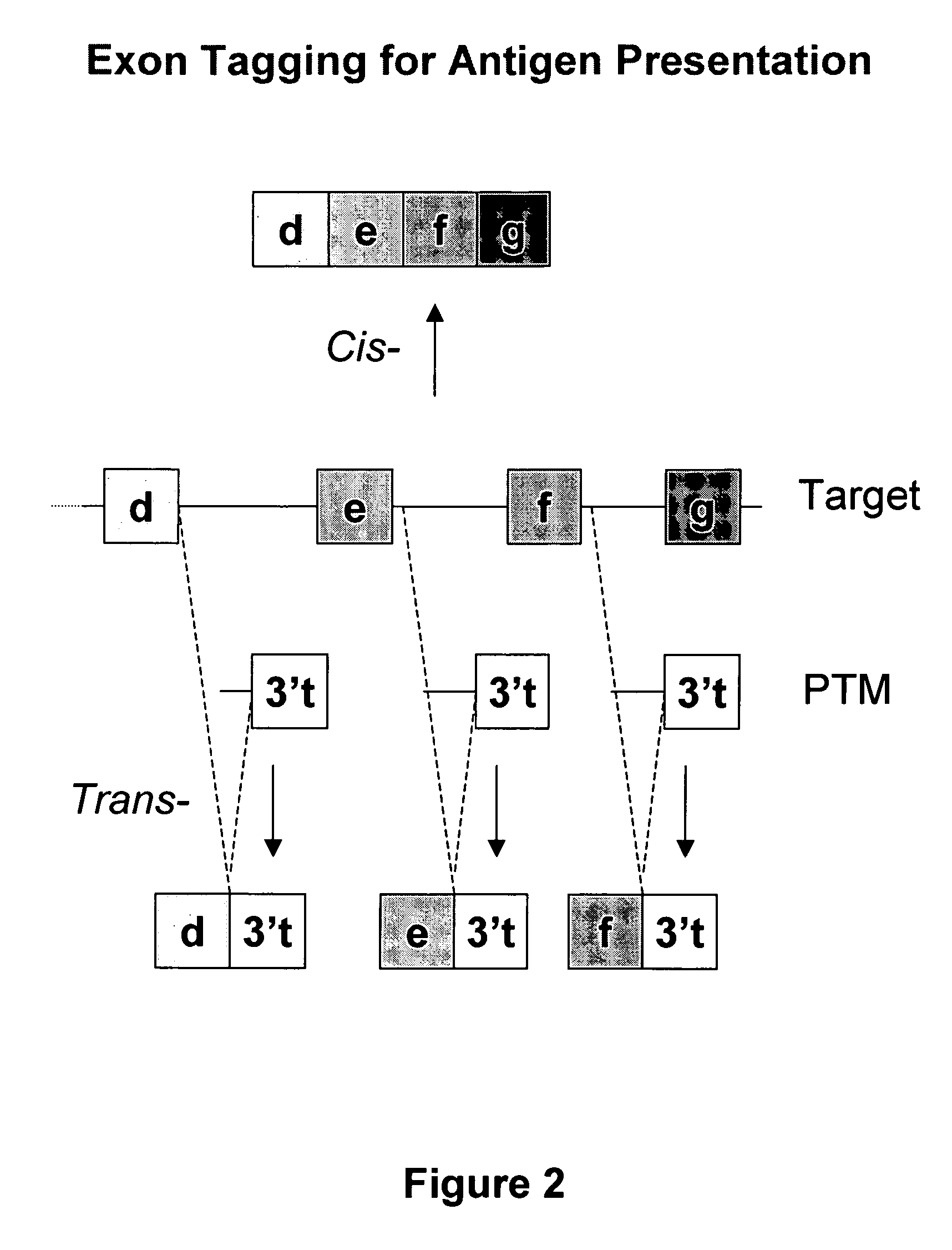
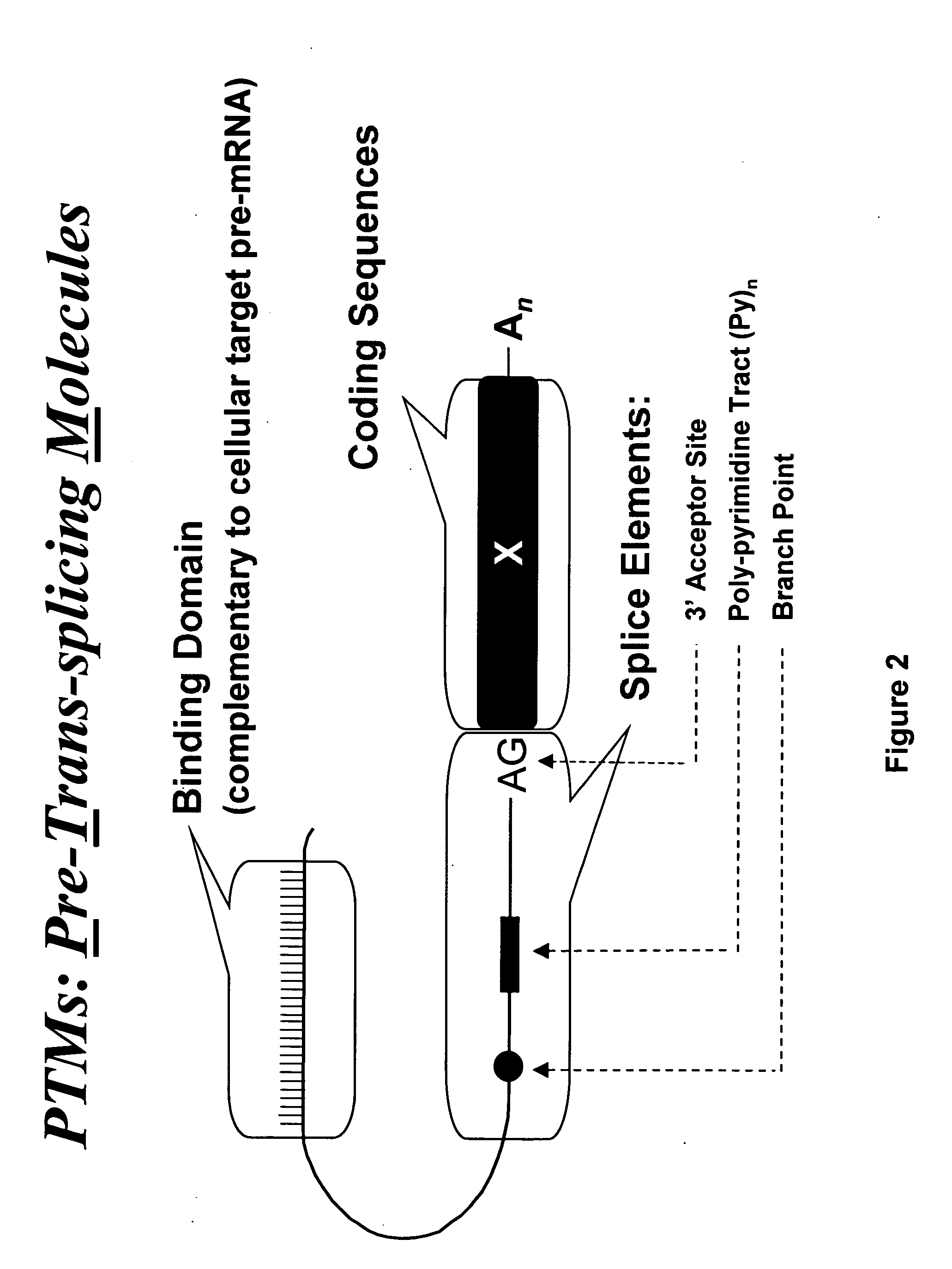
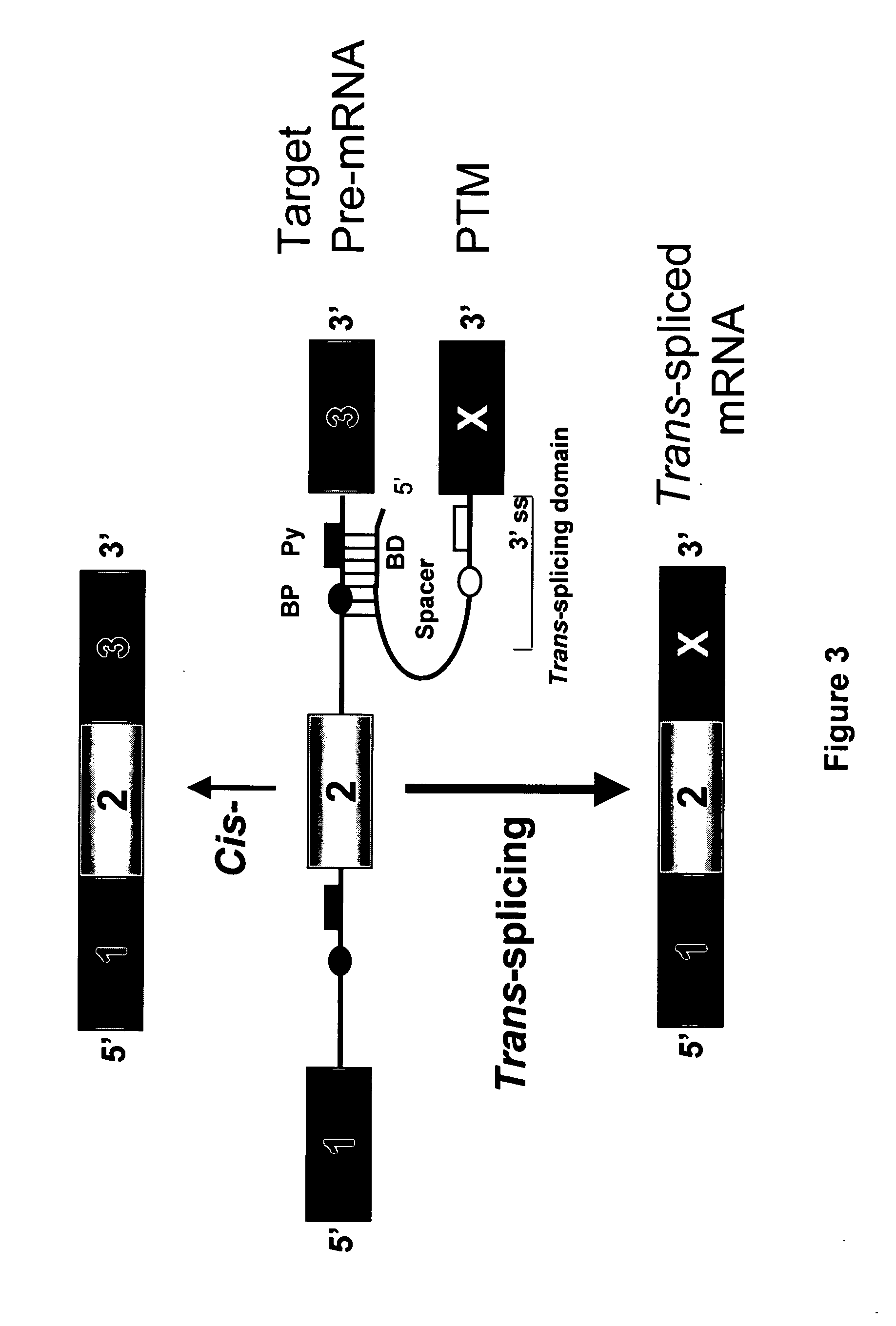
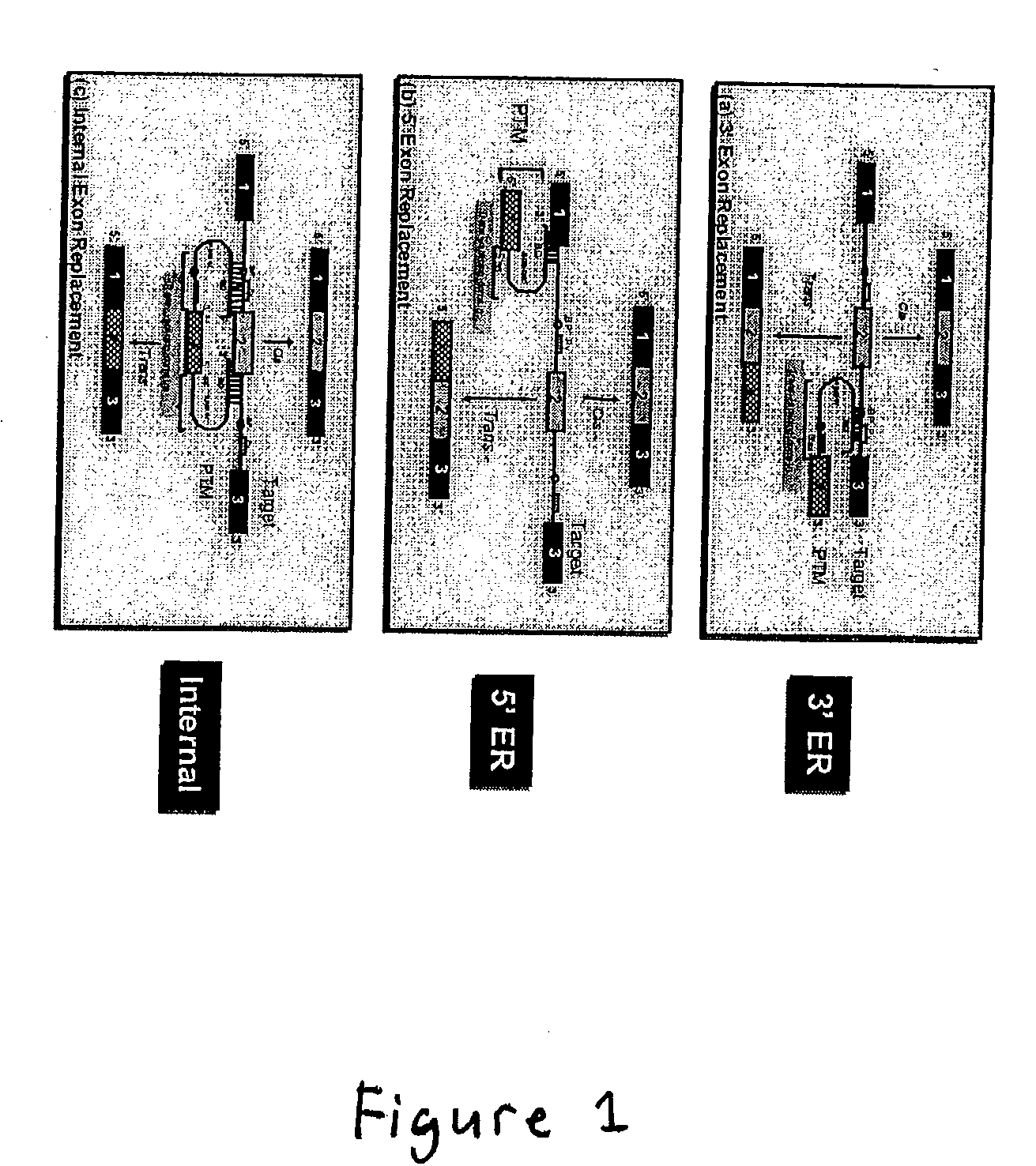
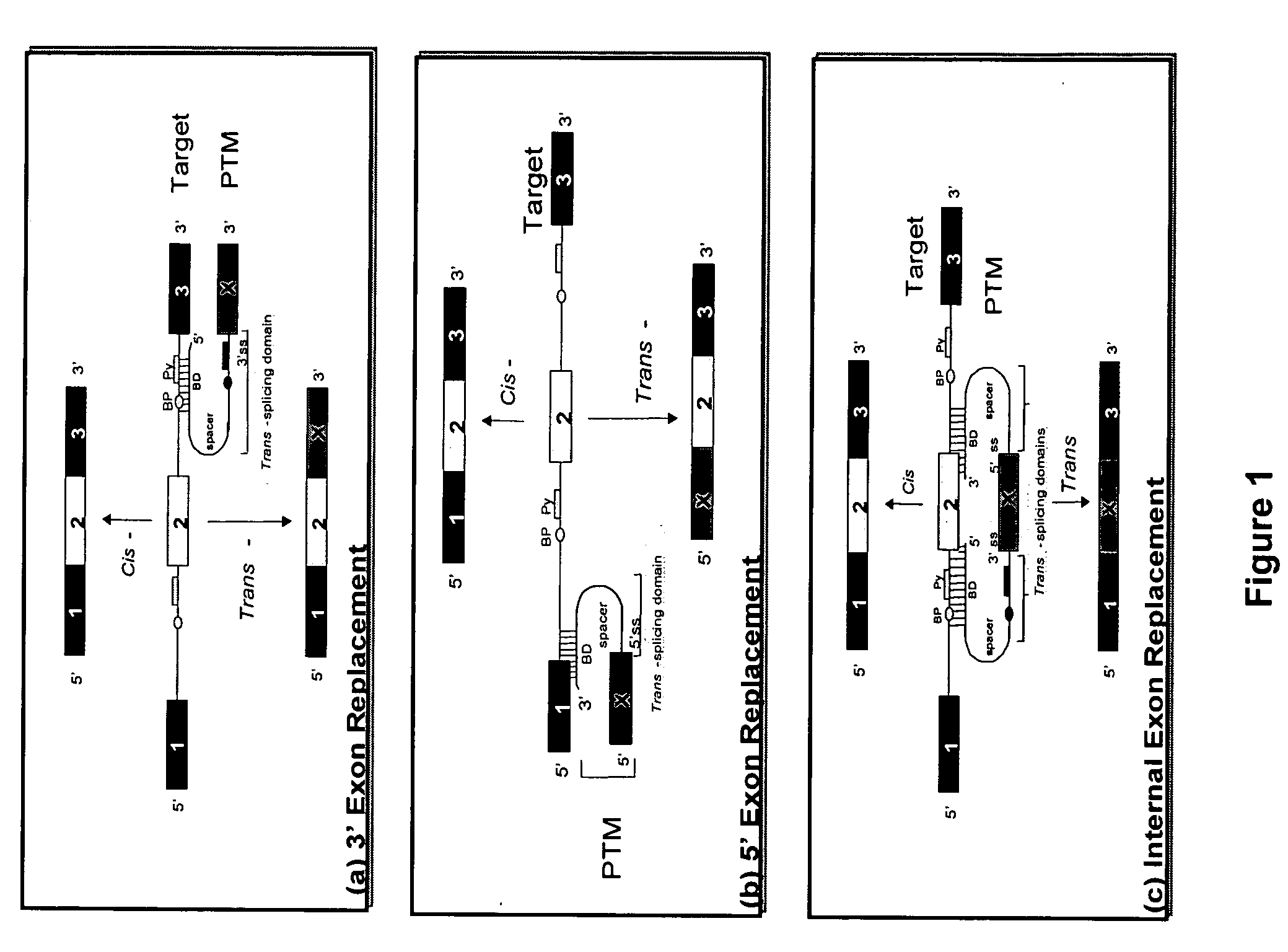
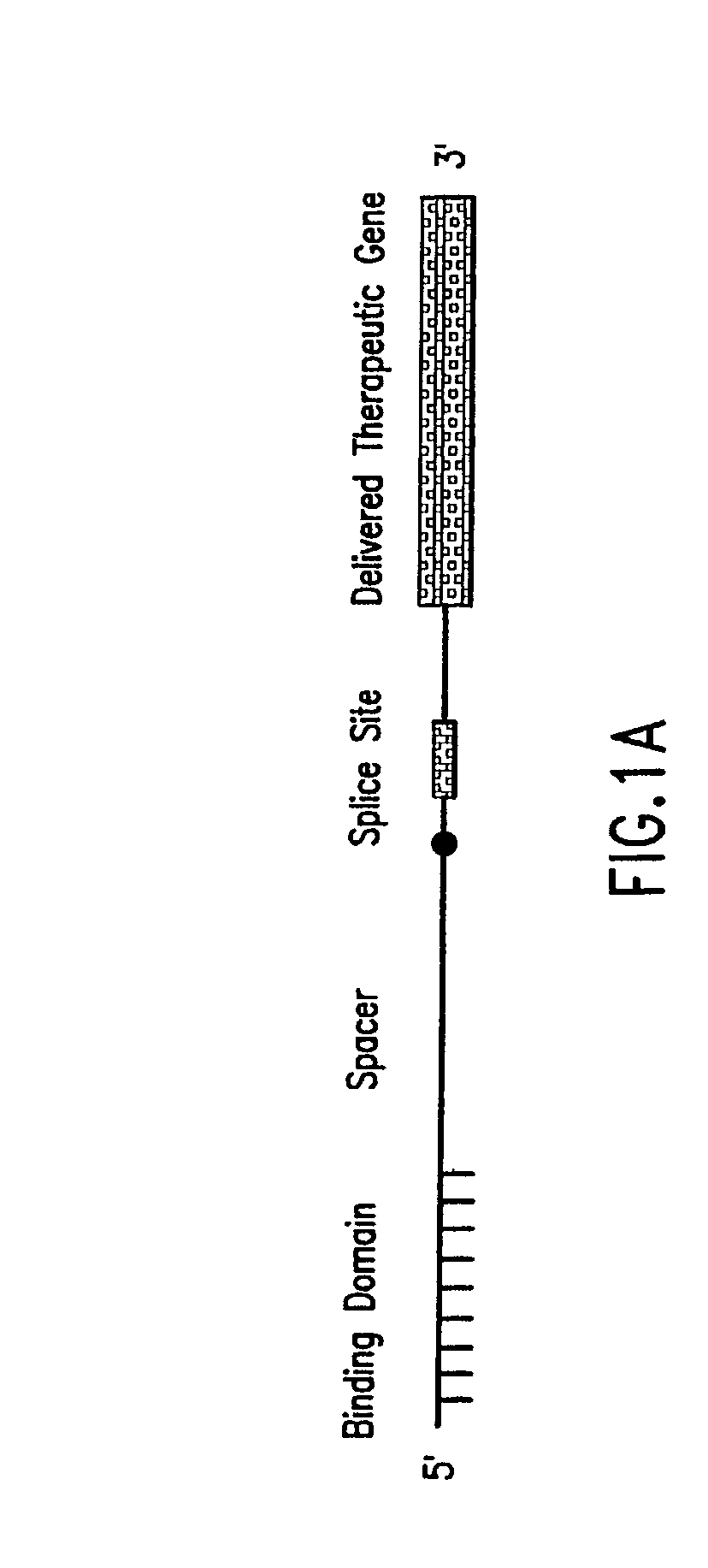
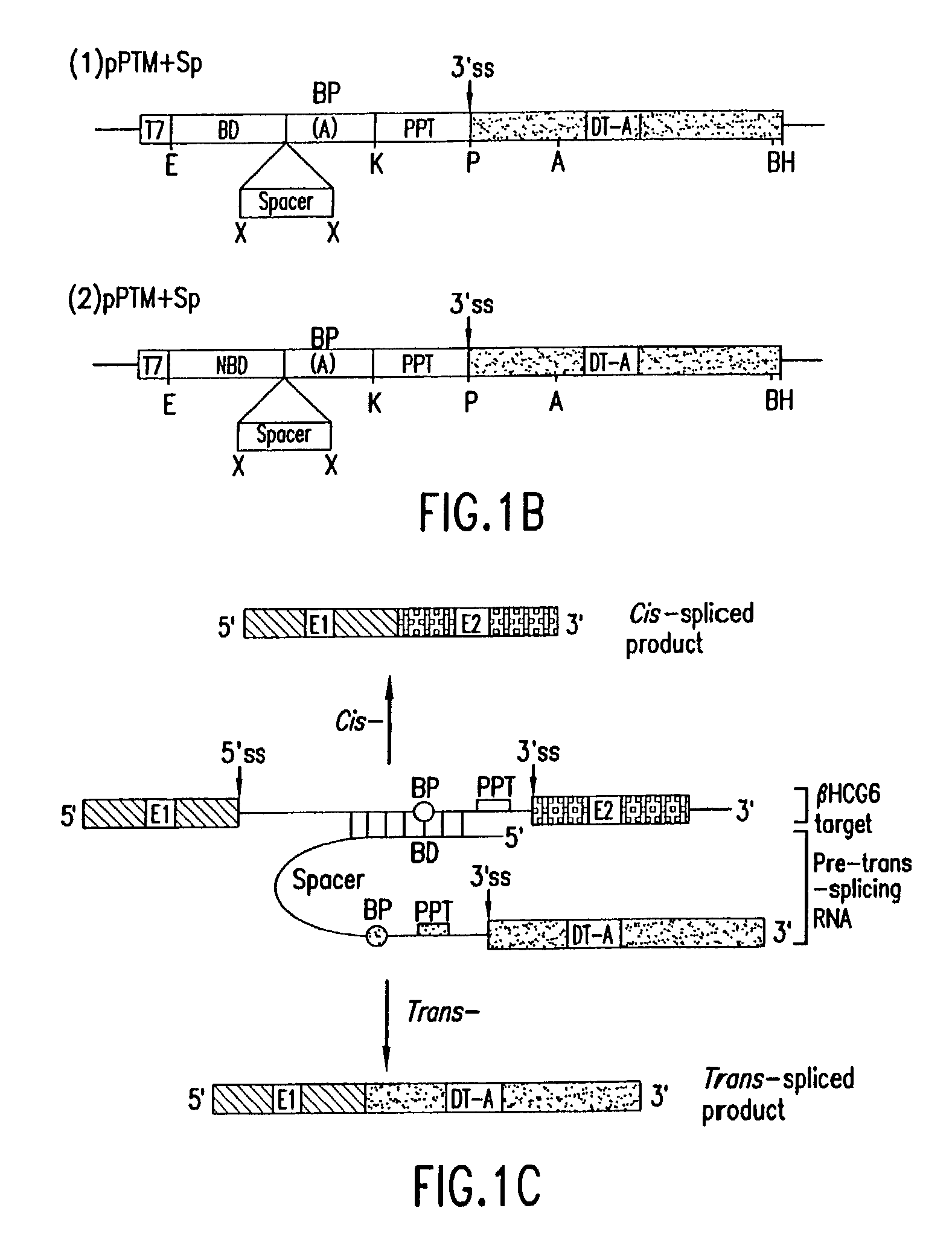
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:INTRONN HLDG +1
Correction of alpha-1-antitrypsin genetic defects using spliceosome mediated RNA trans splicing
InactiveUS20060234247A1Reduce lungReduce liver pathologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseRNA Trans-Splicing
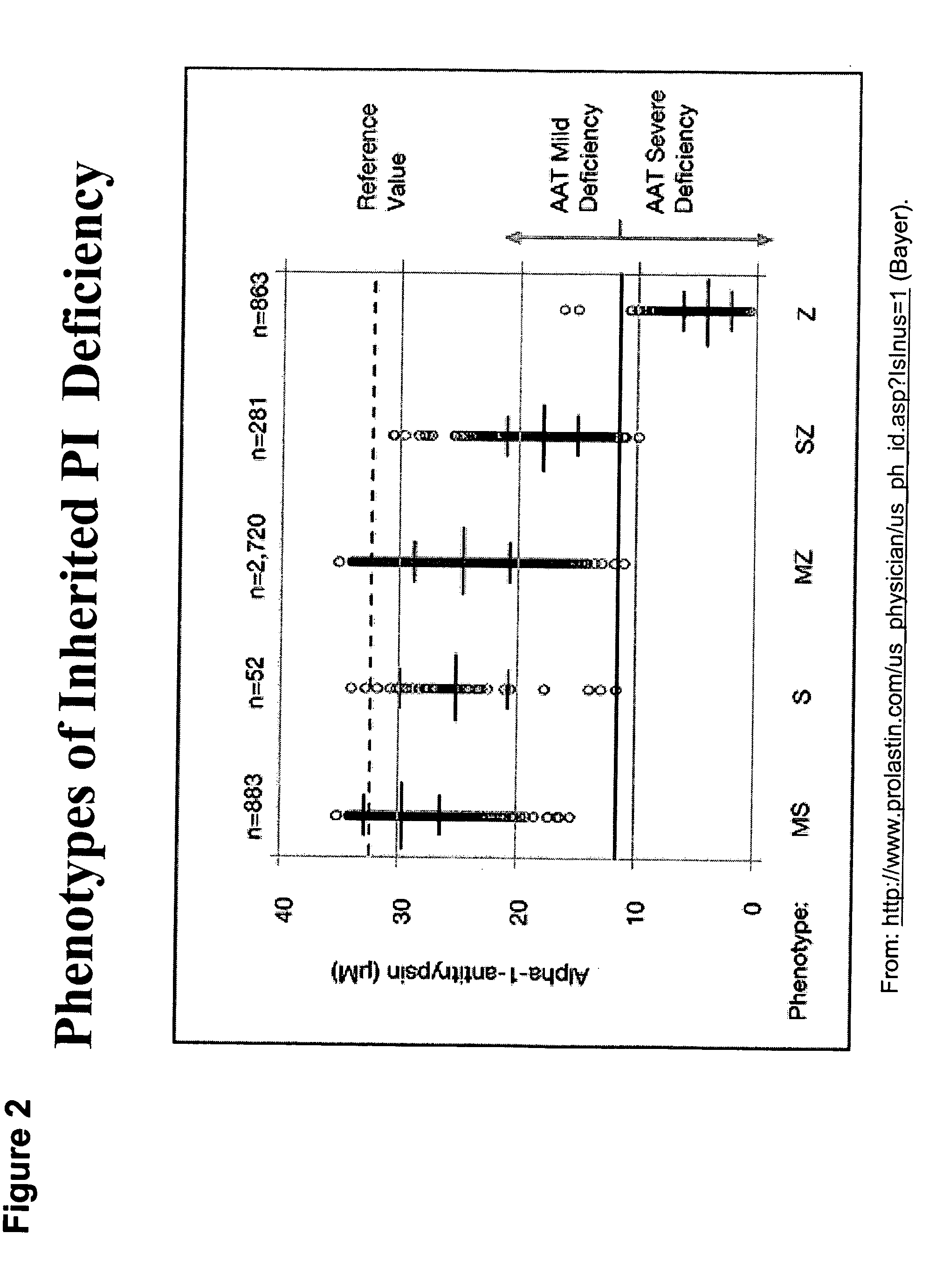
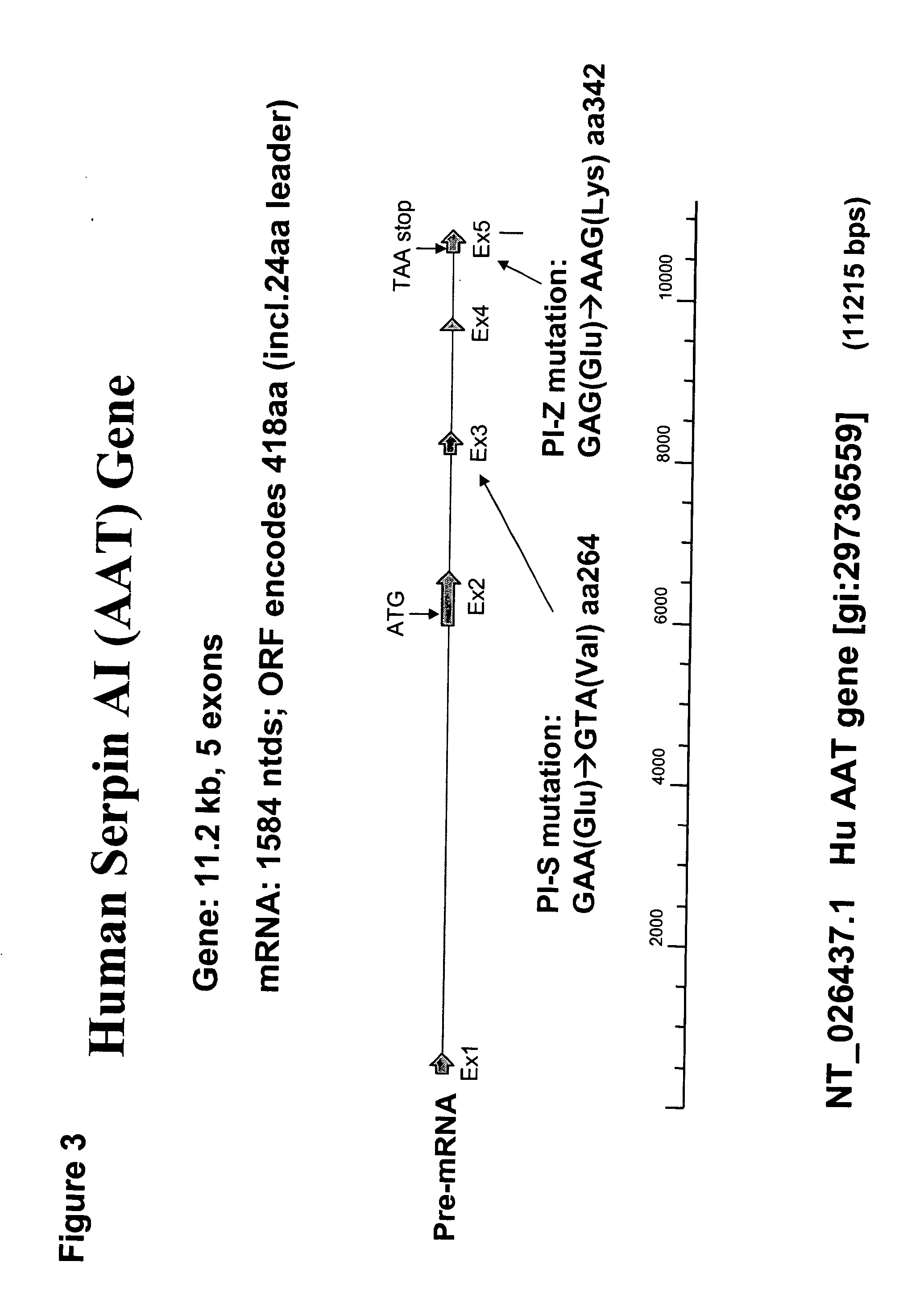
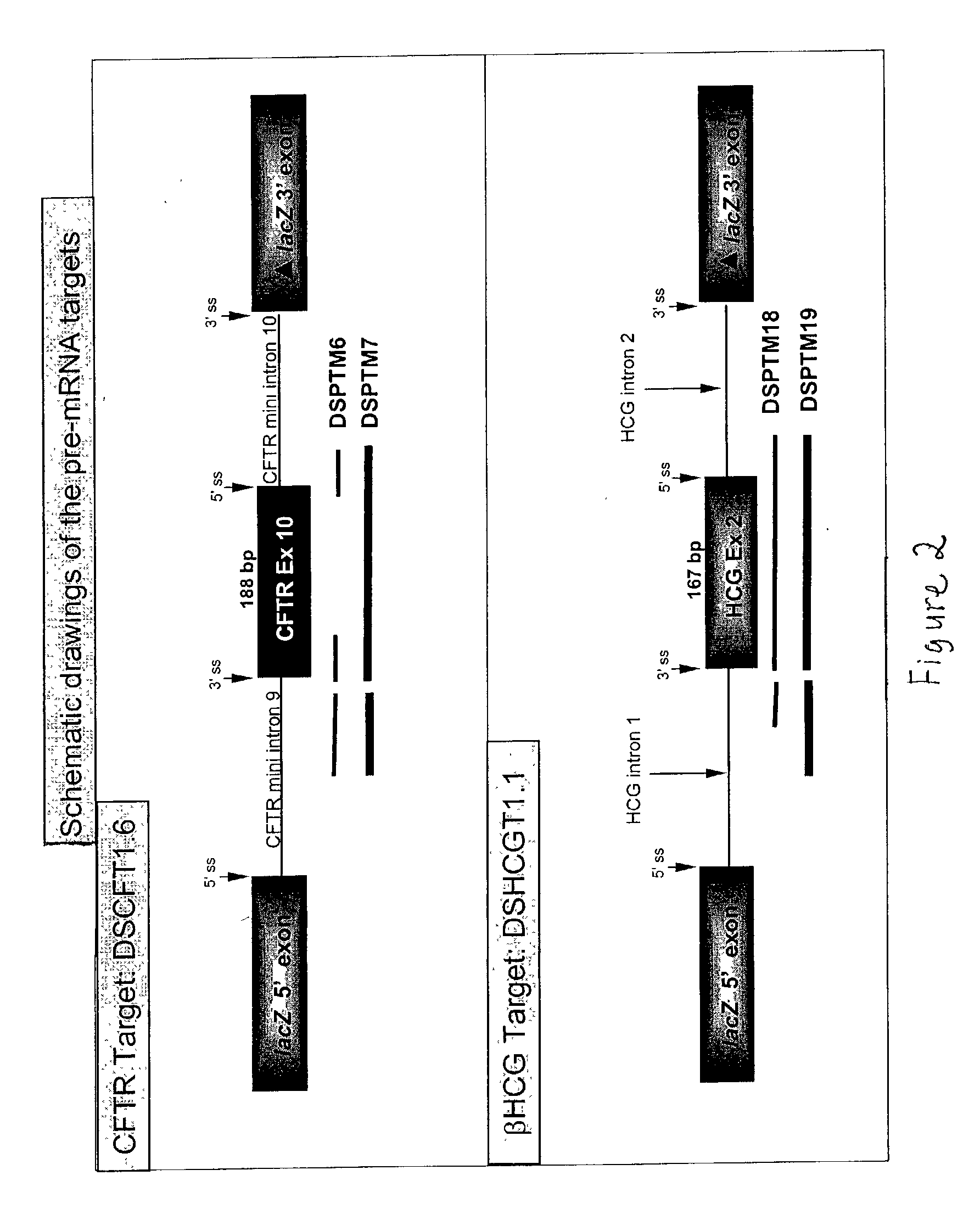
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated RNA trans-splicing. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a SERPINA1 target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). In particular, the PTMs of the present invention include those genetically engineered to interact with SERPINA1 target pre-mRNA so as to result in correction of SERPINA1 genetic defects responsible for AAT deficiency. The PTMs of the invention may also comprise sequences that are processed out of the PTM to yield duplex siRNA molecules directed specifically to mutant SERPIN A1 mRNAs. Such duplexed siRNAs are designed to reduce the accumulation of toxic AAT protein in liver cells. The methods and compositions of the present invention can be used in gene therapy for correction of SERPINA1 disorders such as AAT deficiency.
Owner:VIRXSYS
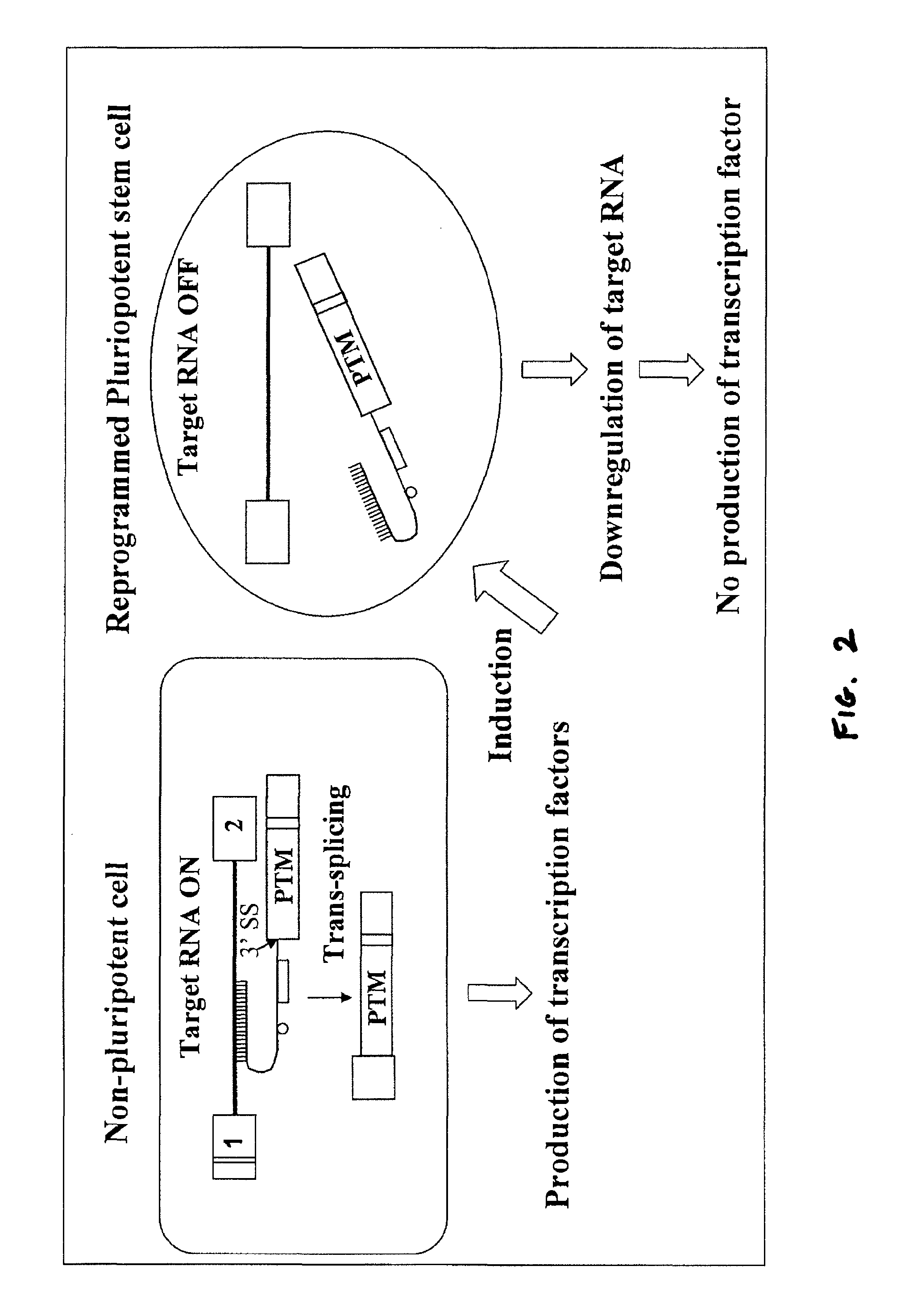
Compositions and methods for generation of pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20110263015A1Genetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsInduced pluripotent stem cellRNA Trans-Splicing
The present invention describes the use of pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) to reprogram human normal and diseased somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells using spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing. More specifically, the present invention describes the use of the SMaRT™ technology to repair or reprogram the newly induced diseased pluripotent stem cells.
Owner:VIRXSYS
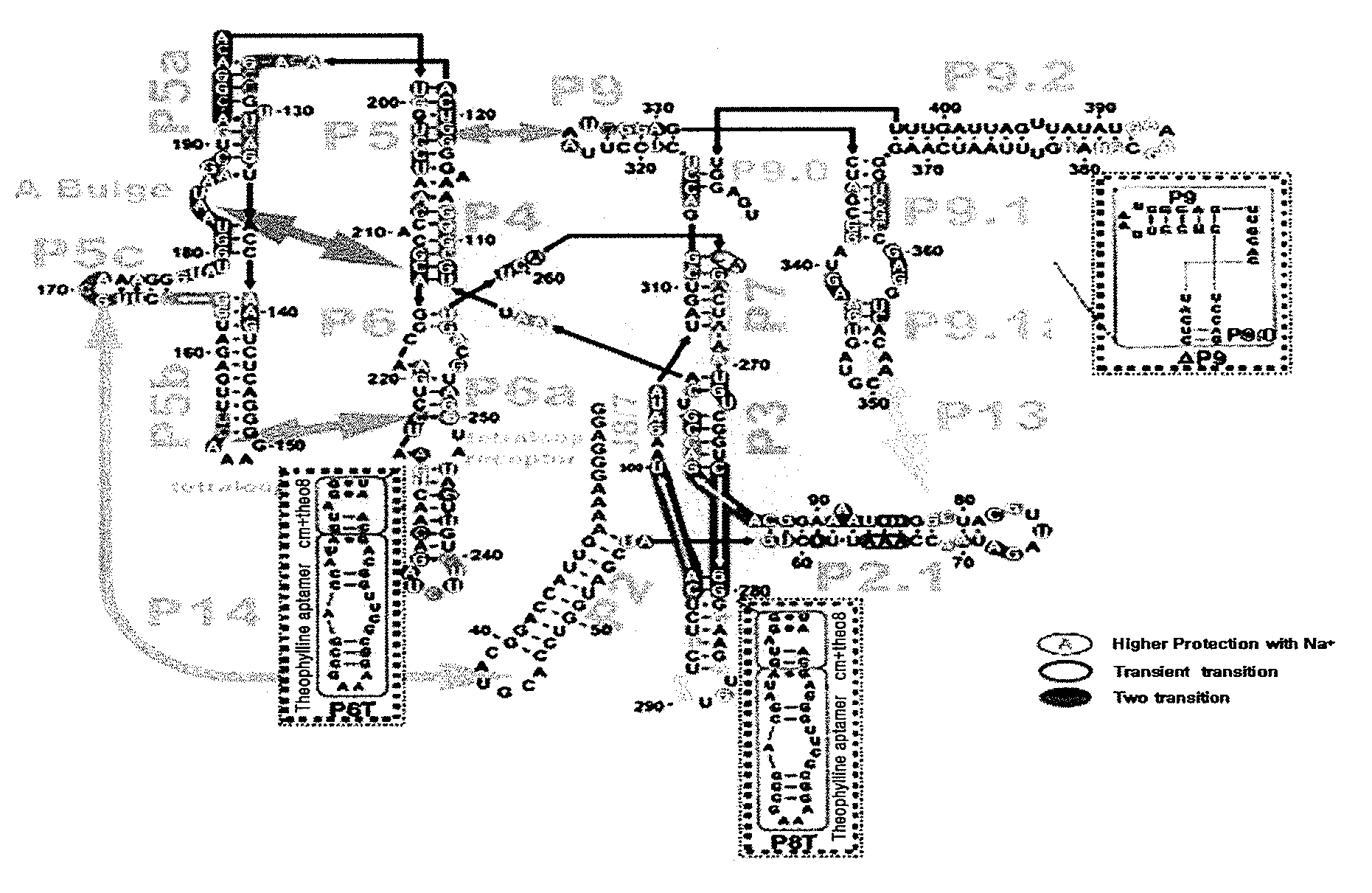
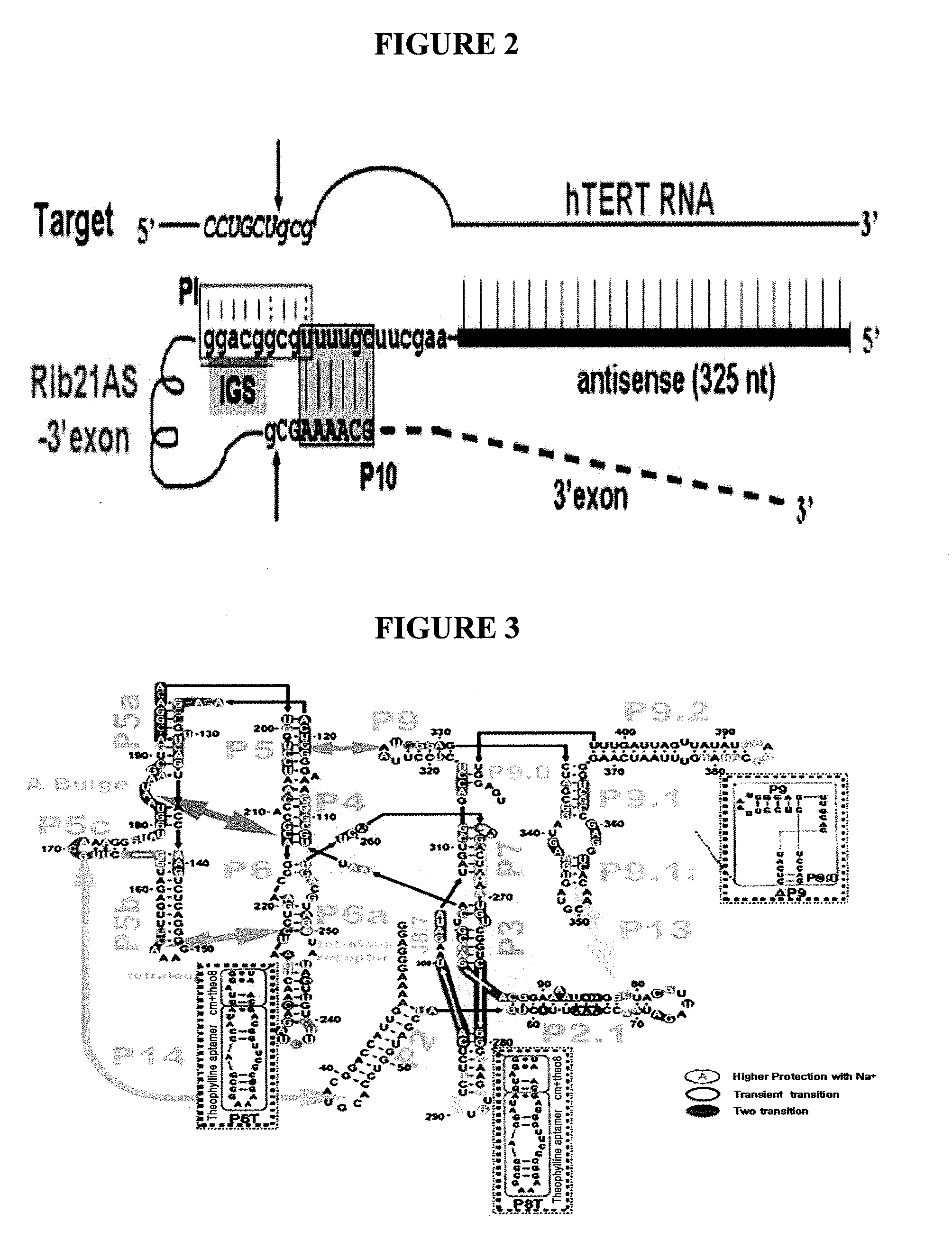
Allosteric trans-splicing group i ribozyme whose activity of target-specific RNA replacement is controlled by theophylline
InactiveUS20110003883A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellReverse transcriptase
Provided is an allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme whose target-specific RNA replacement activity is controlled by theophylline, wherein the hTERT-targeting trans-splicing ribozyme recognizes mRNA of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) as a cancer-specific RNA transcript to bind a theophylline aptamer to an hTERT target trans-splicing ribozyme via a communication module, the hTERT target trans-splicing ribozyme having a verified trans-splicing ability. The allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme may be useful to selectively diagnose only cancer cells that express target hTERT RNA, or induce their apoptosis since the activity of the allosteric trans-splicing group I ribozyme is dependently controlled by theophylline to correct target hTERT RNA by the trans-splicing reaction.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND DANKOOK UNIV
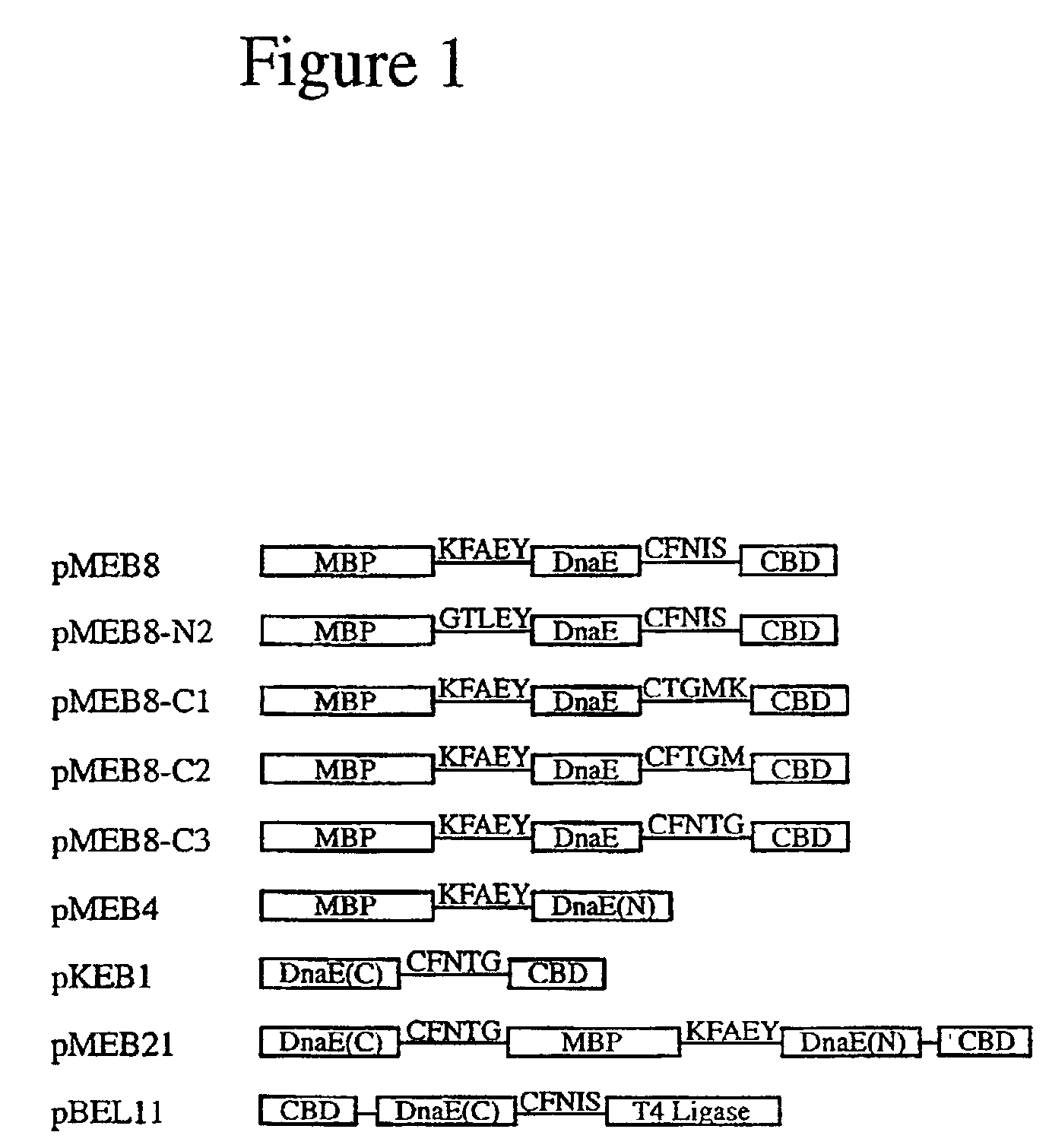
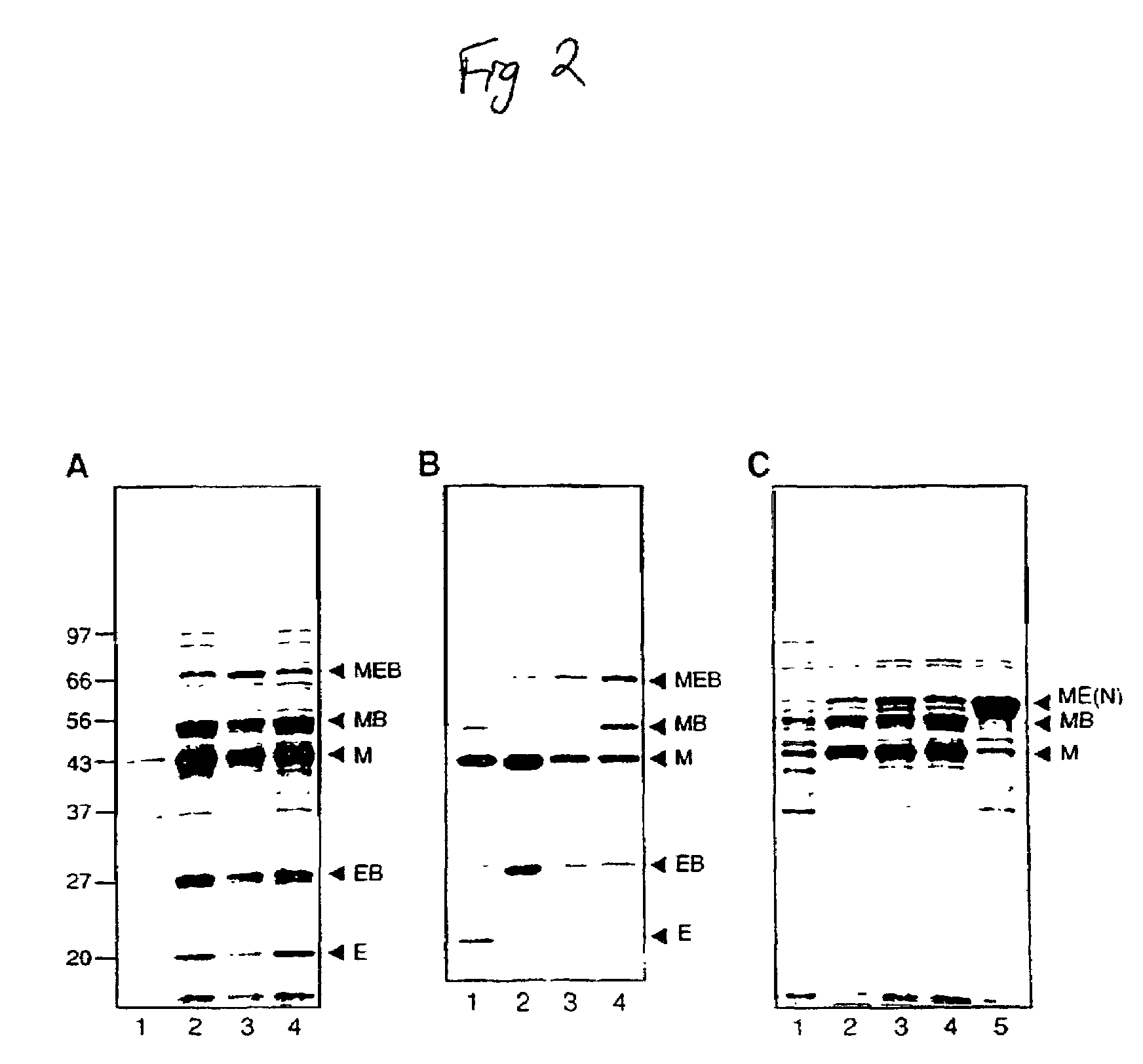
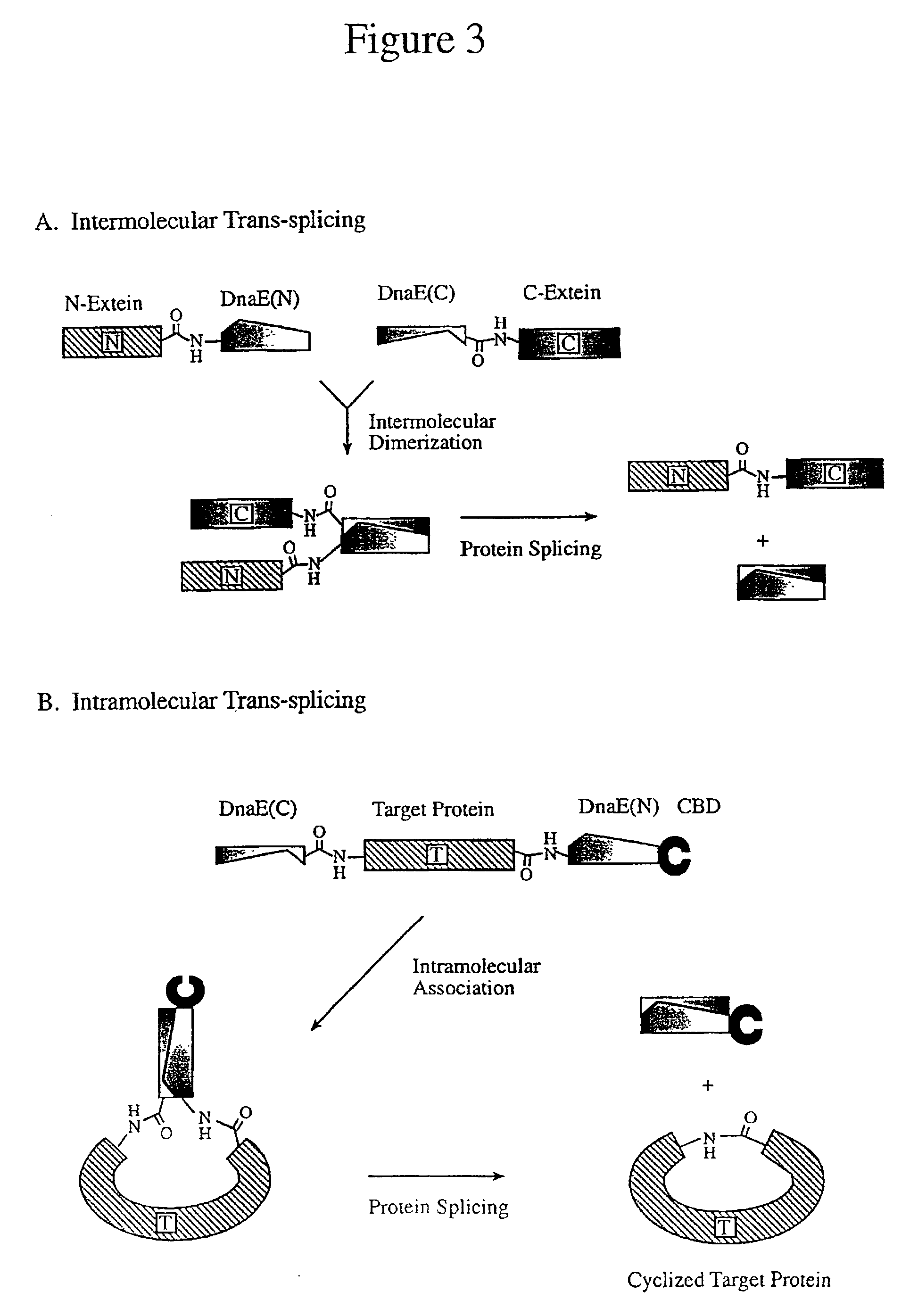
Method of producing biospecific molecules by protein trans-splicing
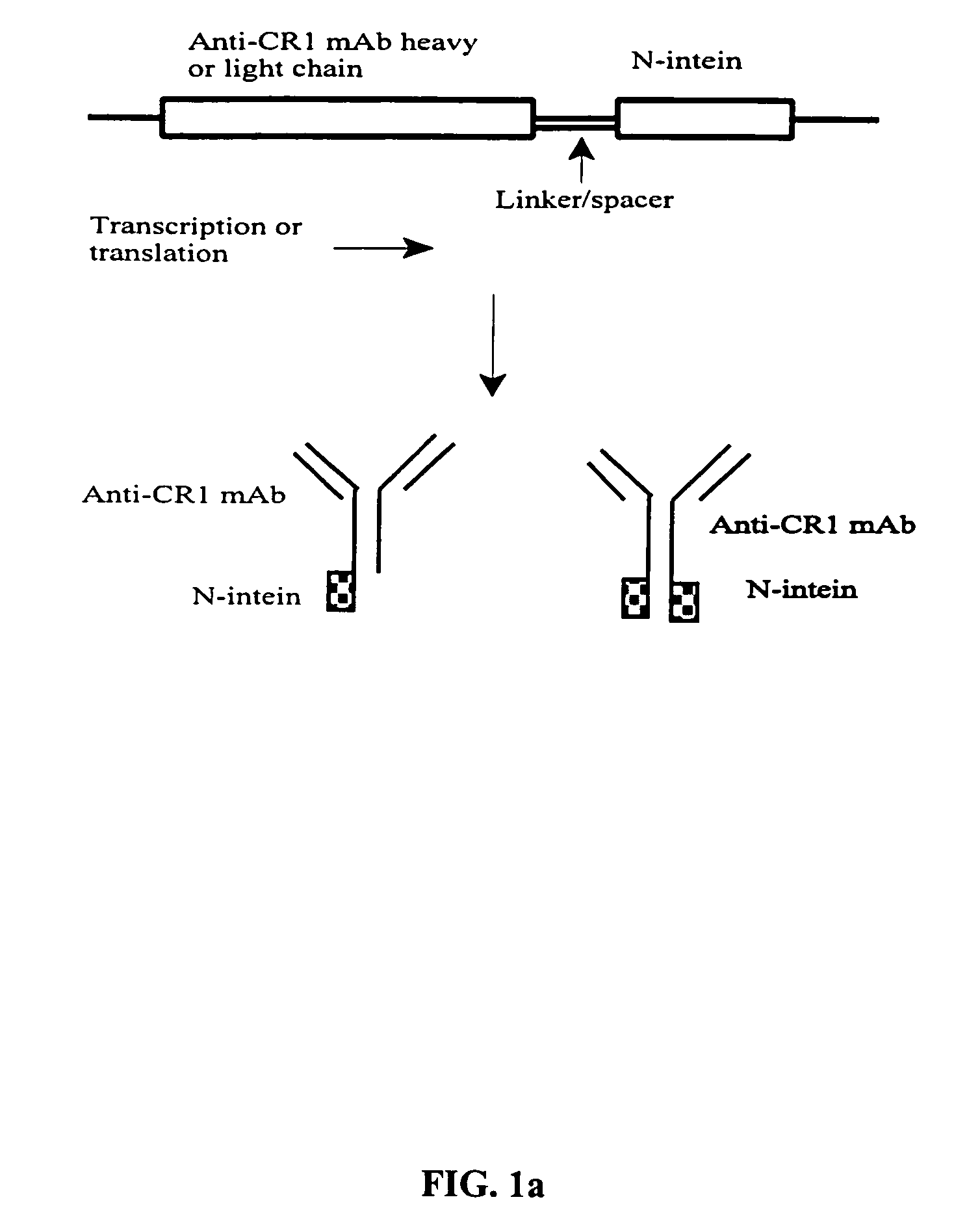
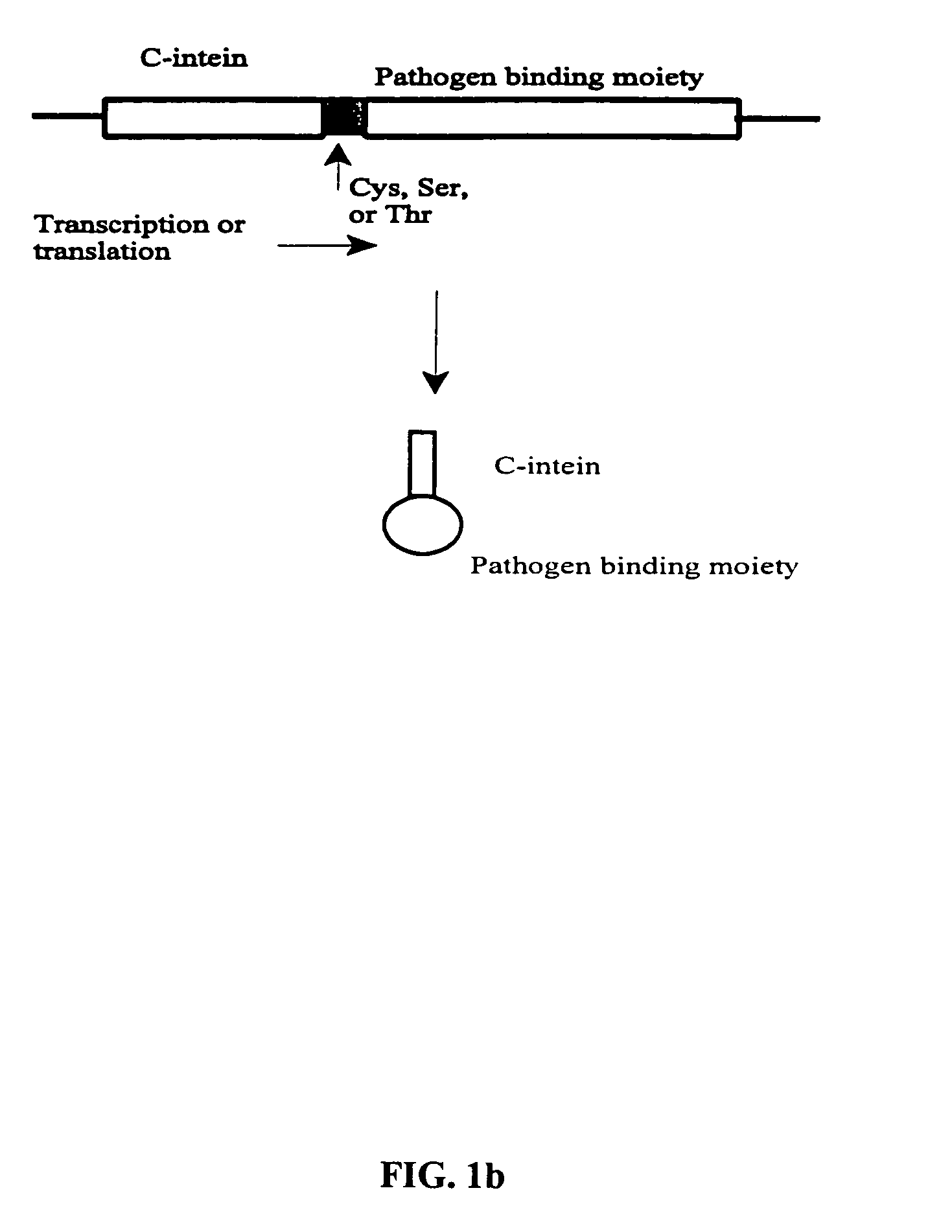
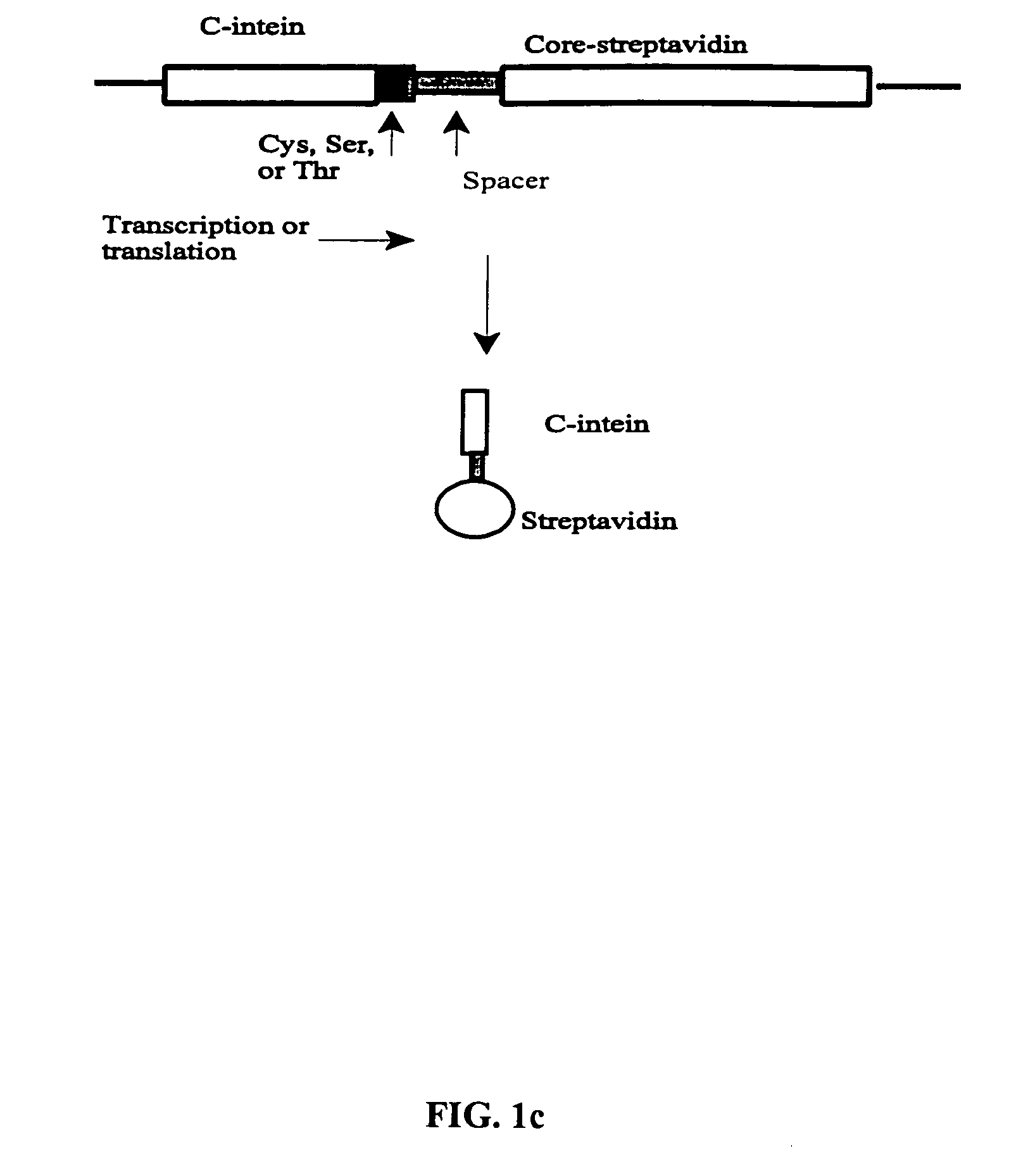
The invention provides methods of using protein trans-splicing for the production of bispecific molecule which has a first antigen recognition portion that binds a C3b-like receptor and a second antigen recognition portion that binds an antigenic molecule present in the circulatory system of a mammal. The invention also provides bispecific molecules produced by protein trans-splicing. The bispecific molecules of the invention can be used for the clearance of pathogenic antigenic molecules from the circulatory system of a mammal. The invention further provides methods of using protein trans-splicing for the production of polyclonal libraries of bispecific molecules, which comprise populations of bispecific molecules with different antigen recognition specificities. Such polyclonal libraries of bispecific molecules can be used for targeting multiple epitopes of a pathogenic antigenic molecule and / or multiple variants of a pathogenic antigenic molecule.
Owner:ELUSYS THERAPEUTICS
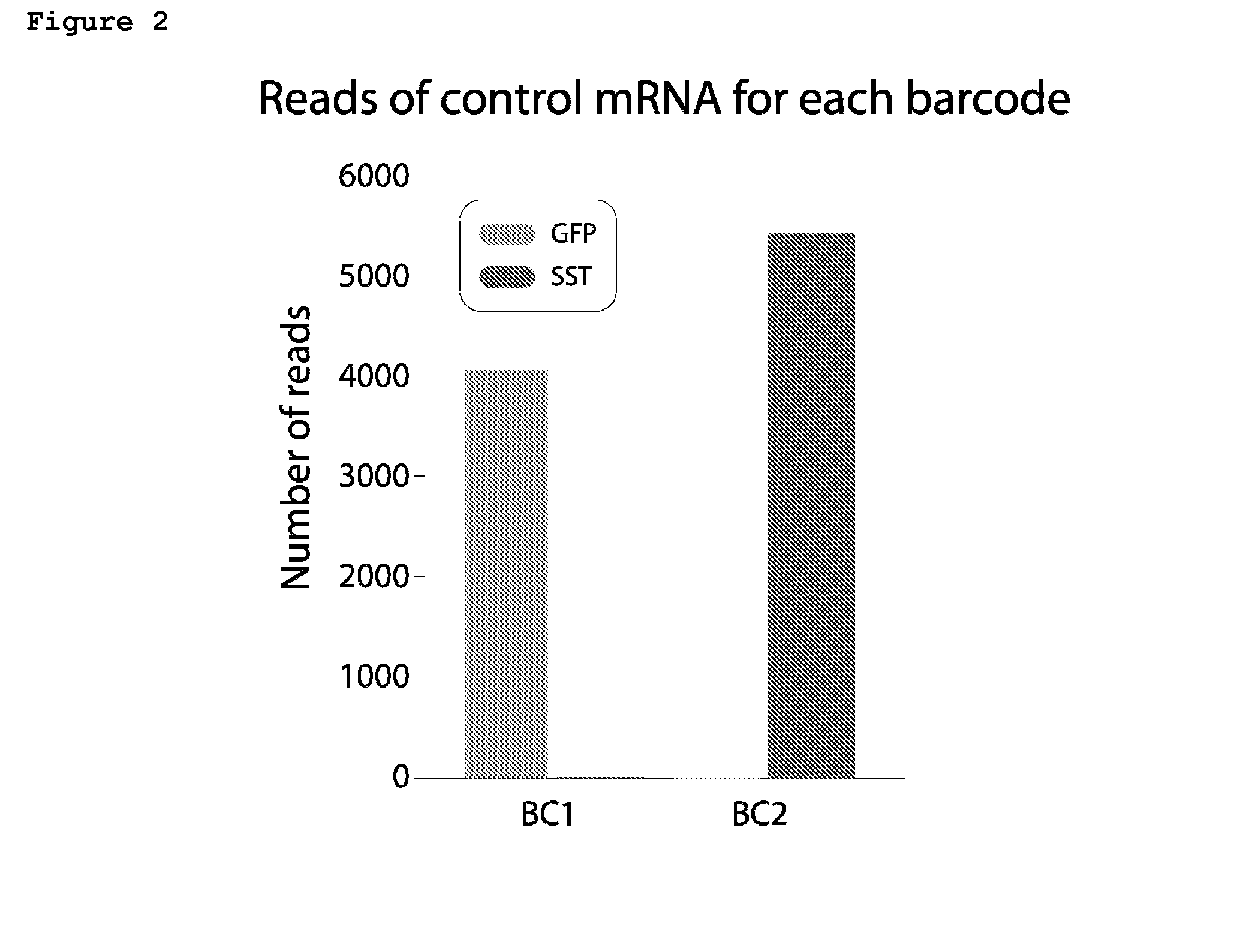
Trans-splicing transcriptome profiling
The present invention provides a method of identifying mRNA transcripts in the transcriptome of a cell comprising i) delivering into the cell a donor expression vector comprising nucleotides in a sequence encoding a trans-splicing barcode cassette, wherein the trans-splicing barcode cassette comprises a) a first portion, the nucleotide sequence of which encodes an intron comprising as part of its 3′ end, or followed at its 3′ end by a splice-site nucleotide sequence; followed at its 3′ end by, b) a second portion, the nucleotide sequence of which encodes a barcode polynucleotide; followed at its 3′ end by c) a third portion, which encodes a nucleotide identification element sequence, ii) exposing the cell to conditions such that the cell produces multiple copies of the trans-splicing barcode cassette encoded by the donor expression vector, which multiple copies of the trans-splicing barcode cassette each splice the barcode polynucleotide onto a mRNA transcript of the cell, thereby forming multiple mRNA transcripts of the cell, each spliced to the barcode polynucleotide; and iii) identifying the multiple mRNA transcripts that are spliced to the barcode polynucleotides, thereby identifying mRNA transcripts in the transcriptome of the cell.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Trans-splicing ribozymes
InactiveUS6015794AAccurate expressionLow efficiencyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsRNA Sequence
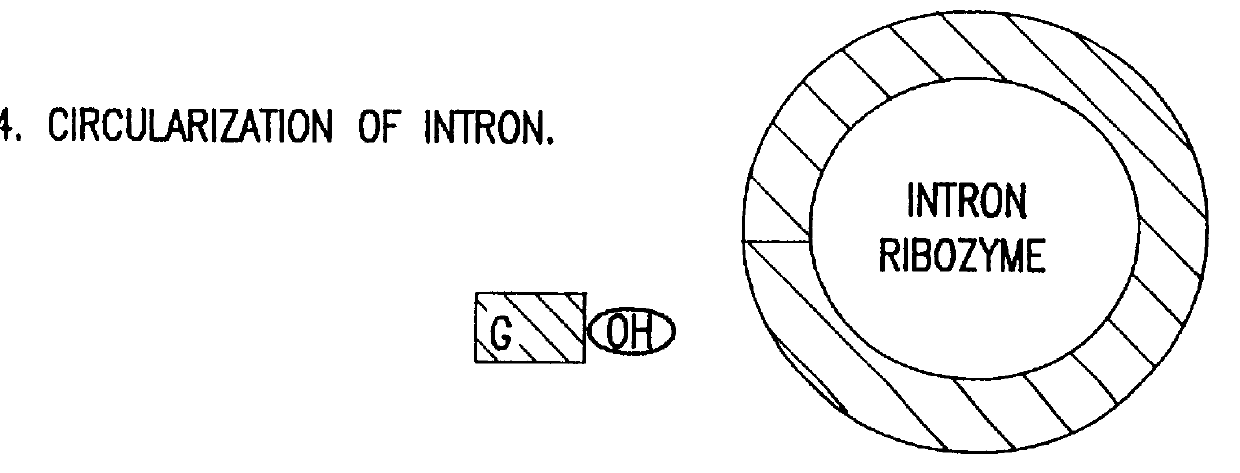
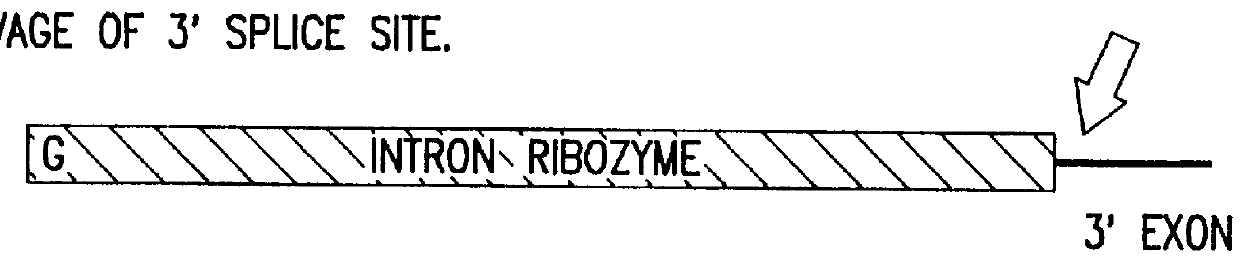
The design of new ribozymes capable of self-catalyzed trans-splicing which are based upon the catalytic core of a Group I intron are described. Using this design, it is possible to construct ribozymes capable of efficiently splicing a new 3' exon sequence into any chosen target RNA sequence in a highly precise manner. Inactive pro-ribozyme forms are also described.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Screening method for identification of efficient pre-trans-splicing molecules
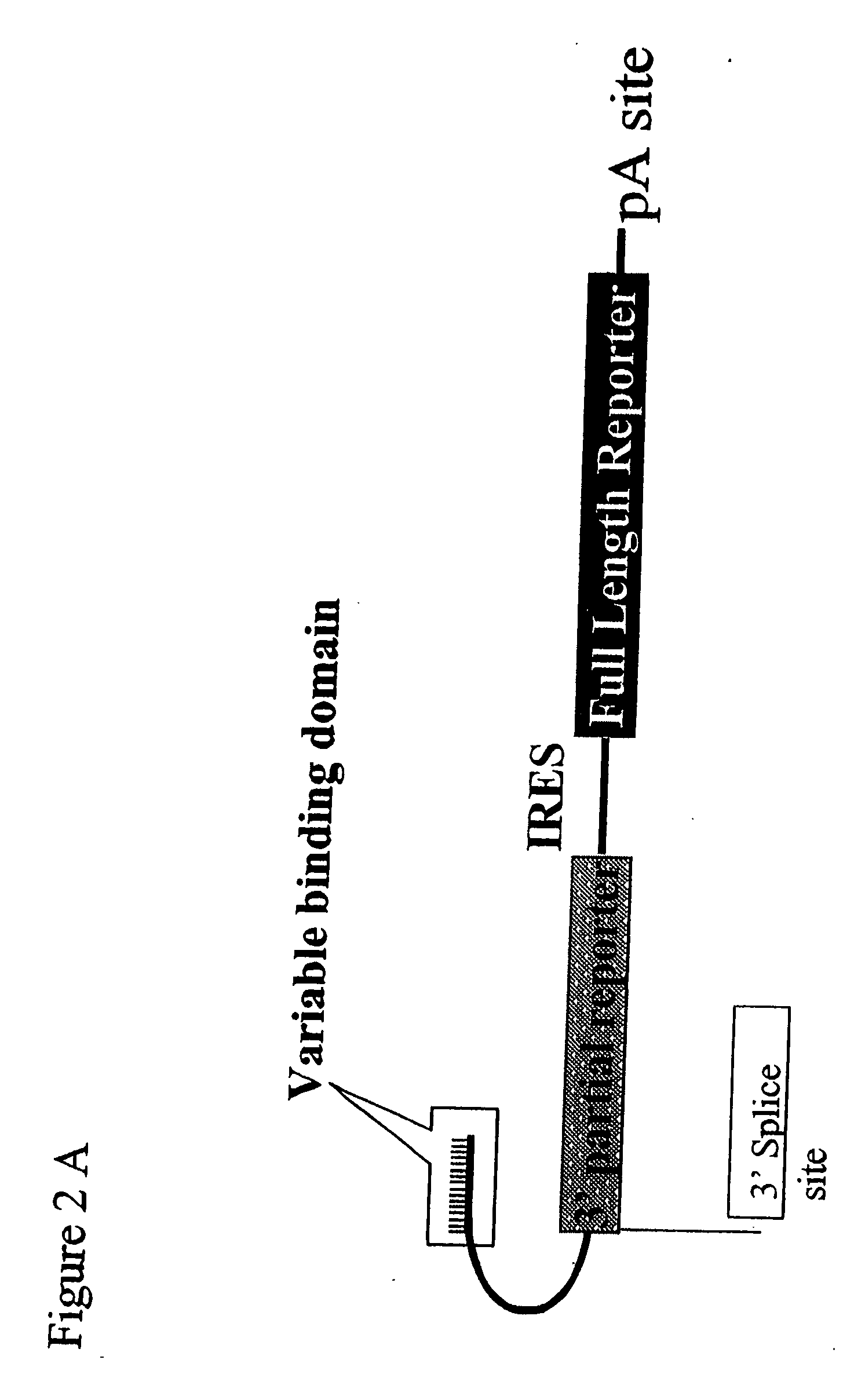
The present invention provides methods and compositions for rapid high capacity functional screening to identify optimal pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs). The compositions of the invention include PTM expression libraries capable of encoding candidate PTMs designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). The candidate PTMs of the invention encode a portion of a first reporter molecule and may encode one or more other reporter molecules, which can be used to select for cells expressing optimal PTMs (efficient and specific). The compositions of the invention also include cells that express a target pre-mRNA encoding the remaining portion of the first reporter molecule. The screening methods of the invention encompass (i) contacting a PTM expression library with cells expressing a target pre-mRNA under conditions in which a trans-splicing reaction will occur in the presence of an optimal PTM (expressed by the library vector) resulting in the formation of a chimeric repaired RNA molecule capable of encoding at least one reporter molecule; (ii) selecting for cells expressing the repaired reporter molecule wherein expression of the reporter molecule indicates the presence of an optimal PTM in the selected cell; and (iii) identifying the optimal PTM expressed in the selected cell(s). The additional reporter molecule(s) can be used to assess both specific and non-specific trans-splicing, as well direct PTM expression.
Owner:VIRXSYS
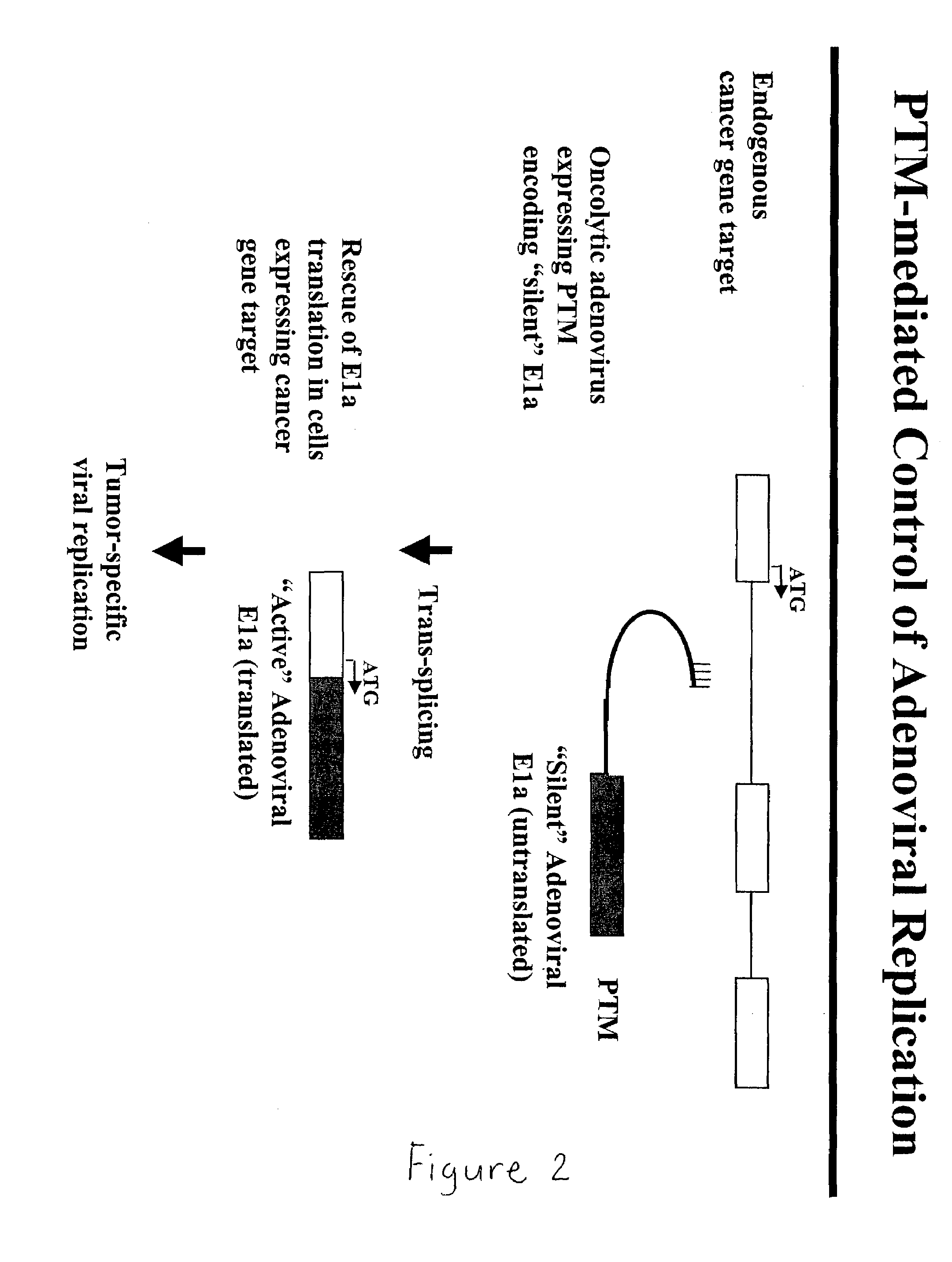
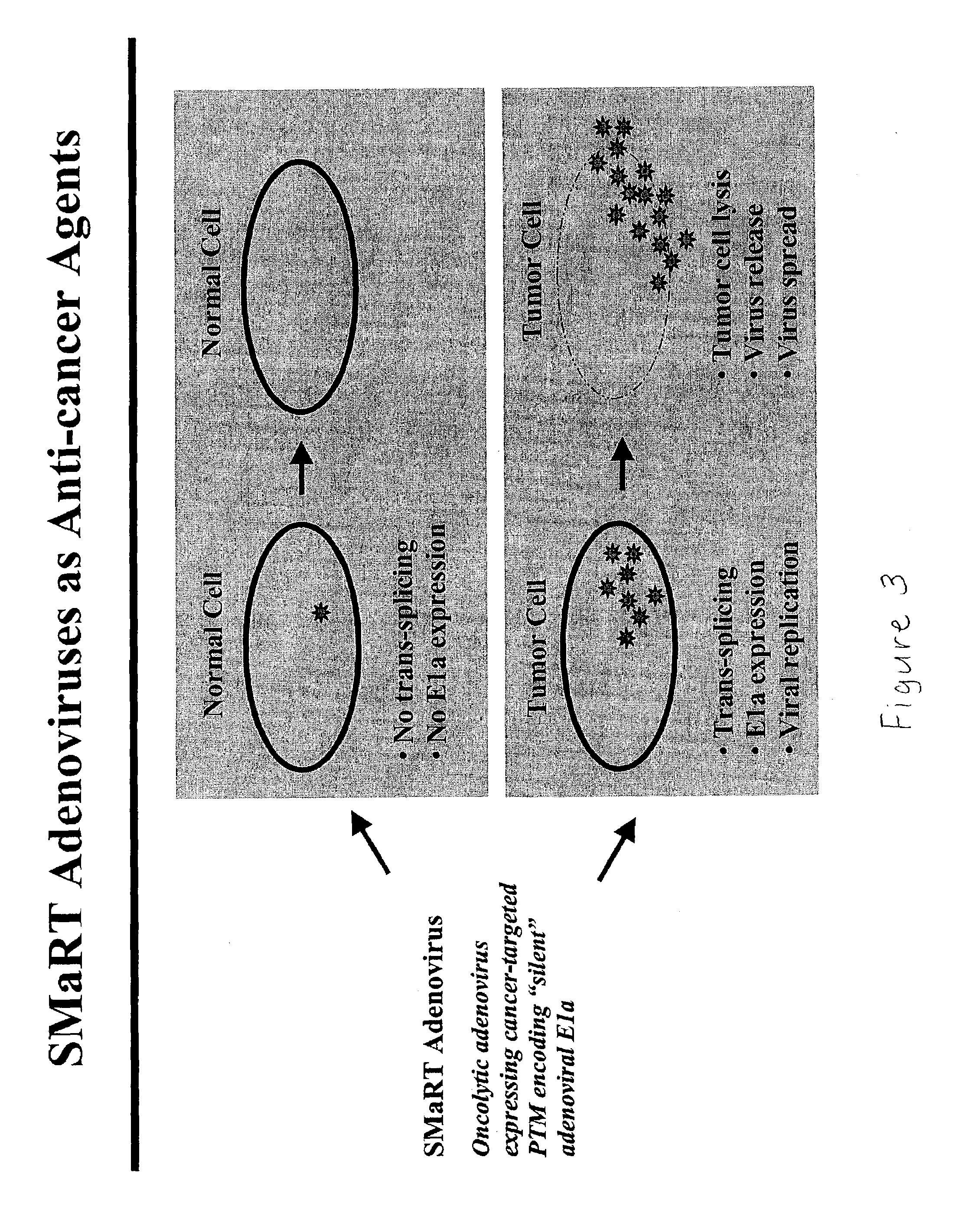
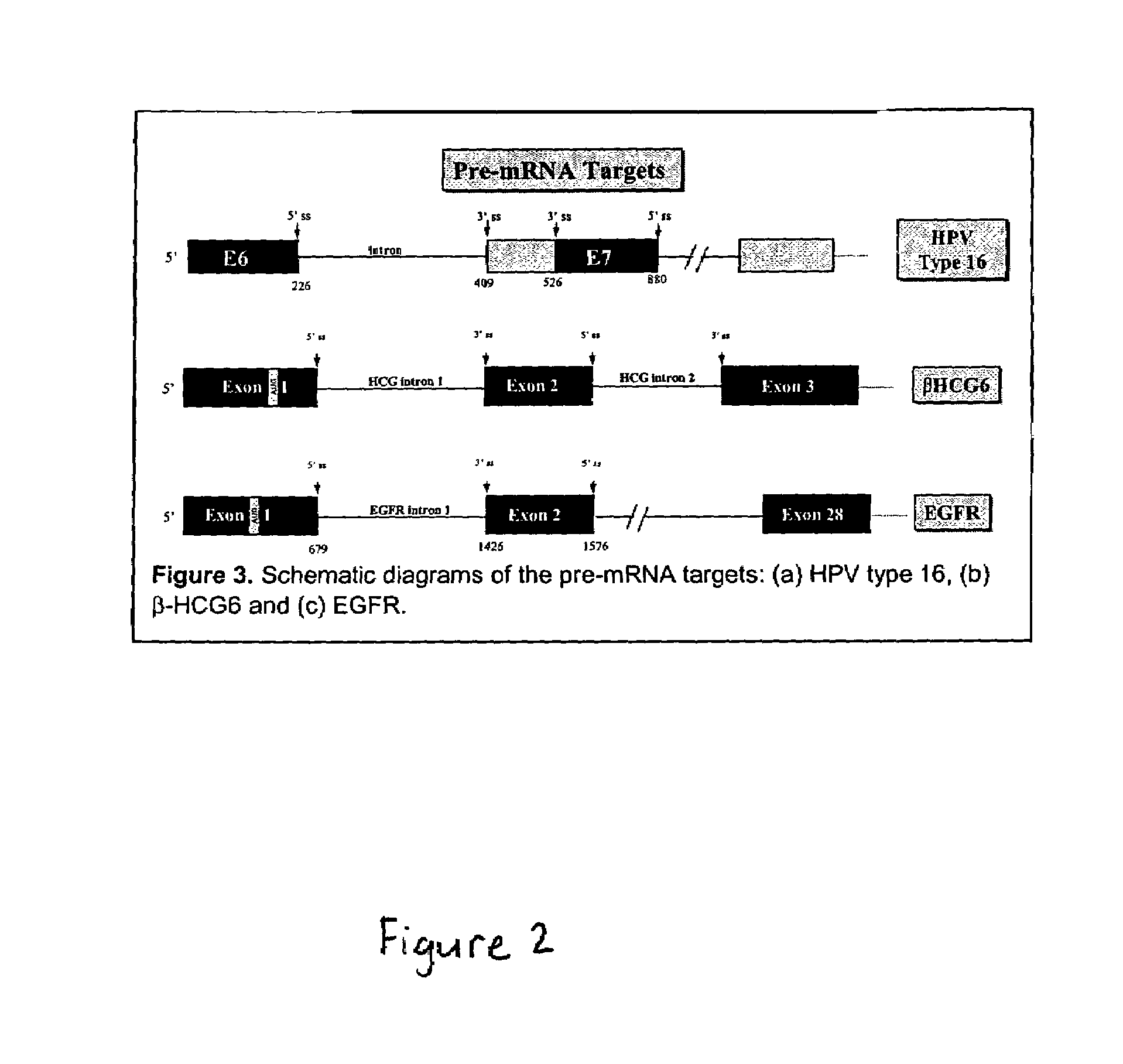
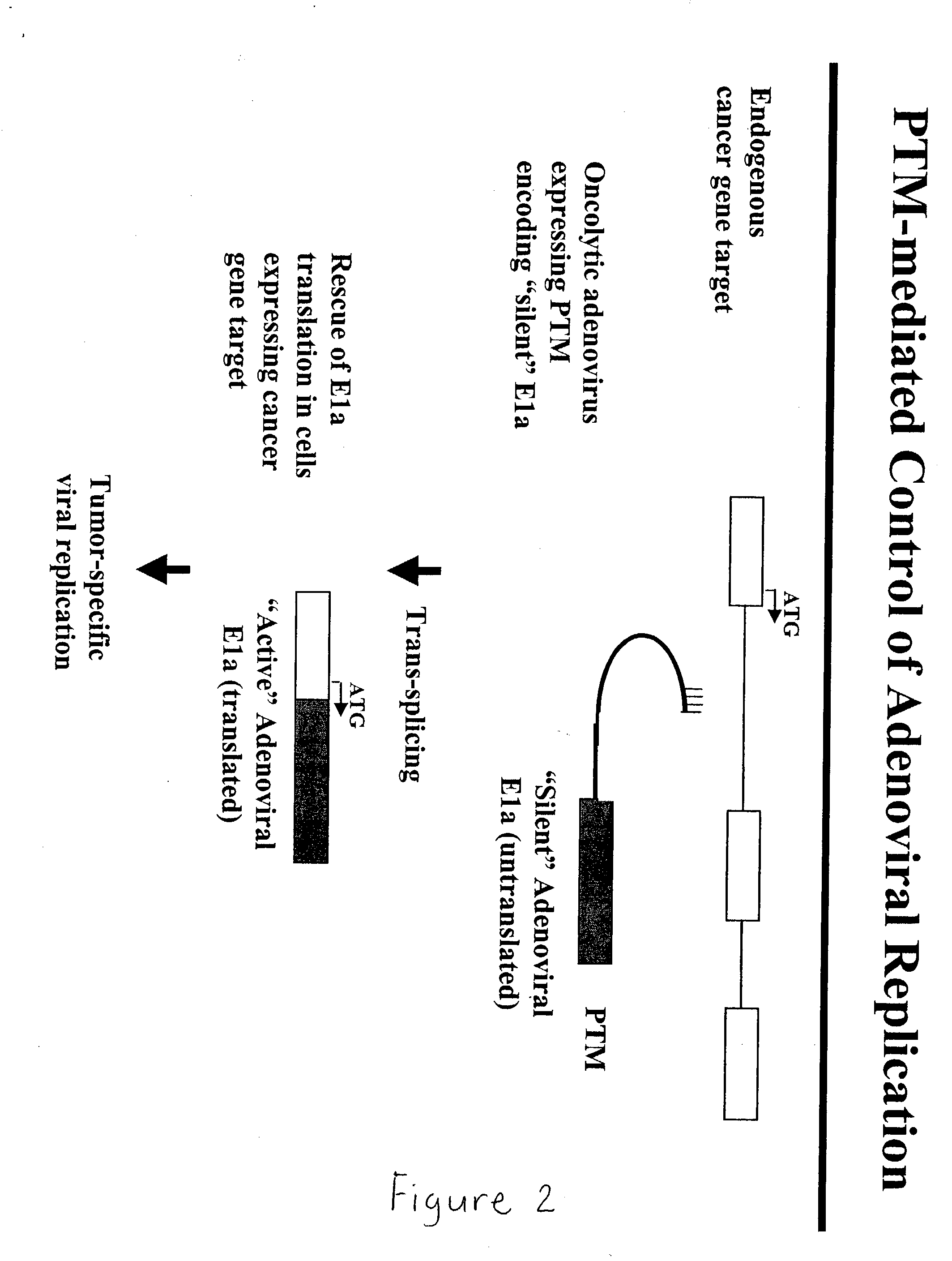
Use of spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing to confer cell selective replication to adenoviruses
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring tumor selective cell death on cancer cells expressing specific target precursor messenger RNA molecules (cancer cell selective target pre-mRNAs). The compositions of the invention include conditionally replicative adenoviruses that have been genetically engineered to express one or more pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with one or more cancer cell target pre-mRNA and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of novel chimeric RNA molecules (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding adenovirus specific protein(s). Adenovirus specific proteins include those proteins complementing an essential activity necessary for replication of a defective adenovirus. The methods and compositions of the invention may be used to target a lytic adenovirus infection to cancer cells thereby providing a method for selective destruction of cancer cells. In addition, the adenoviruses of the invention may be engineered to encode PTMs designed to interact with target pre-mRNAs encoded by infectious agents within a cell, thereby targeting selective destruction of cells infected with such agents.
Owner:VIRXSYS
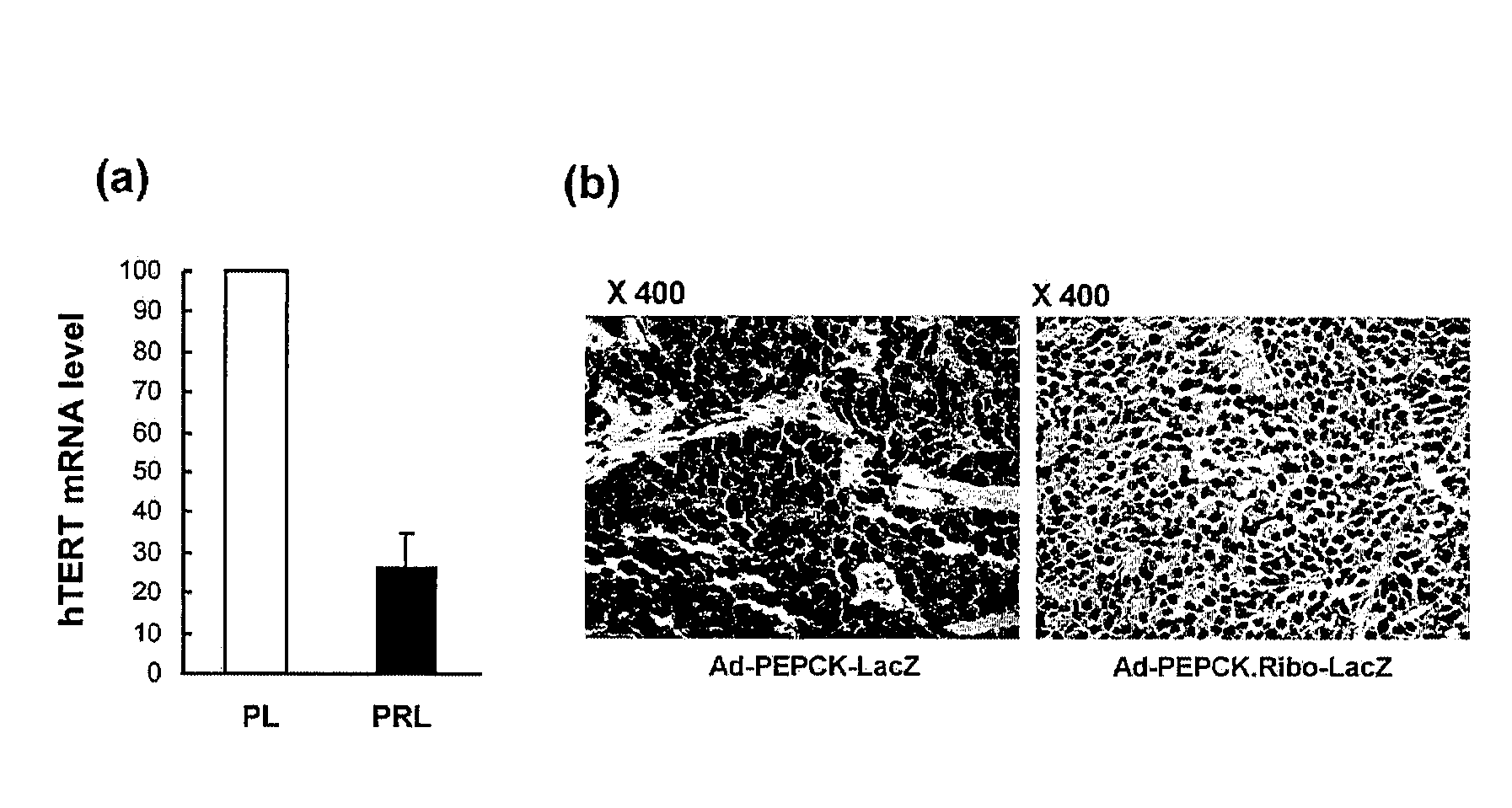
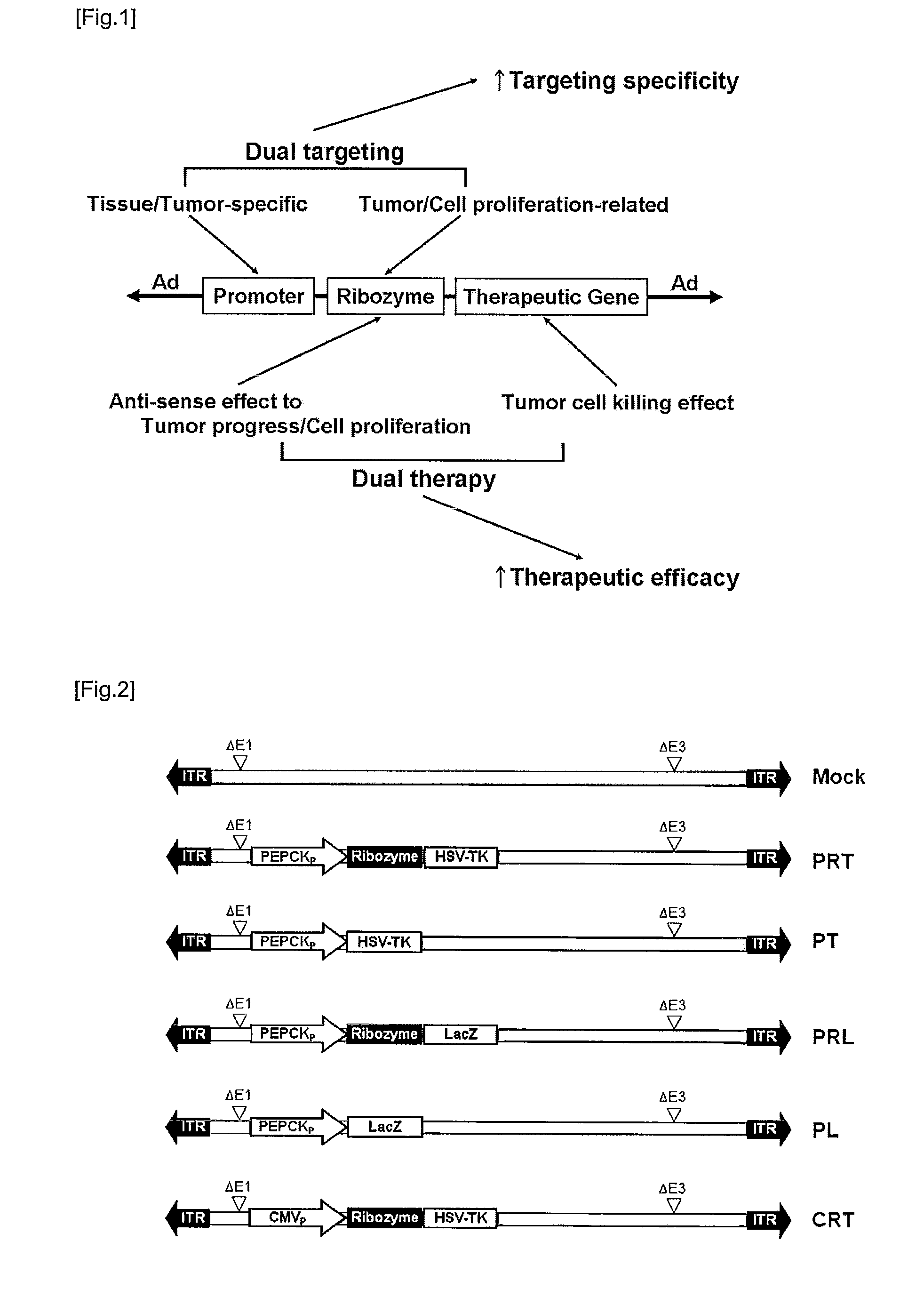
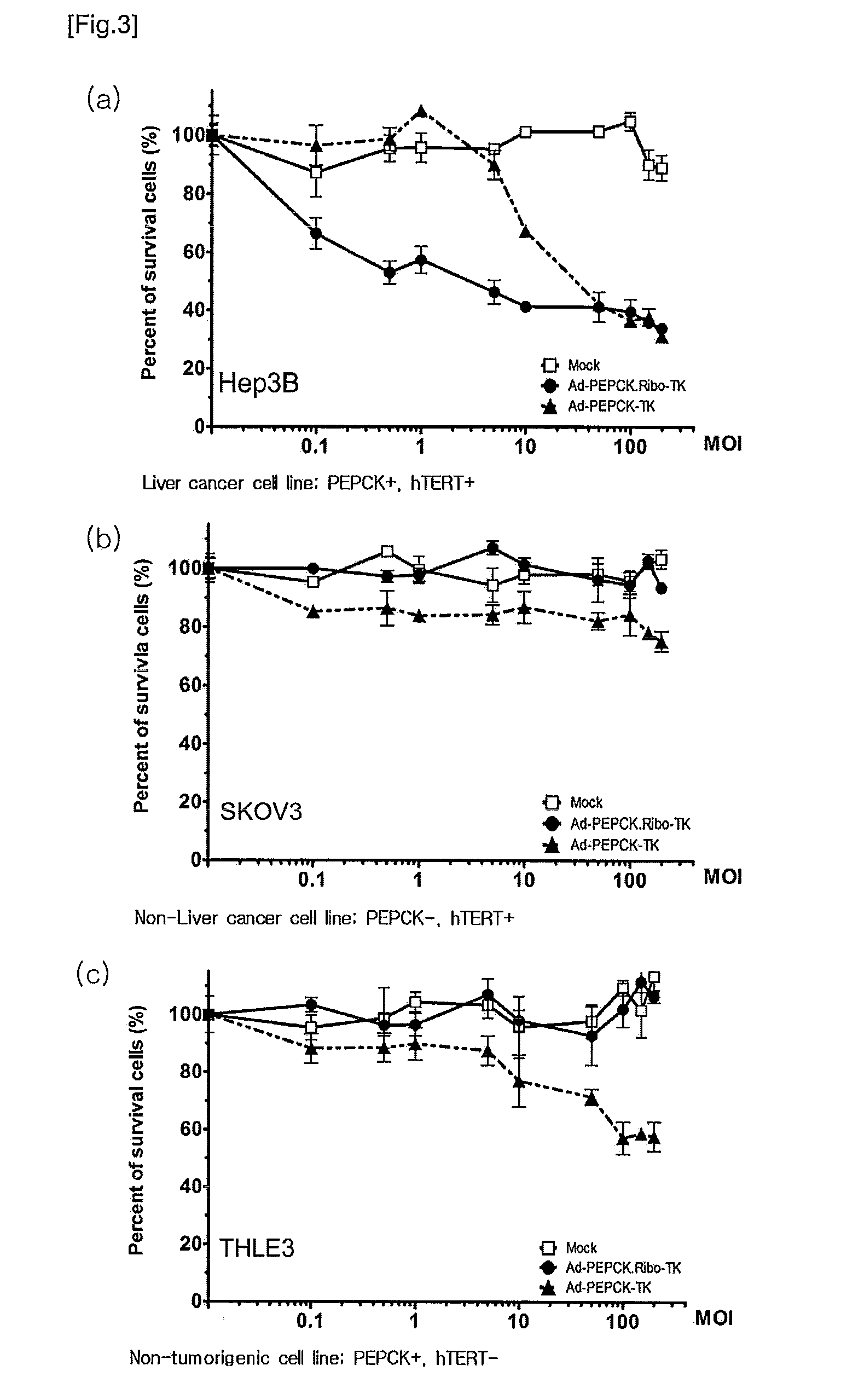
Recombinant adenovirus comprising tissue-specific promoter and tumor-targeting trans-splicing ribozyme and uses thereof
Disclosed herein are a recombinant adenovirus comprising tissue-specific promoters and trans-splicing ribozymes targeting tumor-specific genes, and uses thereof. More specifically, disclosed herein are a recombinant adenovirus comprising (1) a tissue-specific promoter, (2) a trans-splicing ribozyme acting on tumor-specific genes operably linked to the promoter, and (3) a therapeutic or reporter gene linked to 3′ exon of the ribozyme, an anticancer pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, and a composition for cancer diagnosis comprising the same.The recombinant adenovirus exhibits high specificity and significantly improved therapeutic efficacy to gene targeted tissues. Accordingly, the recombinant adenovirus is useful as a gene delivery vector for anticancer agents or cancer diagnostics.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND DANKOOK UNIV
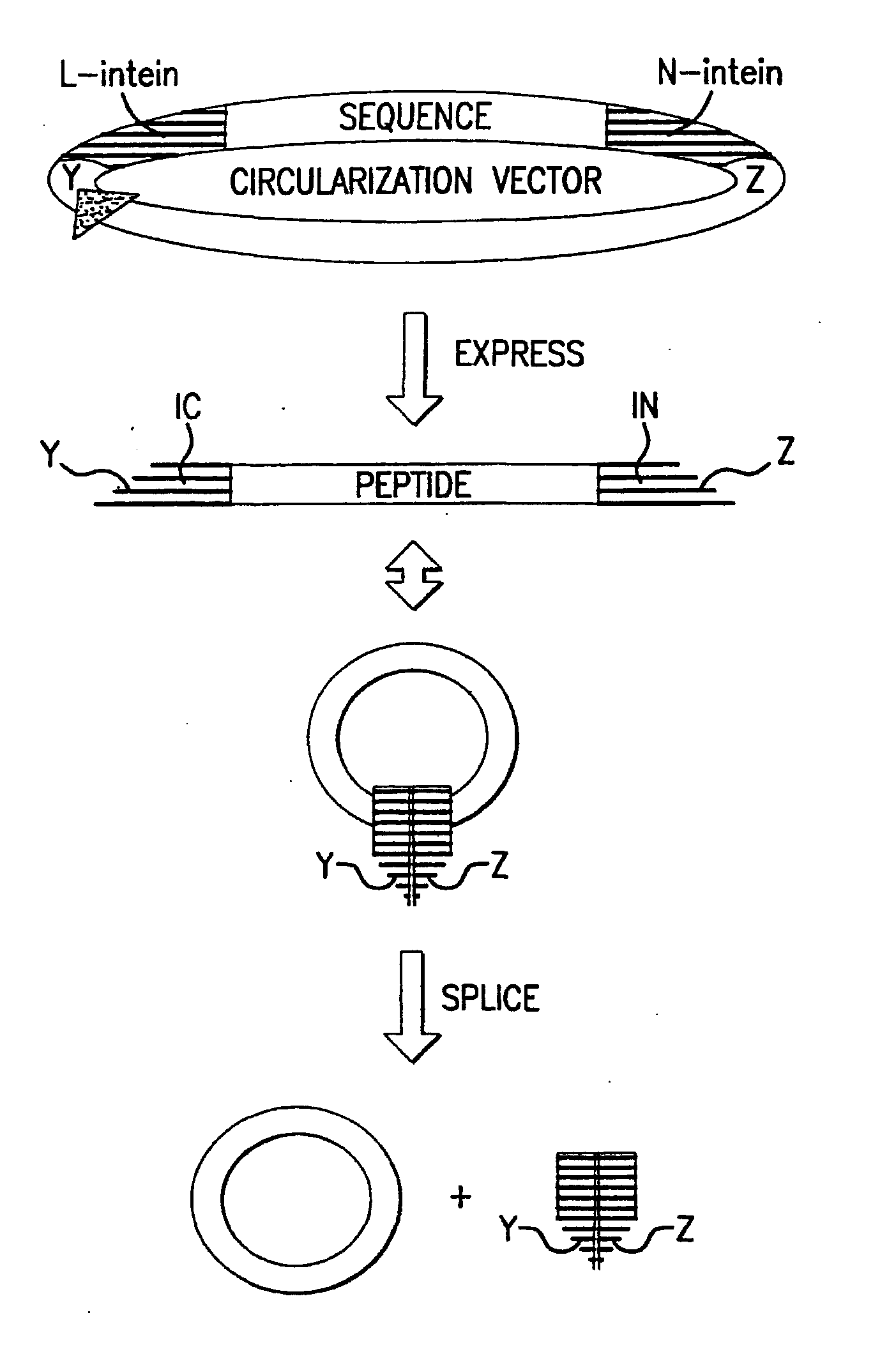
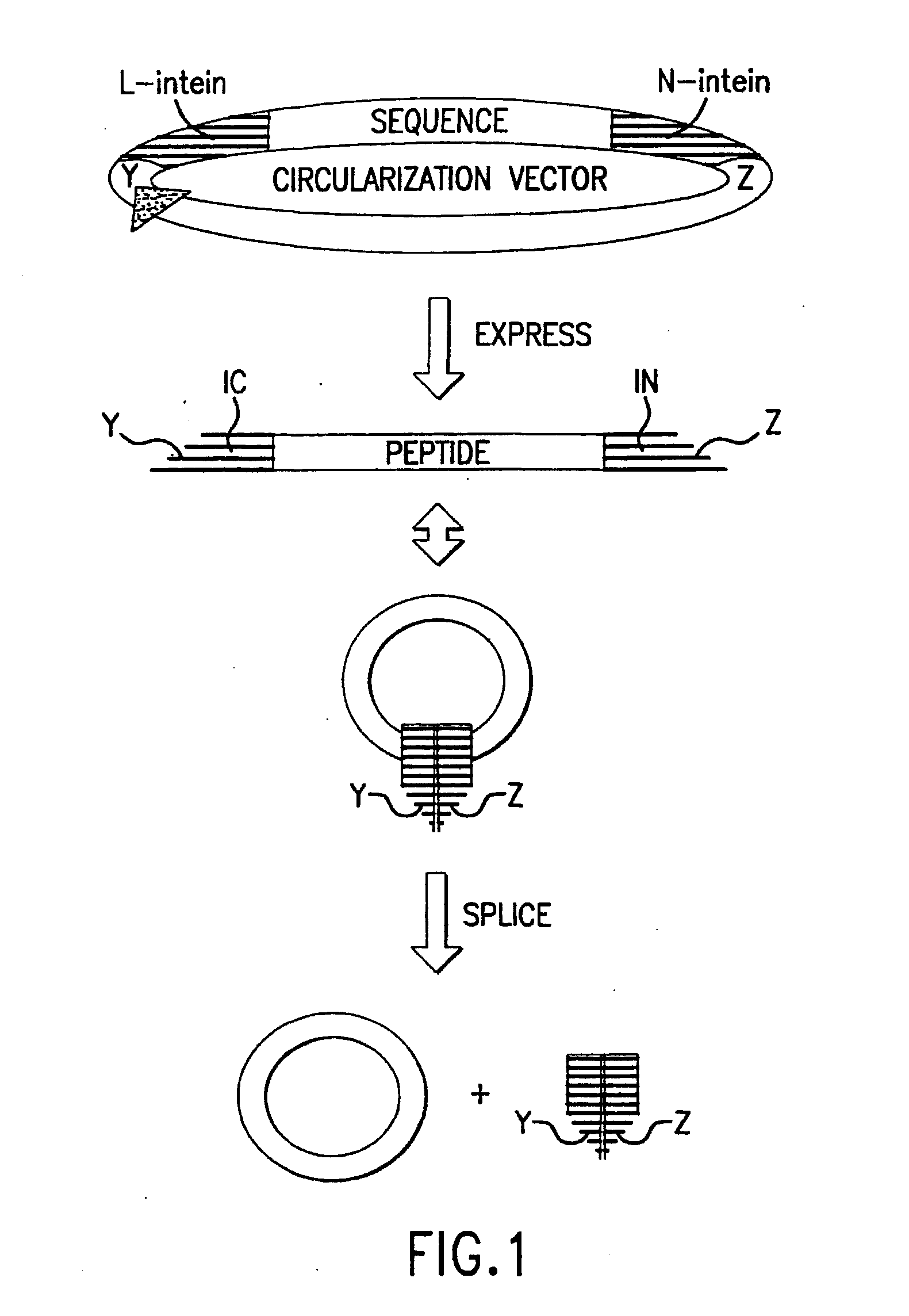
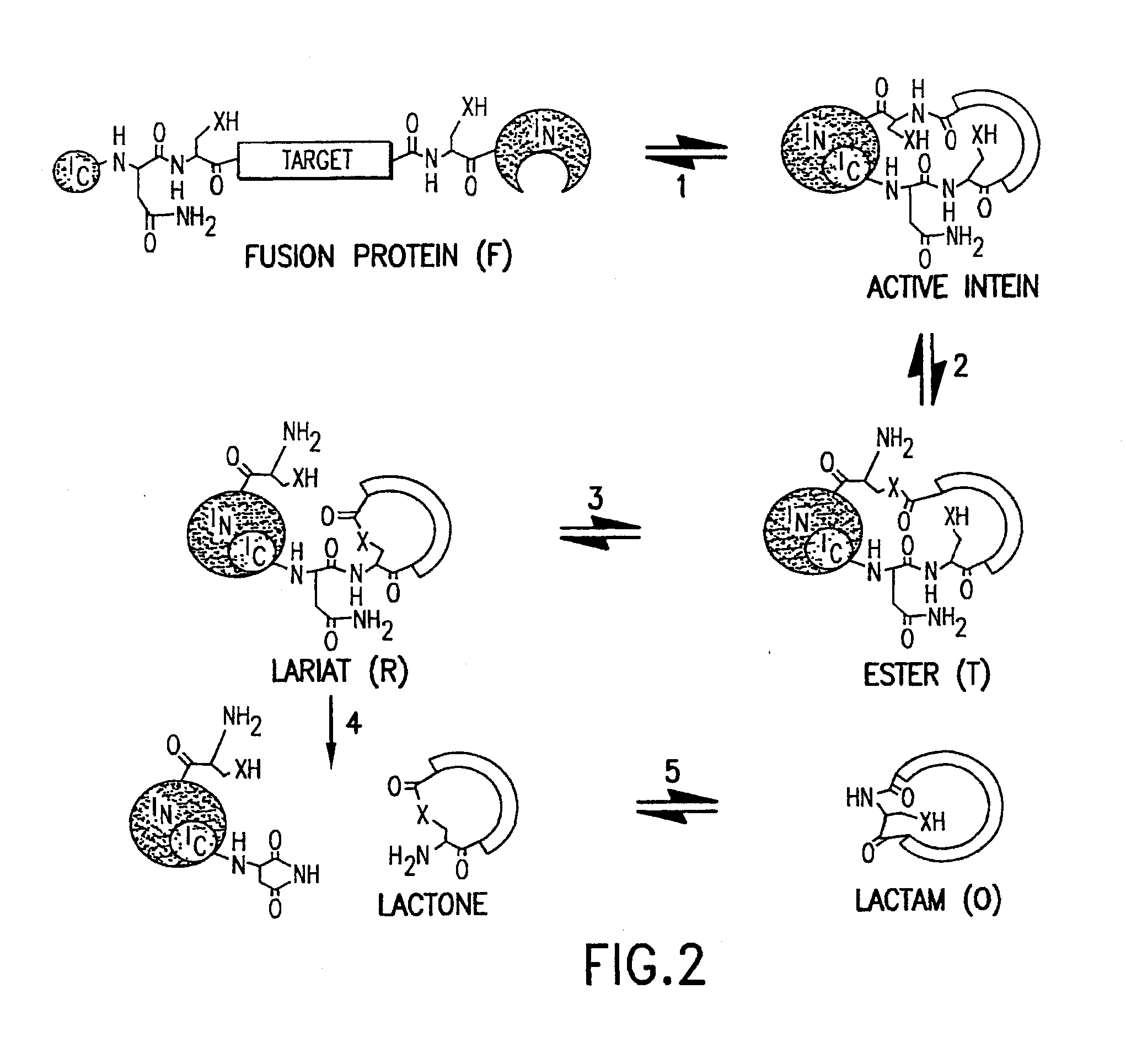
Cyclic peptides
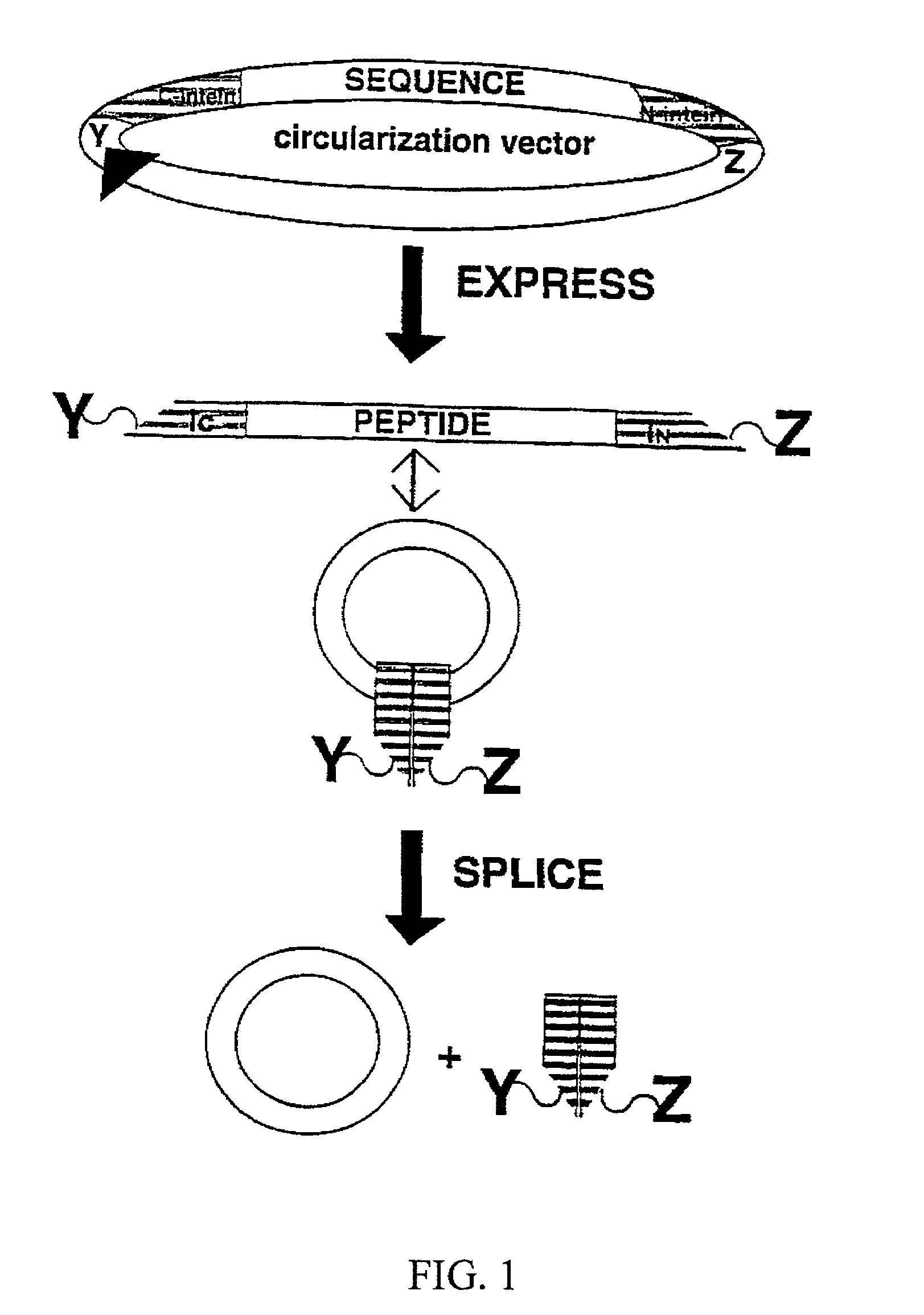
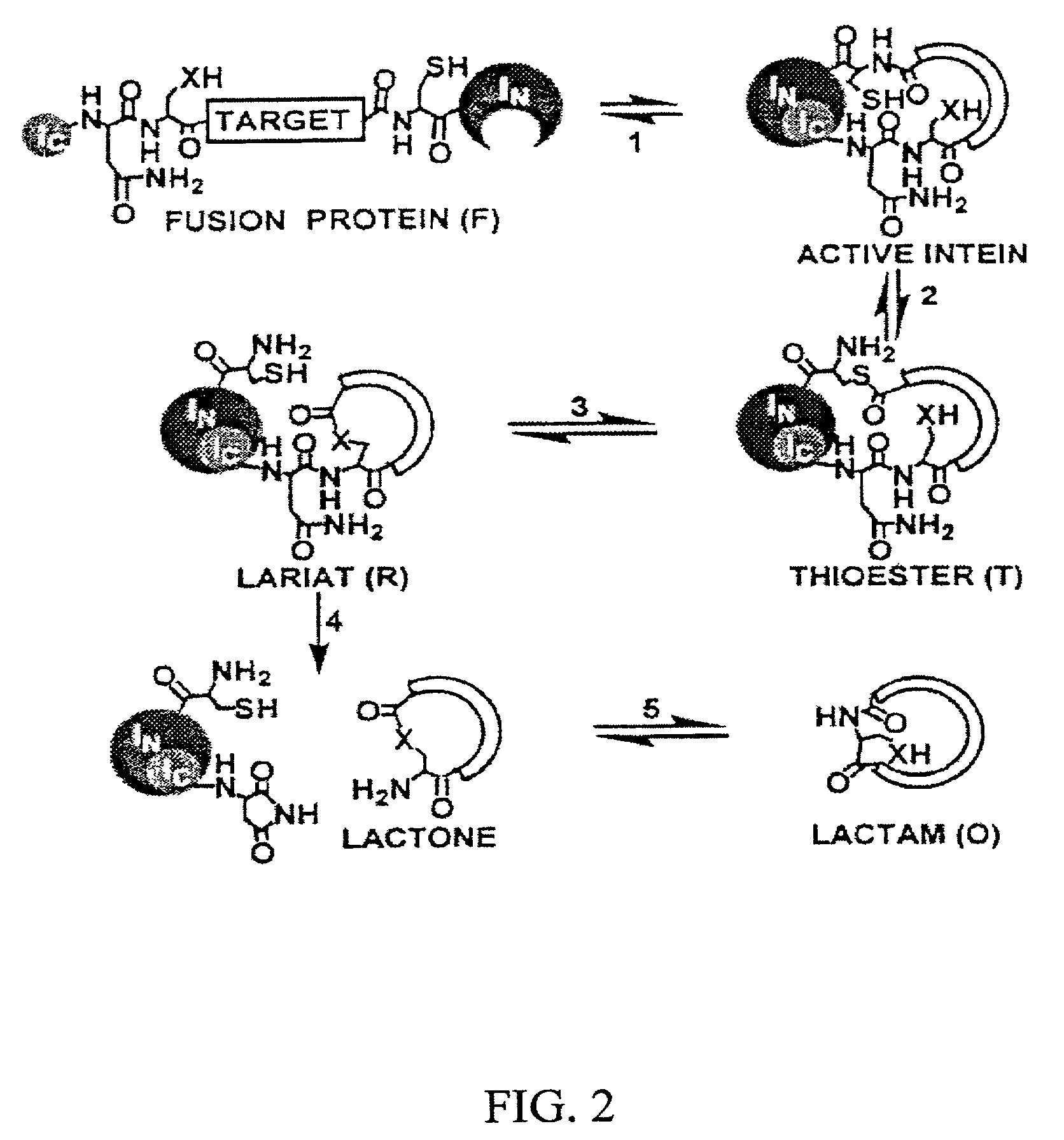
Methods of producing cyclic peptides and splicing intermediates of peptides in a looped conformation are disclosed. The methods utilize the trans-splicing ability of split inteins to catalyze cyclization of peptides from a precursor peptide having a target peptide interposed between two portions of a split intein. The interaction of the two portions of the split intein creates a catalytically-active intein and also forces the target peptide into a loop configuration that stabilizes the ester isomer of the amino acid at the junction between one of the intein portions and the target peptide. A heteroatom from the other intein portion then reacts with the ester to form a cyclic ester intermediate. The active intein catalyzes the formation of an aminosuccinimide that liberates a cyclized form of the target peptide, which spontaneously rearranges to form the thermodynamically favored backbone cyclic peptide product. Also disclosed are nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides, methods for making cyclic peptides, methods of making libraries, and methods of screening peptides.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method for producing circular or multimeric protein species in vivo or in vitro and related methods
InactiveUS20090035814A1Overcome disadvantagesOvercome problemsPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesInteinProtein species
Owner:EVANS THOMAS C +1
Preparation of recombinant polypeptide by intein with trans-splicing function
InactiveCN101884910AAvoid pollutionLow costIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesCross-linkProtein insertion
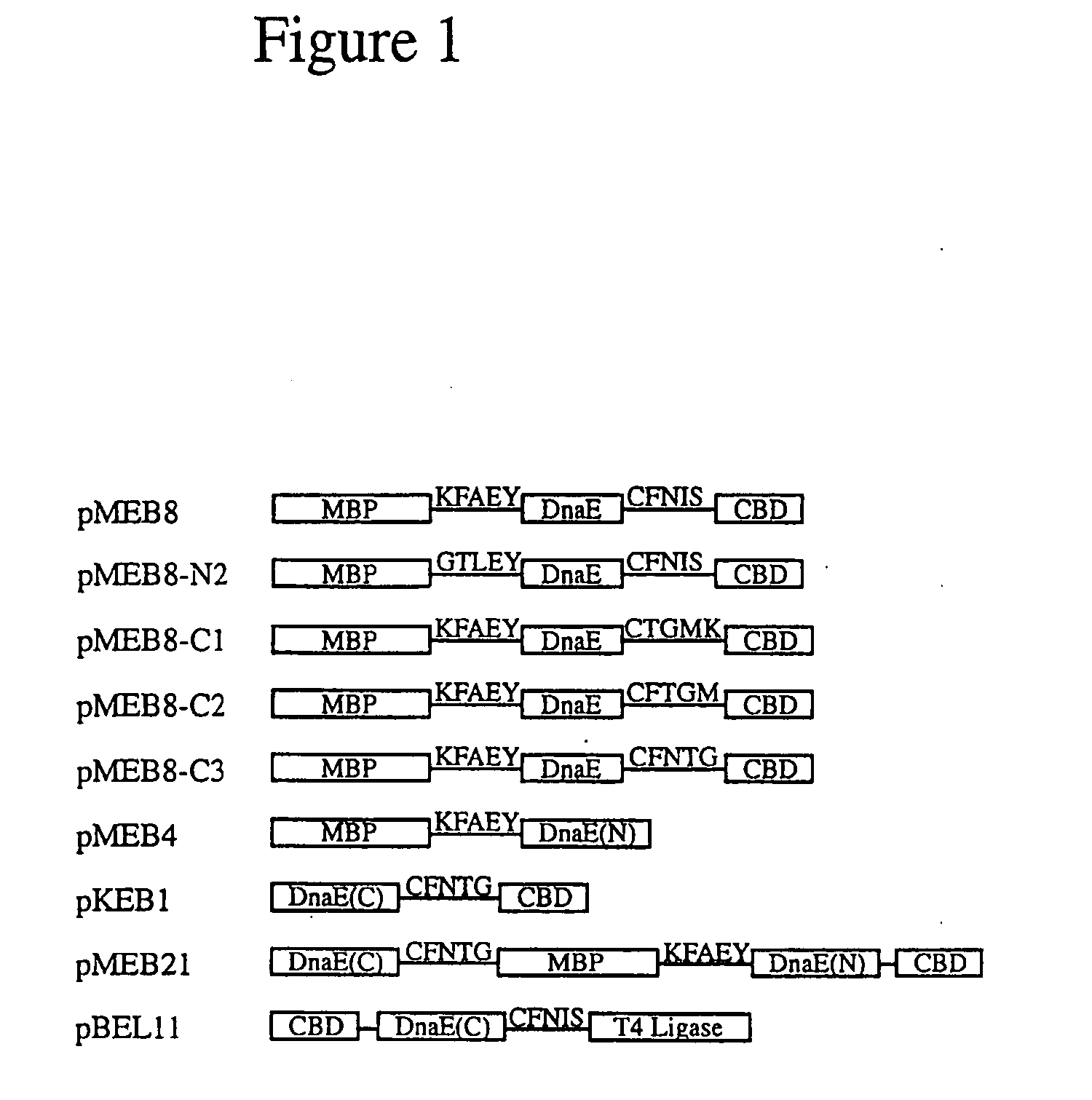
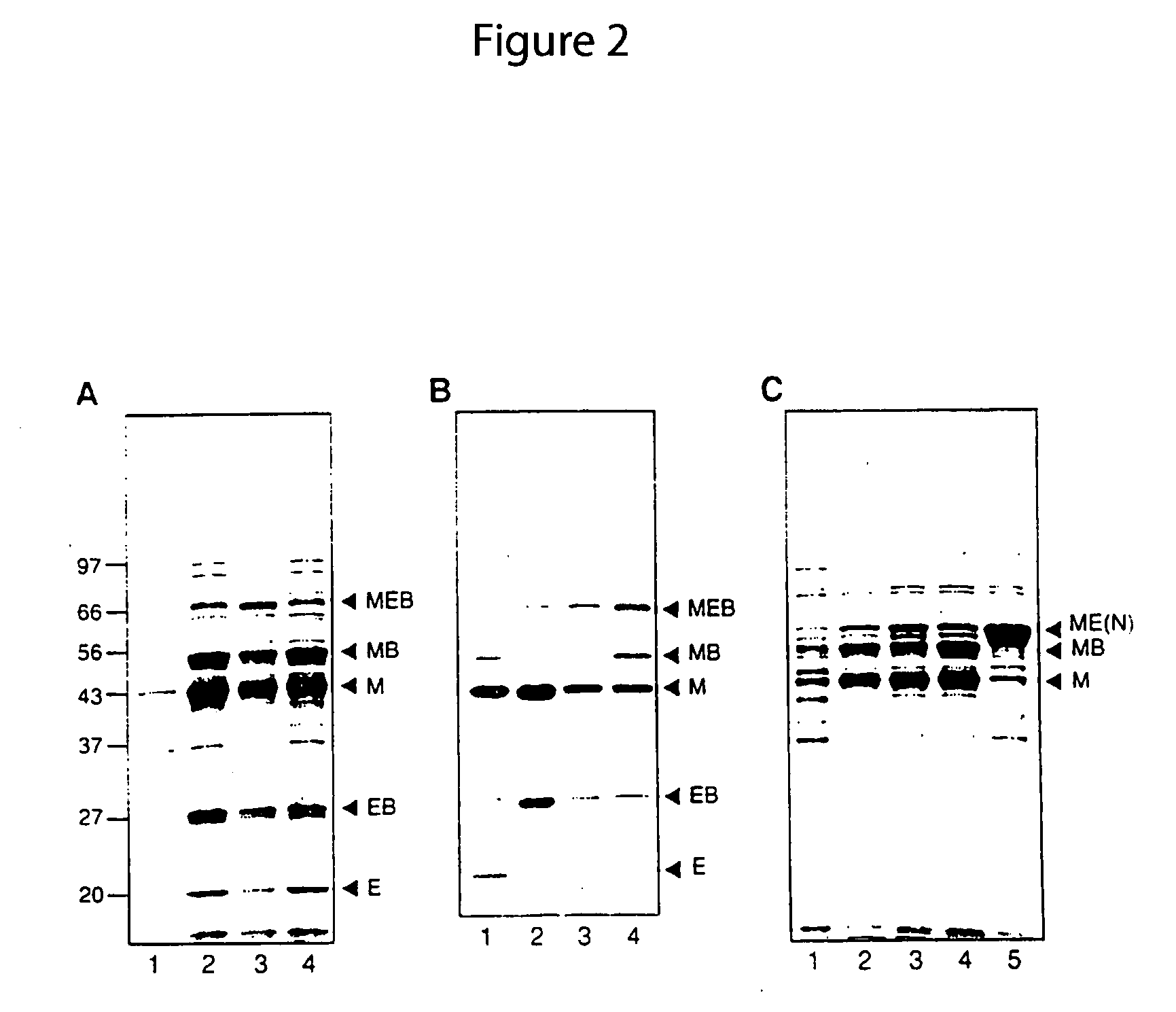
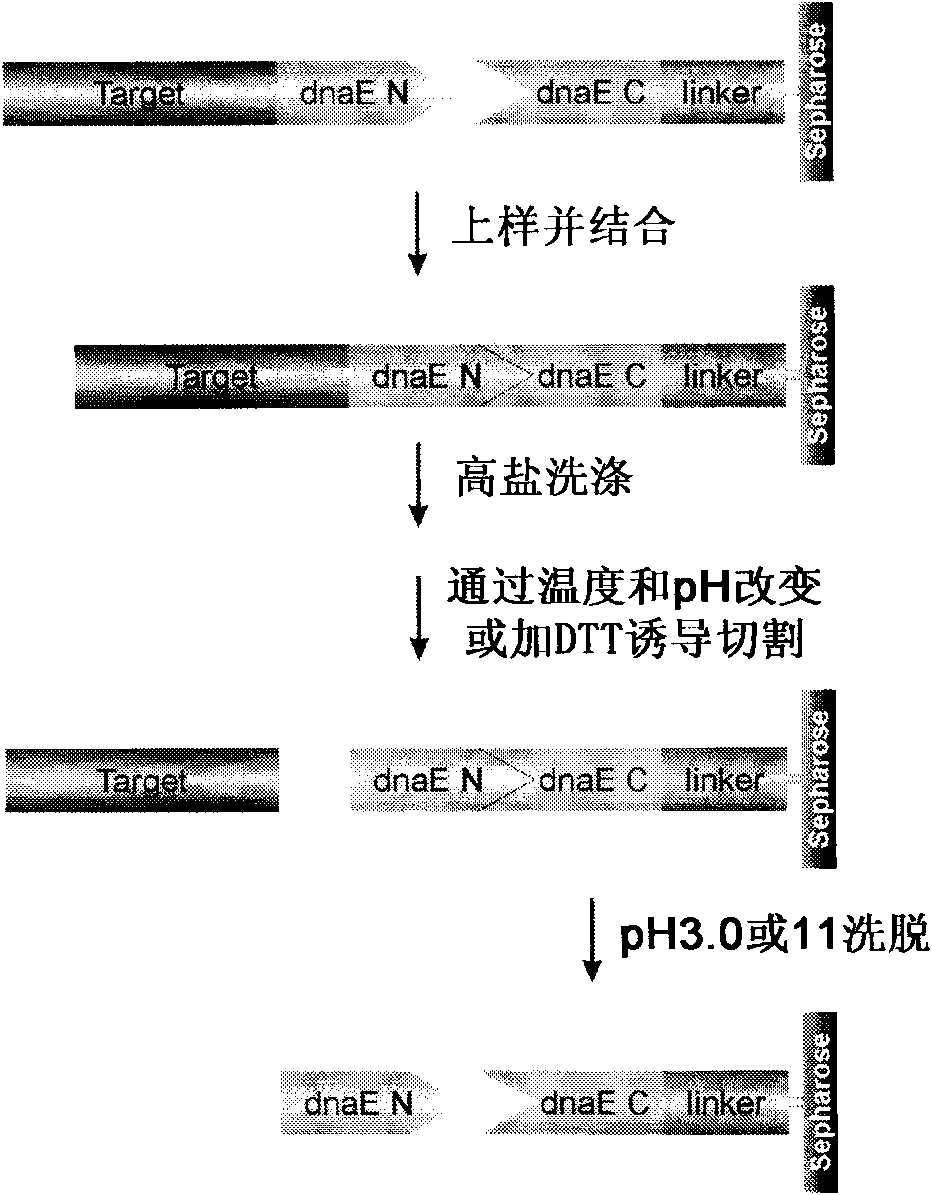
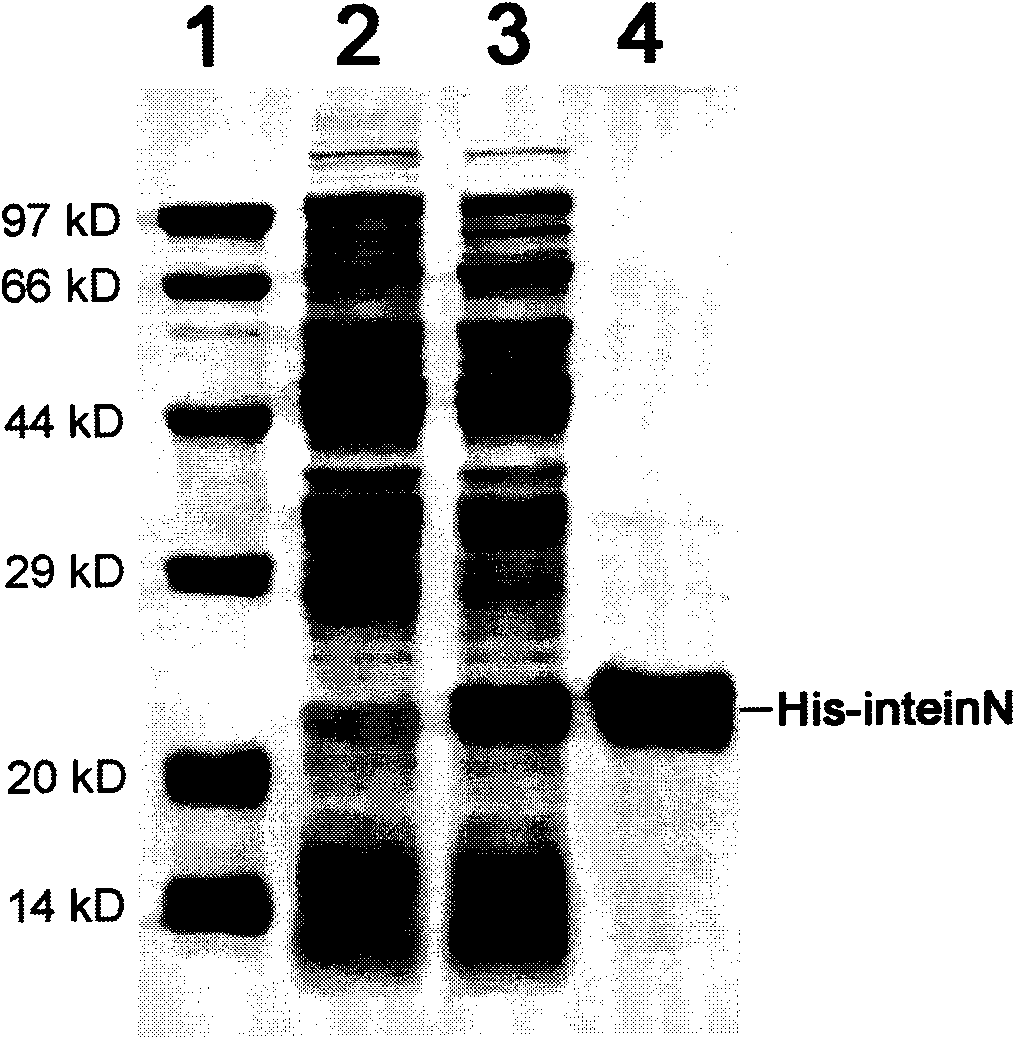
The invention provides preparation of recombinant polypeptide by an intein with a trans-splicing function, wherein the N-end splicing structure domain and the C-end splicing structure domain of the intein with the trans-splicing function can be specifically bound together. One splicing structure domain (the N- or C-end splicing structure domain) of the intein is taken as carrier protein to carry out fusion expression with target polypeptide; the other splicing structure domain (the C- or N-end splicing structure domain) is cross-linked with a supporting medium to prepare an affinity column for adsorbing and purifying the obtained fusion protein containing the target polypeptide; impurities in a fusion protein sample are removed by increasing the salinity of washing liquid in the affinity chromatographic column; and trans-splicing of the intein is induced by changing the pH and the temperature of the chromatographic column or adding a chemical reagent containing a sulfydryl group so as to release the target polypeptide from the fusion protein and purify the target polypeptide at the same time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Pre-MRNA trans-splicing molecule (RTM) molecules and their uses
The present invention relates to specific and markedly improved pre-mRNA trans-splicing molecule (RTM) molecules which are designed to correct specific genes expressed within cells to be targeted, and which are associated with epidermolysis bullosa, cystic fibrosis, pachyonychia congenital, and psoriasis or neurodermitis, as well as cancers of the skin. In particular, the RTMs of the present invention are genetically engineered to interact with a specific target pre-mRNA expressed in cells to be targeted so as to result in correction of genetic defects or reprogramming of gene expression responsible for a variety of different skin disorders.
Owner:BAUER JOHANN +1
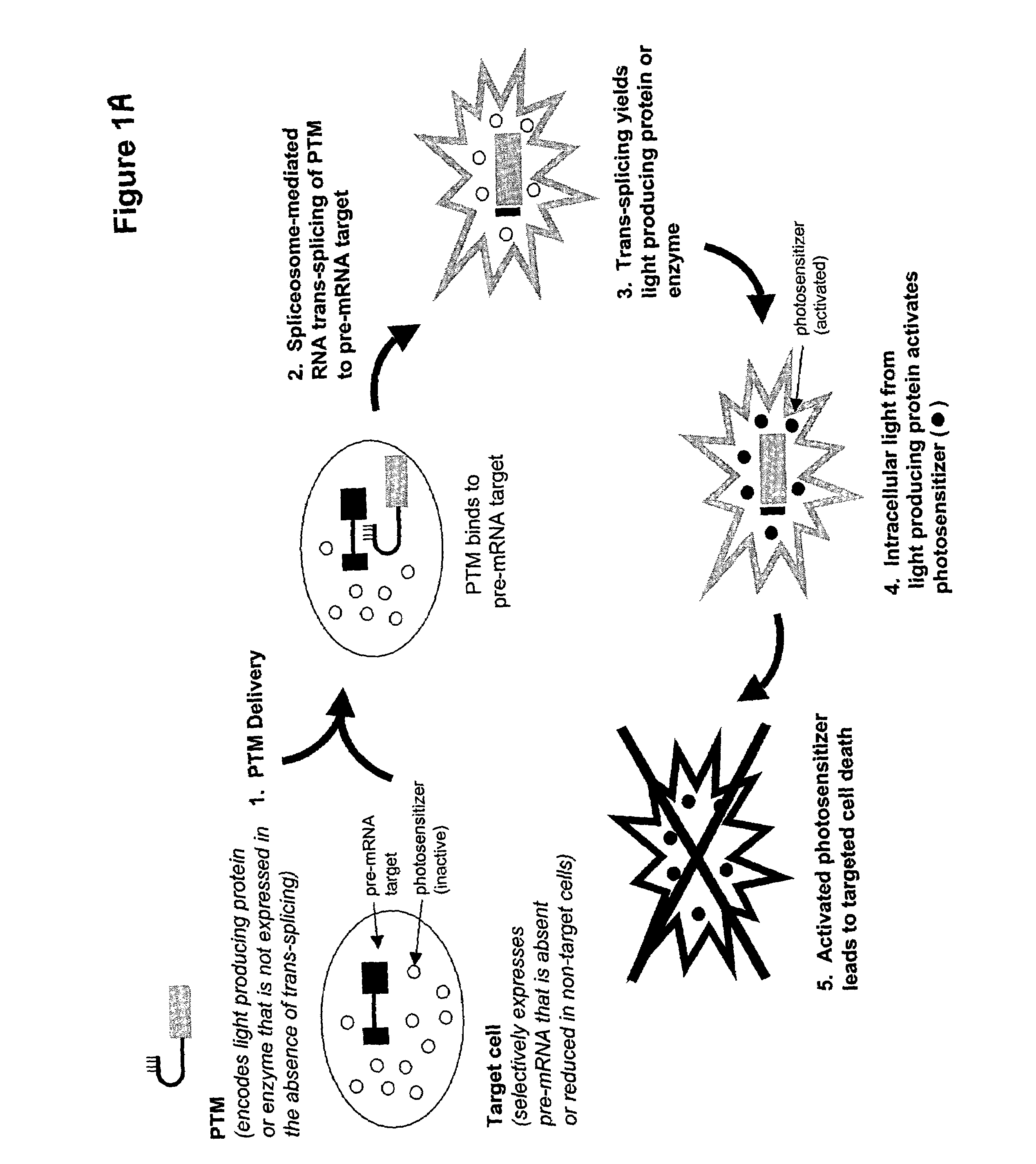
Trans-splicing mediated photodynamic therapy
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring selective death on cells expressing a specific target precursor messenger RNA (selective target pre-mRNA). The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) expressed within a cell and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric mRNA molecule (chimeric mRNA) capable of encoding a light producing protein or enzyme. Cell death is further mediated by the presence of a photosensitizer which upon photoactivation produces cytotoxicity.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES SEC GOVERNMENT OF UNITED STATES +1
Use of spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing to confer cell selective replication to adenoviruses
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring tumor selective cell death on cancer cells expressing specific target precursor messenger RNA molecules (cancer cell selective target pre-mRNAs). The compositions of the invention include conditionally replicative adenoviruses that have been genetically engineered to express one or more pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with one or more cancer cell target pre-mRNA and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of novel chimeric RNA molecules (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding adenovirus specific protein(s). Adenovirus specific proteins include those proteins complementing an essential activity necessary for replication of a defective adenovirus. The methods and compositions of the invention may be used to target a lytic adenovirus infection to cancer cells thereby providing a method for selective destruction of cancer cells. In addition, the adenoviruses of the invention may be engineered to encode PTMs designed to interact with target pre-mRNAs encoded by infectious agents within a cell, thereby targeting selective destruction of cells infected with such agents.
Owner:VIRXSYS
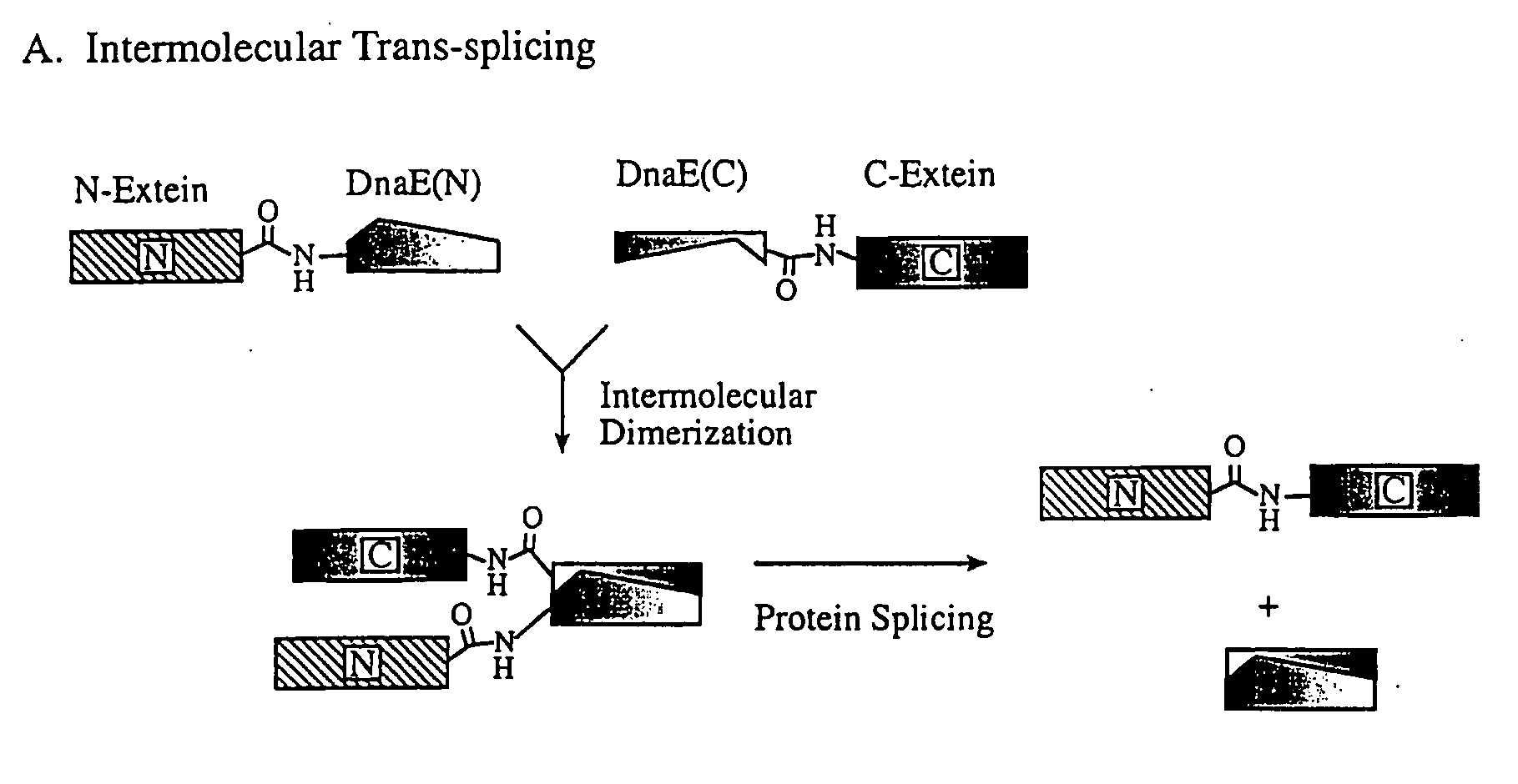
Method for modeling production of fusion protein by utilizing trans-splicing of intein
InactiveCN101899489AShorten the lengthEasy to operatePeptide preparation methodsAlgae/lichens peptidesGeneral functionProtein target
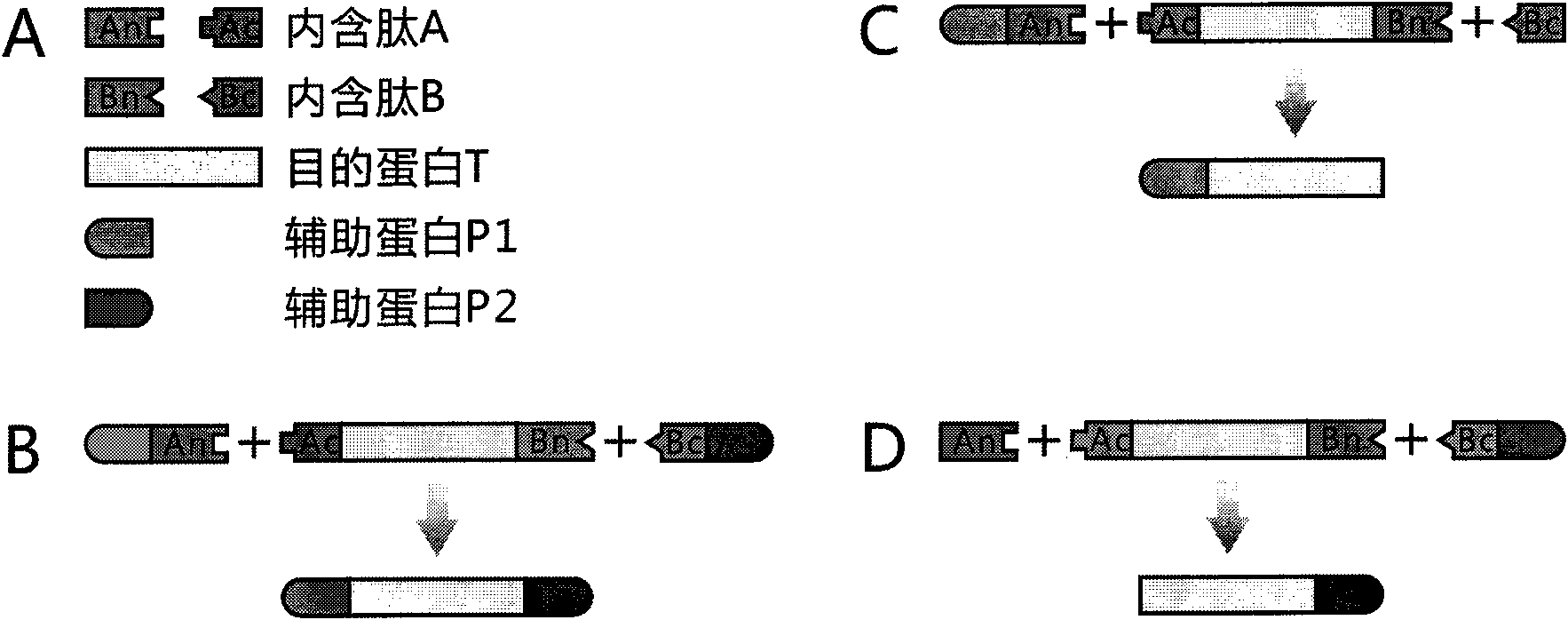
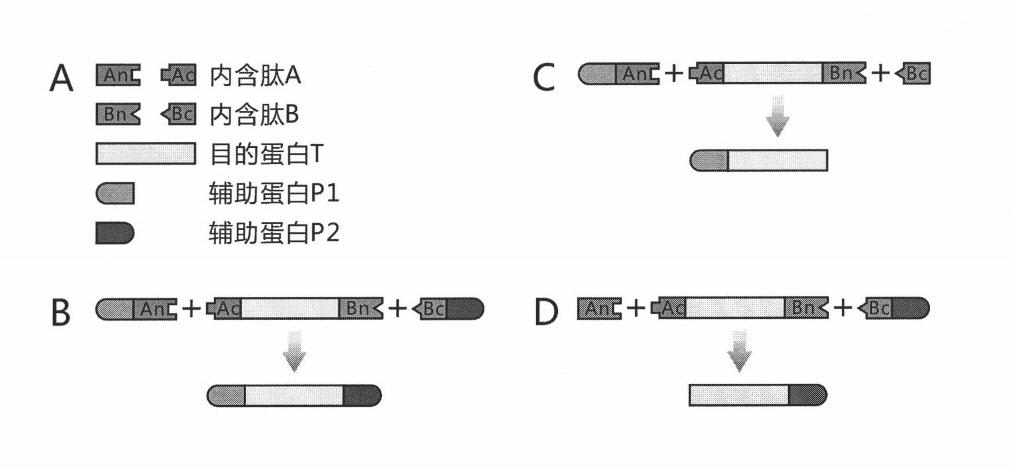
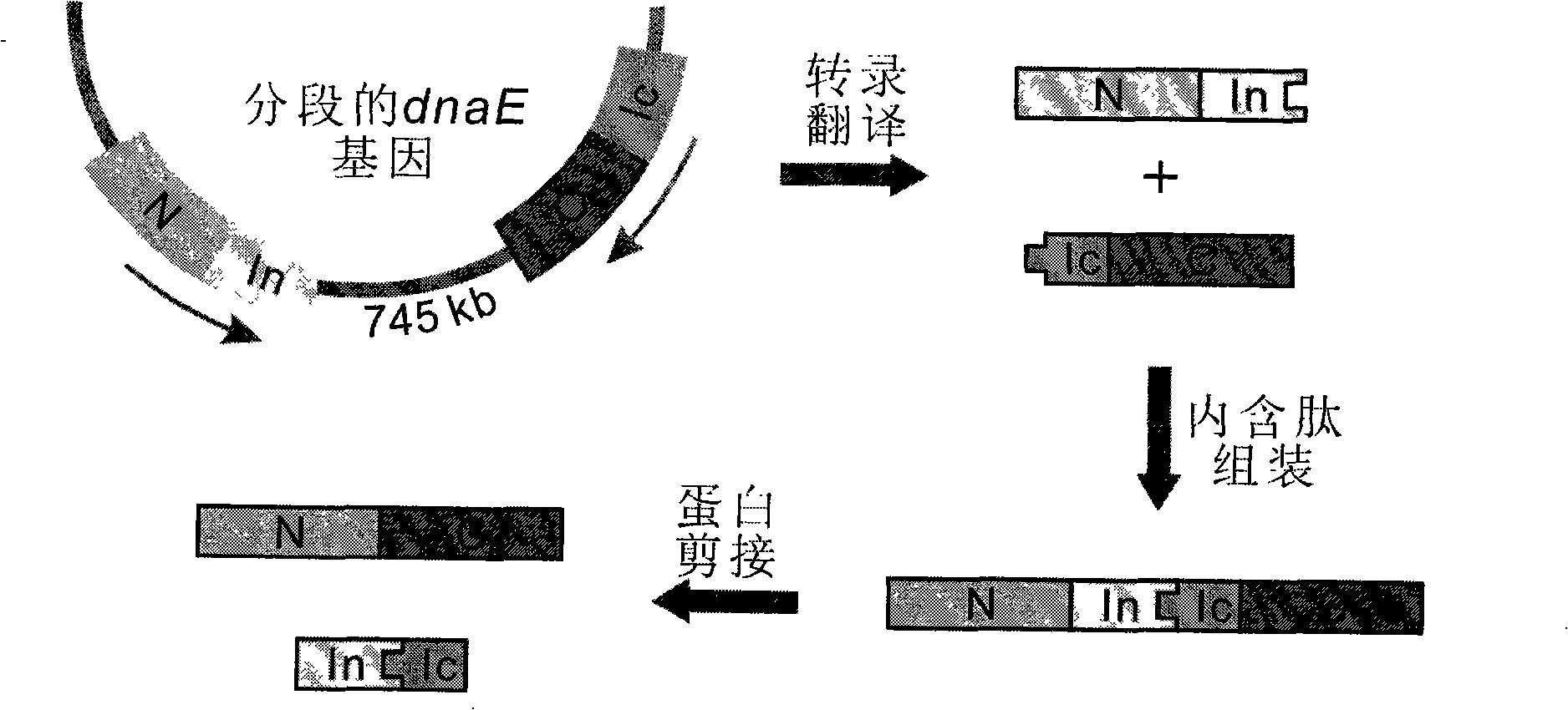
The invention discloses a method for the modeling production of fusion protein by utilizing the trans-splicing of intein, which can be used in fields, such as gene engineering, enzyme production, medicine production, food industry, farming and animal industry, and the like. In the invention, A target protein part with special biological functions and auxiliary protein with general functions are mainly connected together by utilizing the trans-splicing of the intein so as to obtain the fusion protein; the target protein T, the auxiliary protein P1 and P2, the intein A and the intein B which are mutually incompatible (such as blue algae: DnaE and DnaB of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803) are selected; the intein A and intein B are respectively decomposed into an amino terminal (N terminal) and a carboxyl terminal (C terminal), i.e. An, Ac, Bn and Bc; after different carrier systems are constructed; protein segments Ac-T-Bn, P1-An, Bc-P2, An and Bc are respectively obtained through host expression; the obtained protein segments are mixed; and the trans-splicing of the intein is carried out to generate the fusion protein P1-T-P2, P1-T or T-P2.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Intein-mediated cyclization of peptides
Methods of producing cyclic peptides and splicing intermediates of peptides in a looped conformation are disclosed. The methods utilize the trans-splicing ability of split inteins to catalyze cyclization of peptides from a precursor peptide having a target peptide interposed between two portions of a split intein. The interaction of the two portions of the split intein creates a catalytically-active intein and also forces the target peptide into a loop configuration that stabilizes the ester isomer of the amino acid at the junction between one of the intein portions and the target peptide. A heteroatom from the other intein portion then reacts with the ester to form a cyclic ester intermediate. The active intein catalyzes the formation of an aminosuccinimide that liberates a cyclized form of the target peptide, which spontaneously rearranges to form the thermodynamically favored backbone cyclic peptide product. Also disclosed are nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides, methods for making cyclic peptides, methods of making libraries, and methods of screening peptides.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20020115207A1Inhibition of translationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSpliceosomeExon intron
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Cell ablation using trans-splicing ribozymes
InactiveUS6071730AAccurate expressionSusceptibilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsInteinRNA Sequence
The design of new ribozymes capable of self-catalyzed trans-splicing which are based upon the catalytic core of a Group I intron are described. Using this design, it is possible to construct ribozymes capable of efficiently splicing a new 3' exon sequence into any chosen target RNA sequence in a highly precise manner. A method of cell ablation is also described that provides a toxic product to a host cell in vivo in a targetted, regulated manner utilizing novel trans-splicing ribozymes of the invention. Inactive pro-ribozyme forms are also described.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Amplification vectors based on trans-splicing
InactiveUS20050221323A1Efficient processingNegligible effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsRNA Sequence
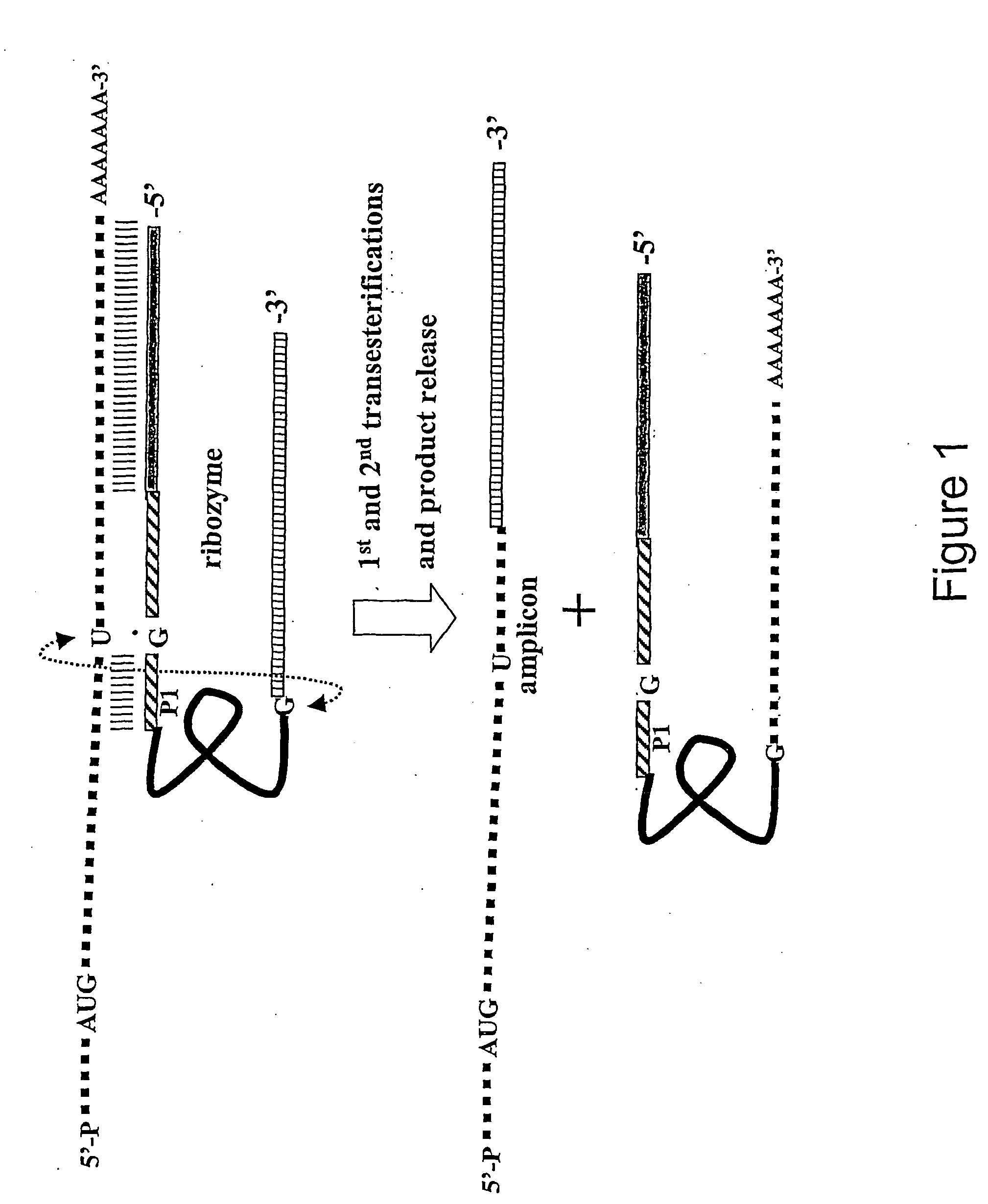
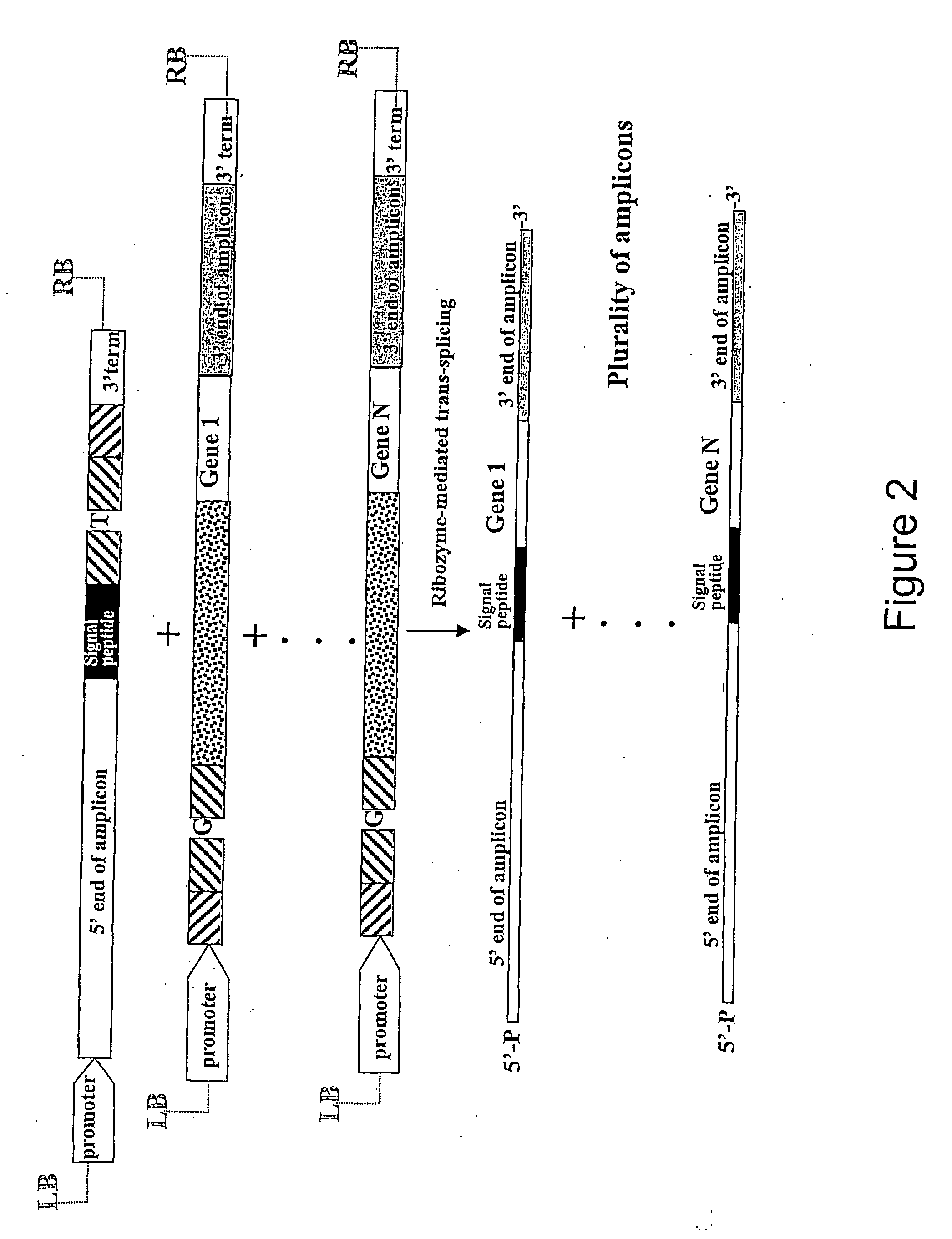
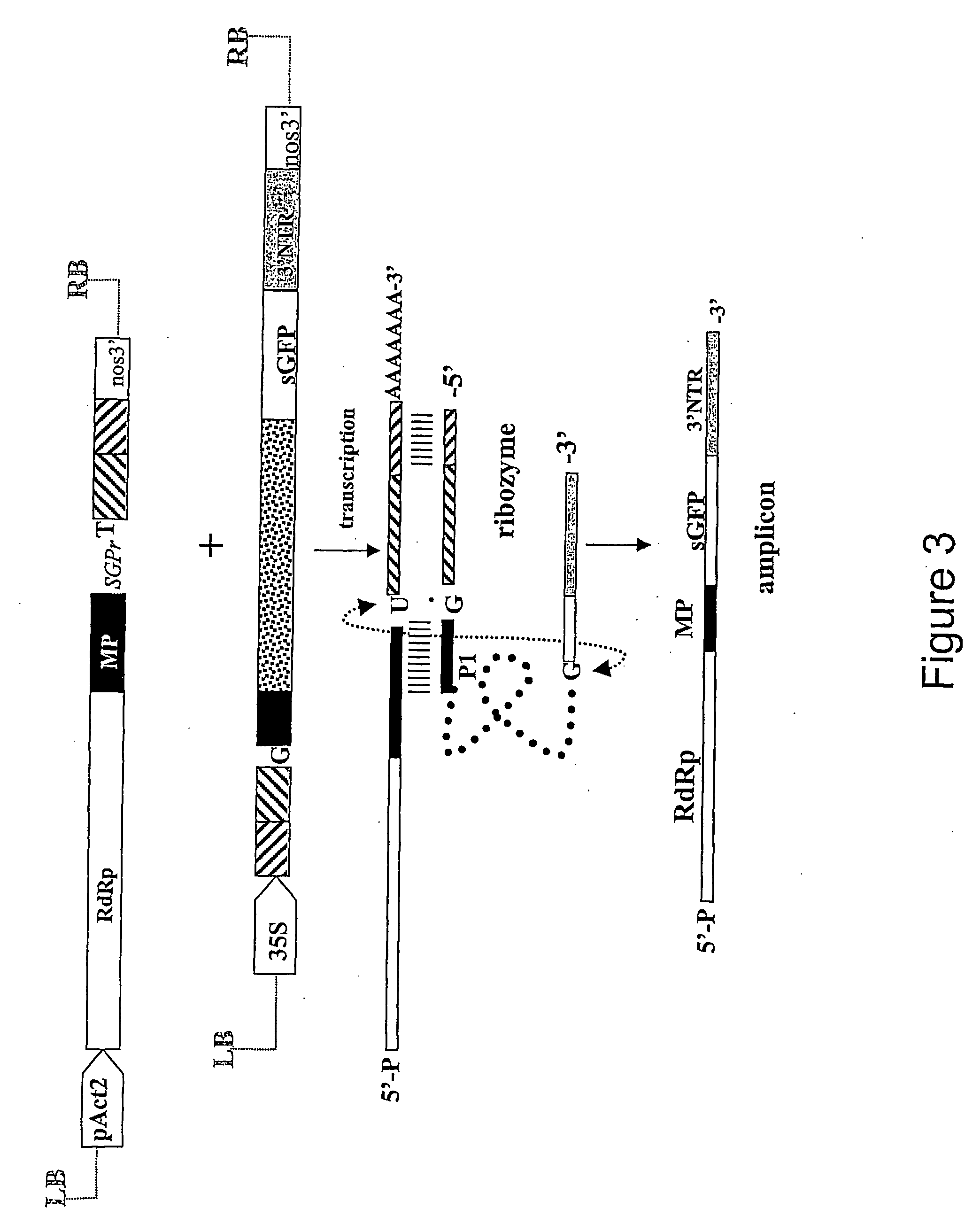
This invention provides process of amplification and / or expression of a sequence of interest in a cell by providing for generating within said cell at least one amplicon by trans-splicing between an RNA sequence designed for being capable of trans-splicing and a target RNA, whereby said amplicon is capable of amplifying in said cell and capable of expressing a sequence of interest.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
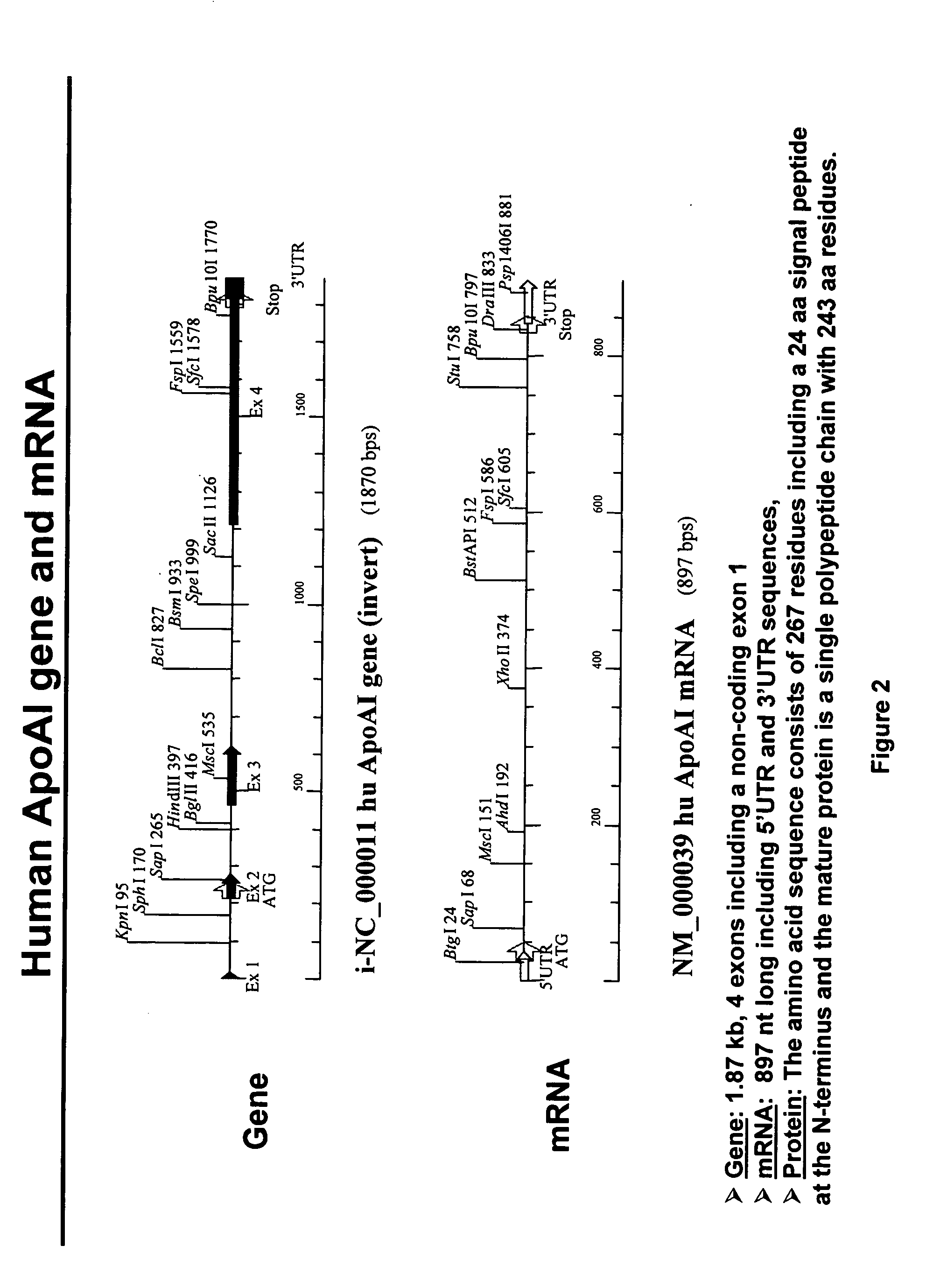
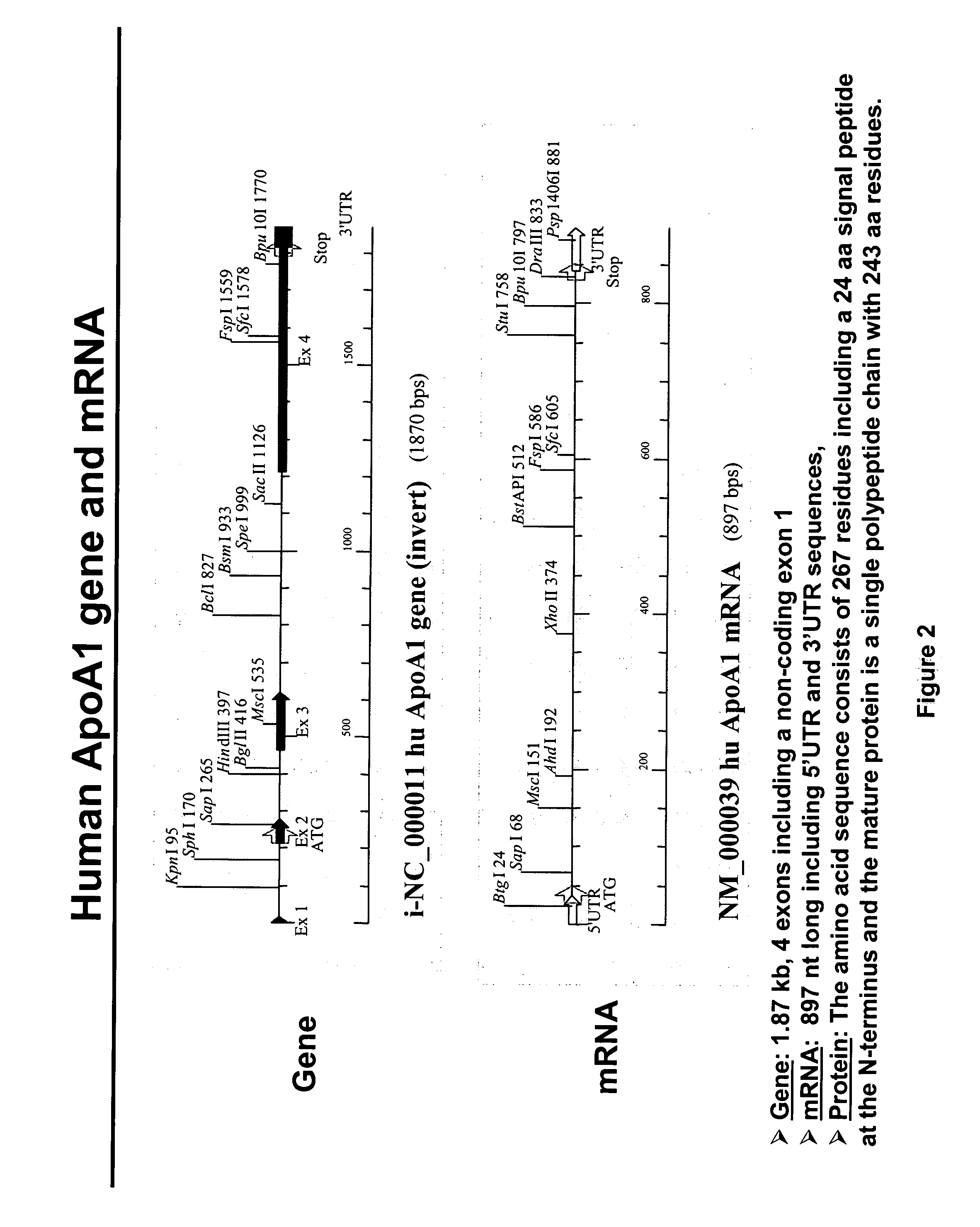
Expression of apoAI and variants thereof using spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20060194317A1Improving biological half lifeFunction increaseSplicing alterationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRNA Trans-SplicingMessenger RNA
Methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing that result in expression of a apoAI protein, an apoAI variant, the preferred embodiment referred to herein as the apoAI Milano variant, a pre-pro-apoAI or an analogue of apoAI. The methods and compositions include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding apoAI, the apoAI Milano variant, or an analogue of apoAI. The expression of this apoAI protein results in protection against vascular disorders resulting from plaque build up, i.e., atherosclerosis, strokes and heart attacks.
Owner:VIRXSYS
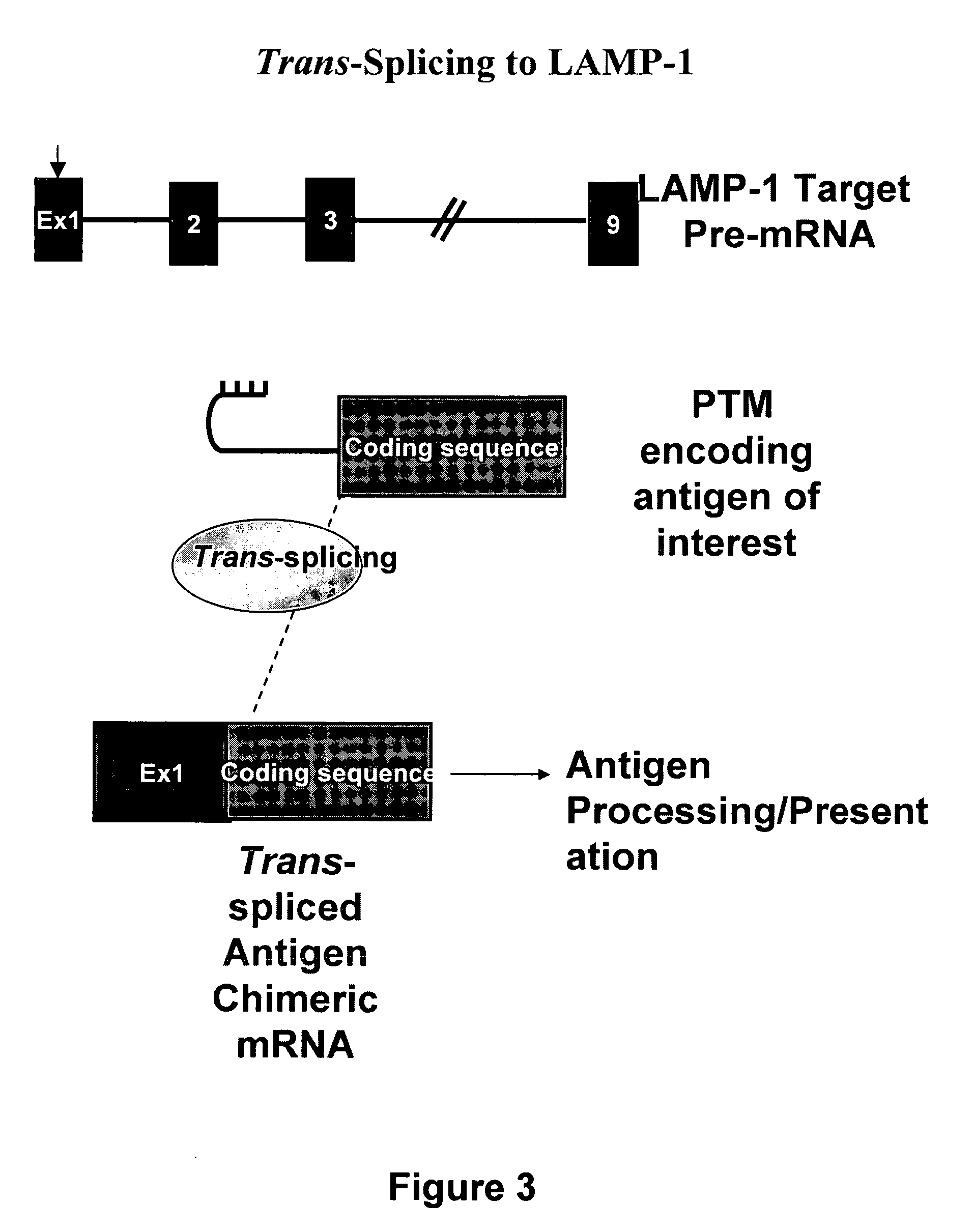
Use of spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing for immunotherapy
InactiveUS20060094110A1Stimulate immune responseGood health benefitsSugar derivativesTissue cultureRNA Trans-SplicingMessenger RNA
Methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated trans-splicing that result in expression of an immunogenic polypeptide. The invention includes pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding the immunogenic polypeptide, recombinant vector systems capable of expressing the PTMs of the invention, and cells expressing said PTMs. The target pre-mRNA are those encoding proteins that function in antigen uptake, antigen presentation and chaperoning. The methods of the invention encompass contacting the PTMs of the invention with a target pre-mRNA, under conditions in which a portion of the PTM is trans-spliced to a portion of the target pre-mRNA to form a chimeric mRNA molecule capable of encoding an immunogenic polypeptide.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Targeted trans-splicing of highly abundant transcripts for in vivo production of recombinant proteins
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through RNA trans-splicing that target a highly expressed pre-mRNA and contain the coding sequence of a protein or polypeptide of interest. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with the target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) that is abundantly expressed, and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding a protein or polypeptide of interest. The invention provides for the in vivo production of chimeric RNA molecules that encode and result in the production of a protein or polypeptide of interest.
Owner:VIRXSYS
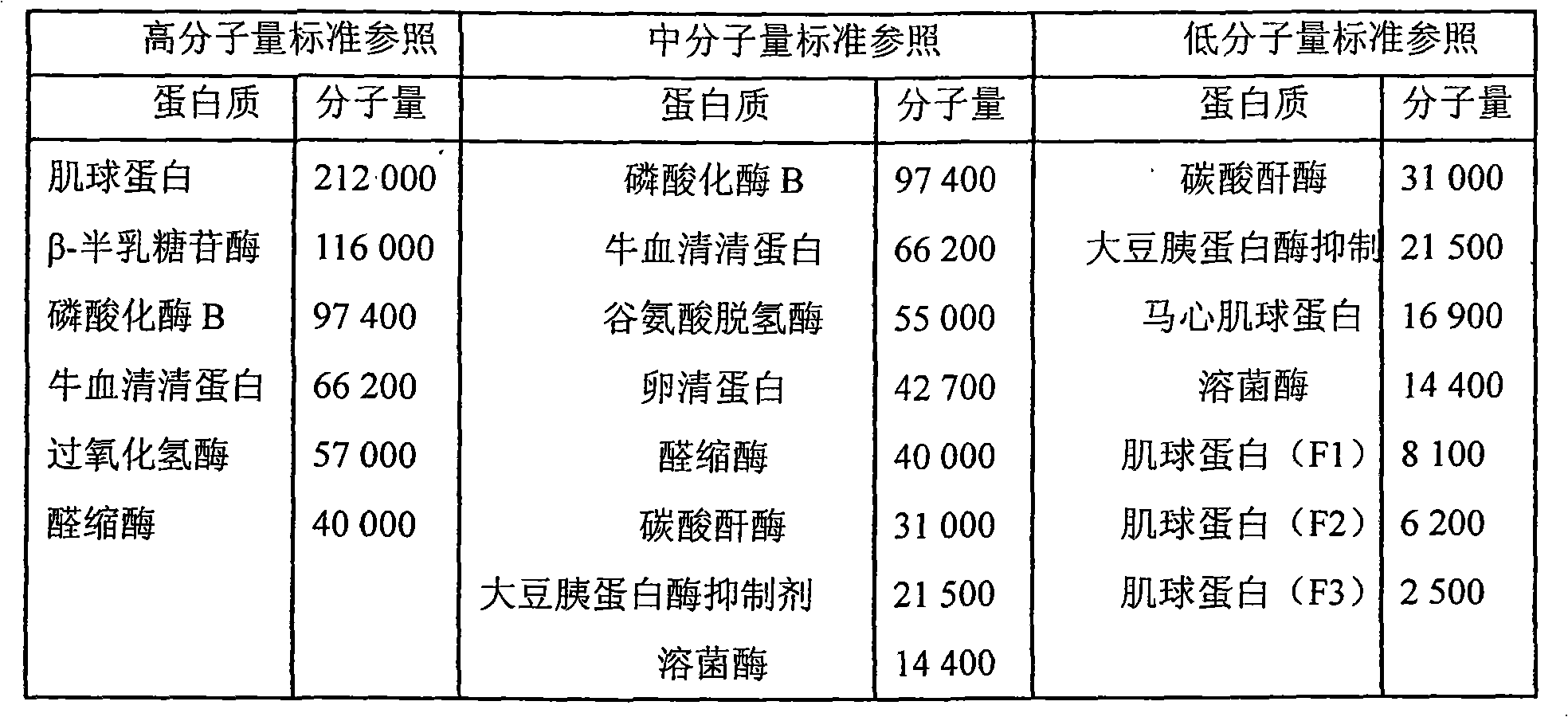
Method using implicit peptides trans splicing to manufacture protein molecular weight standard
InactiveCN101281201APreparing sample for investigationBiological testingProtein moleculesProtein insertion
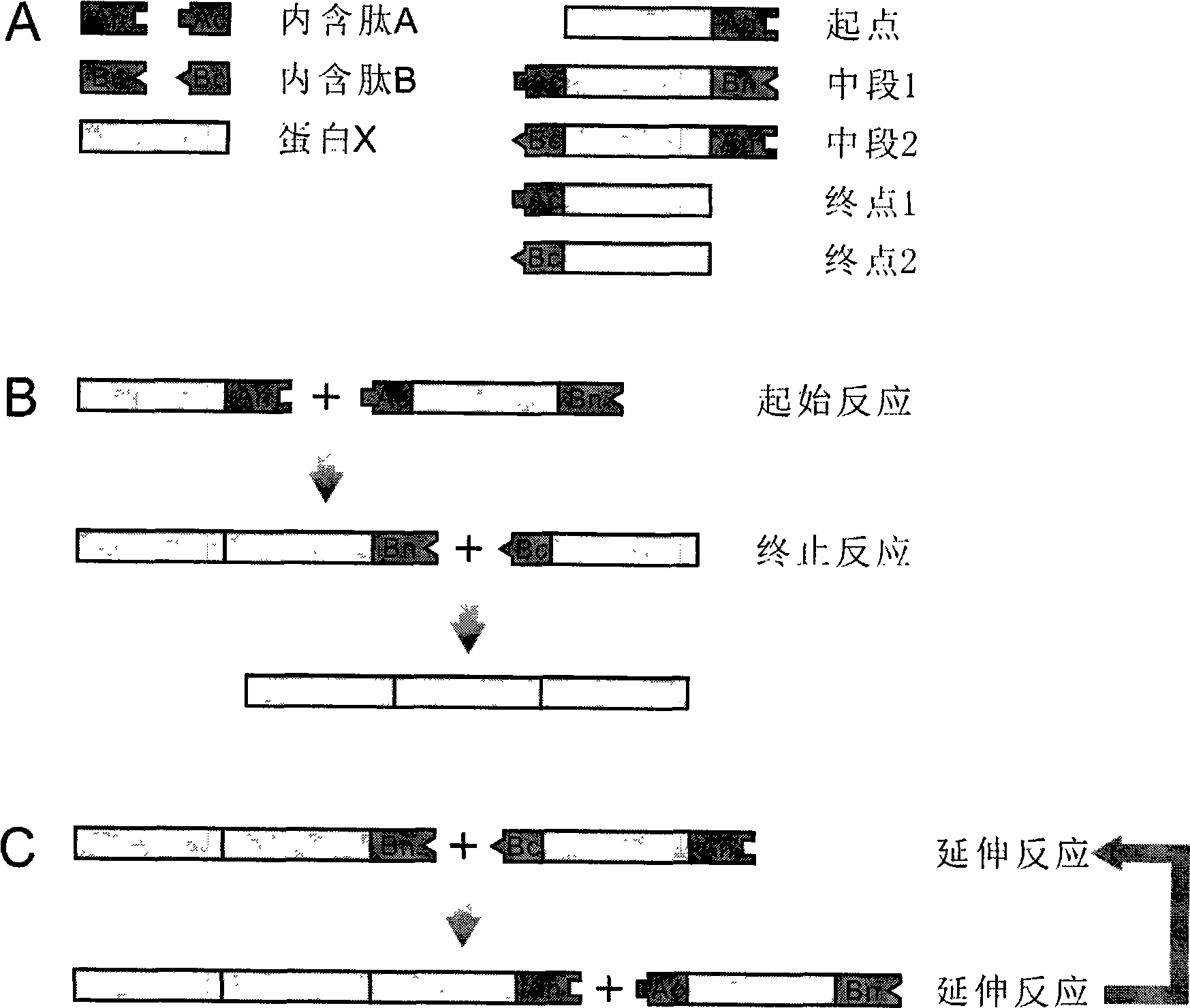
The invention discloses a method utilizing internal peptide inverse splicing to prepare protein molecular weight standard, which includes: selecting a section of known protein X with a certain molecular weight, selecting two internal peptides A and B not compatible to each other, and then respectively decompounding internal peptides A and B into amino terminal (N terminal) and carboxyl terminal (C terminal), namely An, Ac, Bn, Bc; and then using them to consist five recombinant proteins, namely an initial point protein (X-An), an intermediate section 1 protein(Ac-X-Bn), an intermediate section 2 protein(Bc-X-An), an end point 1 protein(Ac-X), and an end point 2 protein(Bc-X); obtaining protein molecular weight standard with multiple molecular weight distribution by mutually combining, connecting and overlapping the five proteins.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
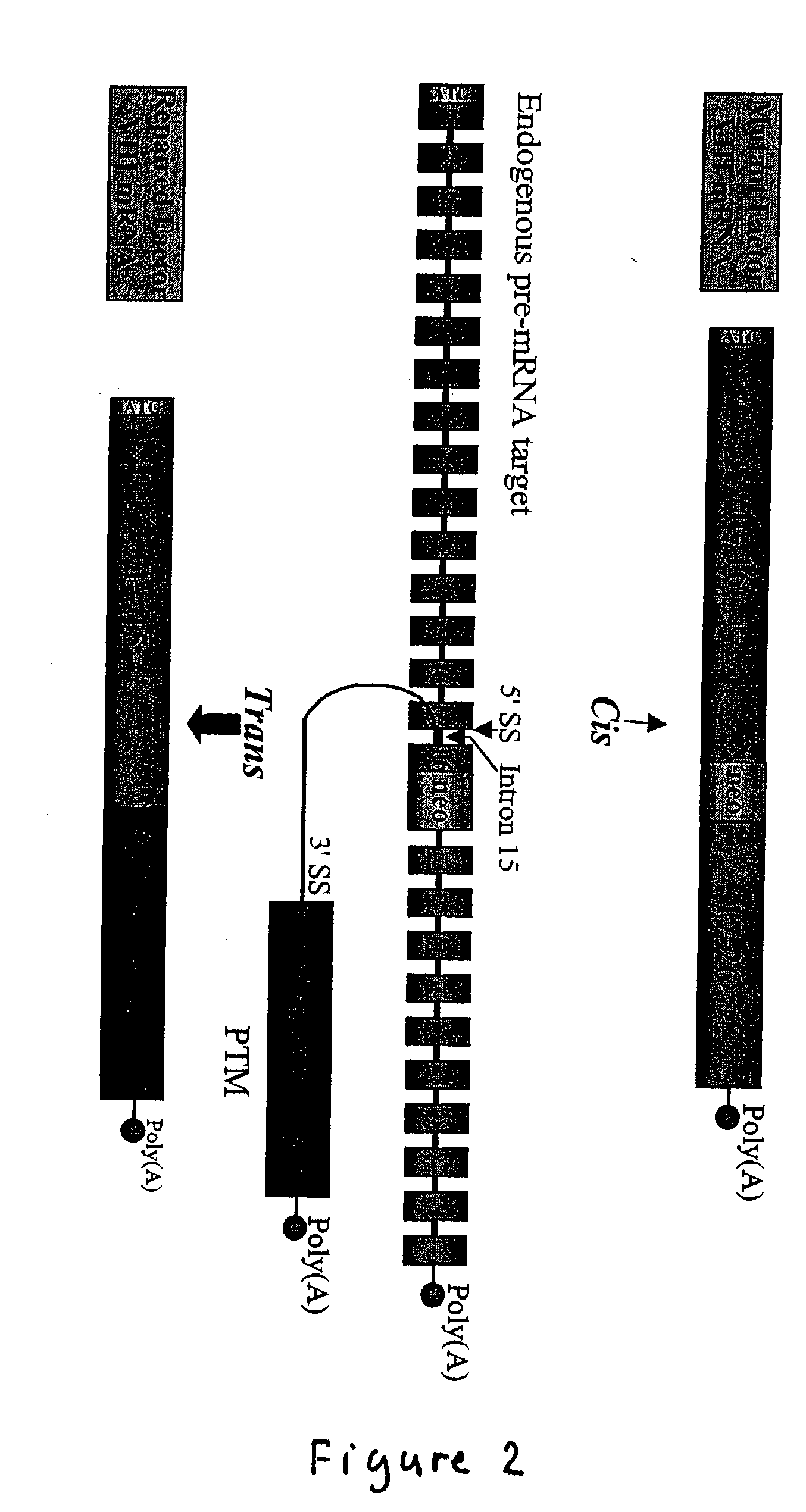
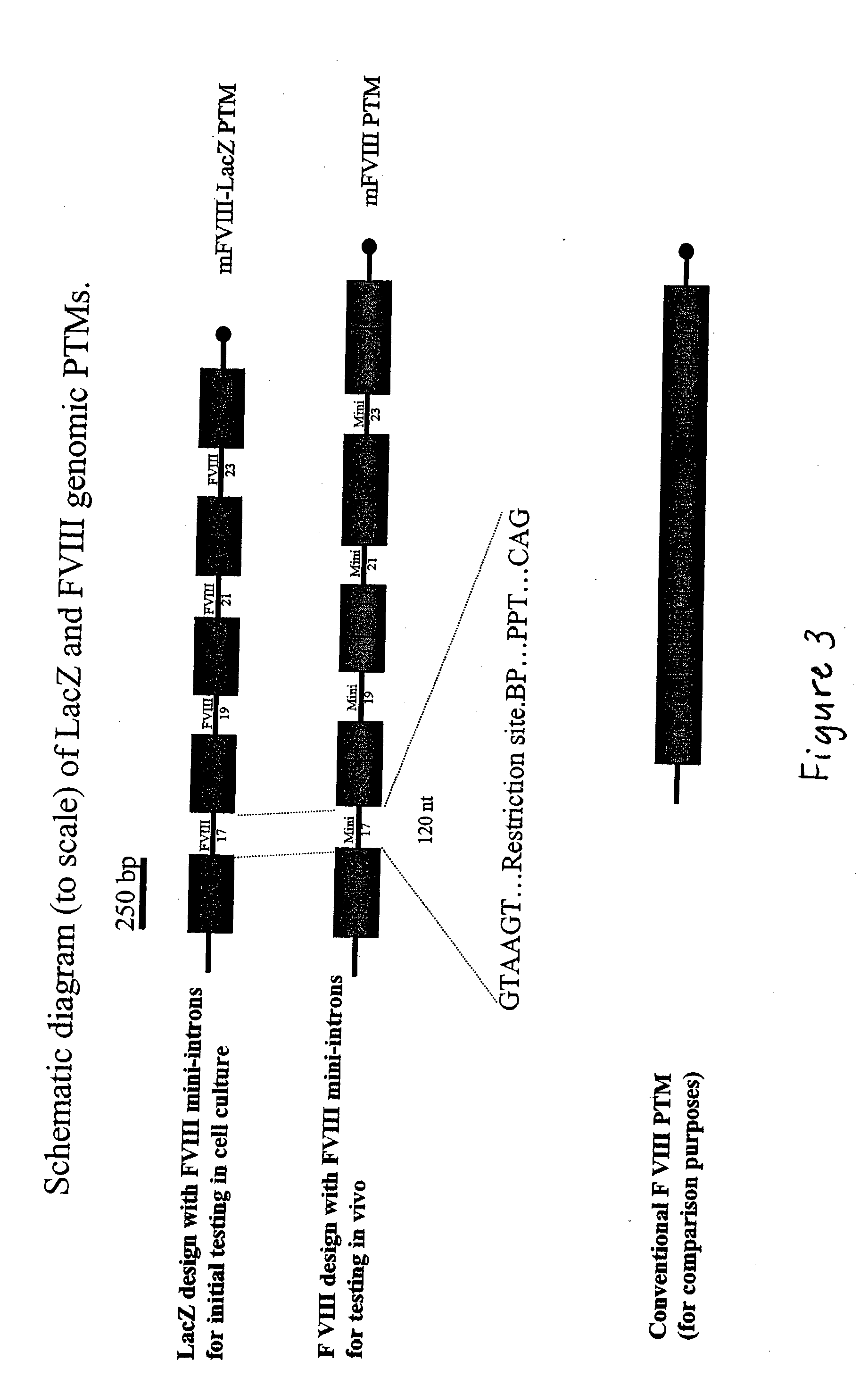
Correction of factor VIII genetic defects using spliceosome mediated RNA trans splicing
InactiveUS20040126774A1Splicing alterationMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA Trans-SplicingVector system
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated trans-splicing. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). In particular, the PTMs of the present invention are genetically engineered to interact with factor VIII (FVIII) target pre-mRNA so as to result in correction of clotting FVIII genetic defects responsible for hemophilia A. The compositions of the invention further include recombinant vector systems capable of expressing the PTMs of the invention and cells expressing said PTMs. The methods of the invention encompass contacting the PTMs of the invention with a FVIII target pre-mRNA under conditions in which a portion of the PTM is trans-spliced to a portion of the target pre-mRNA to form a RNA molecule wherein the genetic defect in the FVIII gene has been corrected. The methods and compositions of the present invention can be used in gene therapy for correction of FVIII disorders such as hemophilia A.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Expression of apoA-1 and variants thereof using spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20060177933A1Reduce buildReduce usageSplicing alterationApolipeptidesRNA Trans-SplicingMessenger RNA
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing that result in expression of an apoA-1 variant, the preferred embodiment referred to herein as the apoA-1 Milano variant. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding the apoA-1 Milano variant. The expression of this variant protein results in protection against vascular disorders resulting from plaque build up, i.e., strokes and heart attacks. In particular, the PTMs of the present invention include those genetically engineered to interact with the apoA-1 target pre-mRNA so as to result in expression of the apoA-1 Milano variant. In addition, the PTMs of the invention include those genetically engineered to interact with the apoB or albumin or other specific target pre-mRNAs so as to result in expression of an apoB / apoA-1 and / or alb / apoA-1 wild type or Milano fusion protein thereby reducing apoB expression and simultaneously produce ApoA-1 function.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Method for producing circular or multimeric protein species in vivo or in vitro and related methods
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20020193580A1Improve abilitiesEfficient processVectorsSugar derivativesTrans-splicingSpliceosome complex
The present invention provides methods and compositions for delivery of synthetic pre-trans-splicing molecules (synthetic PTMs) into a target cell. The compositions of the invention include synthetic pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) with enhanced stability against chemical and enzymatic degradation. The synthetic PTMs are designed to interact with a natural target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA).
Owner:VIRXSYS
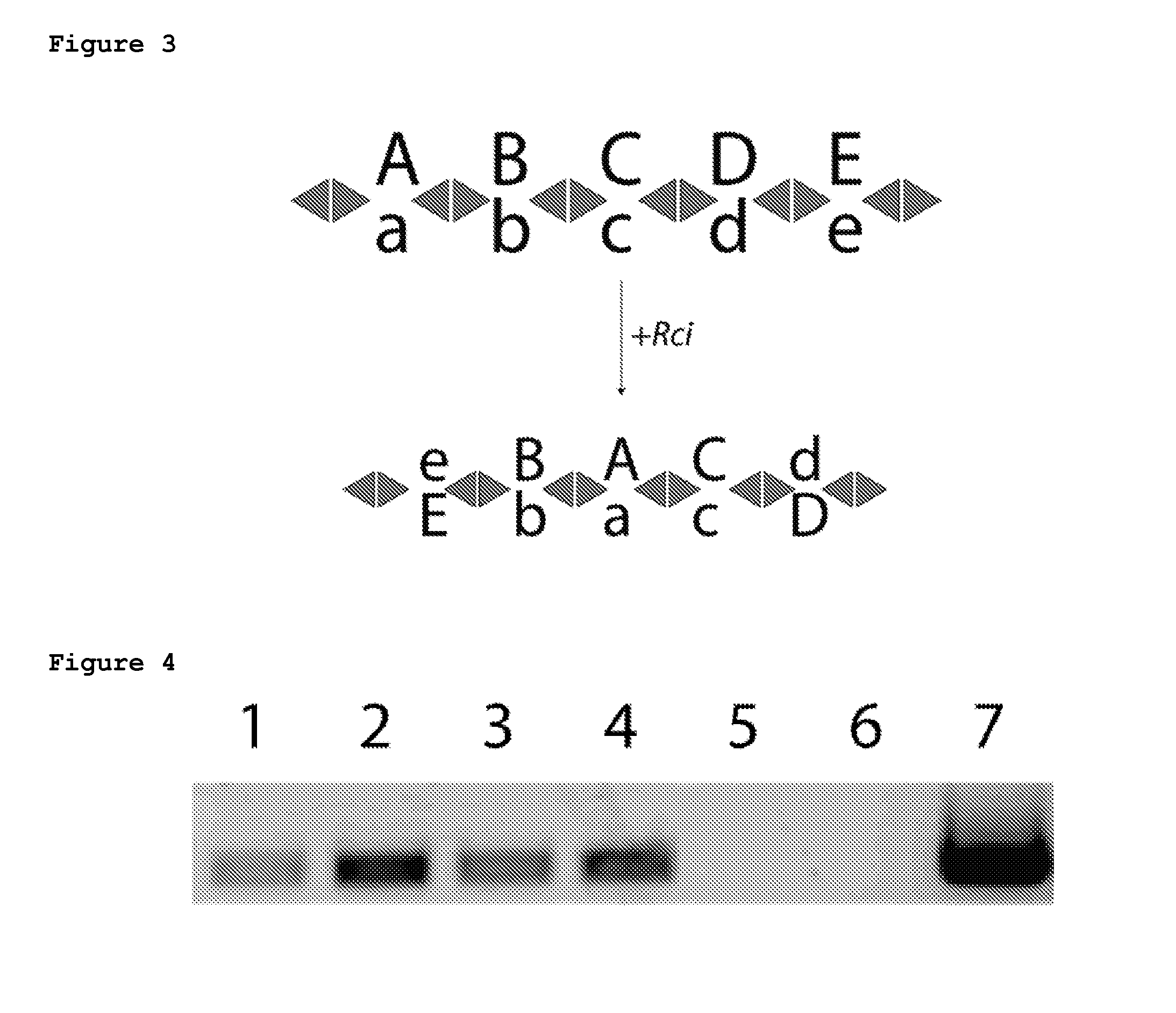
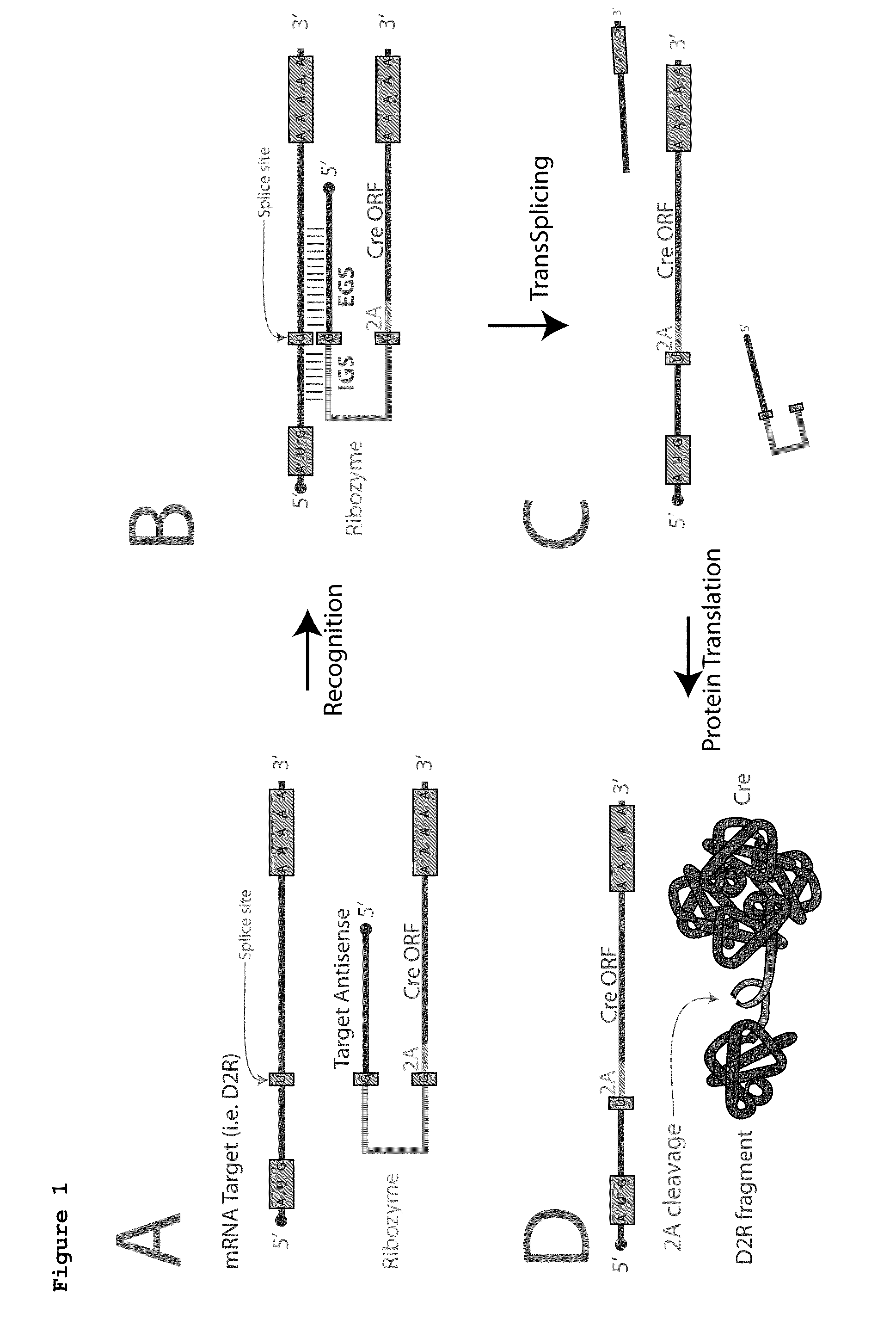
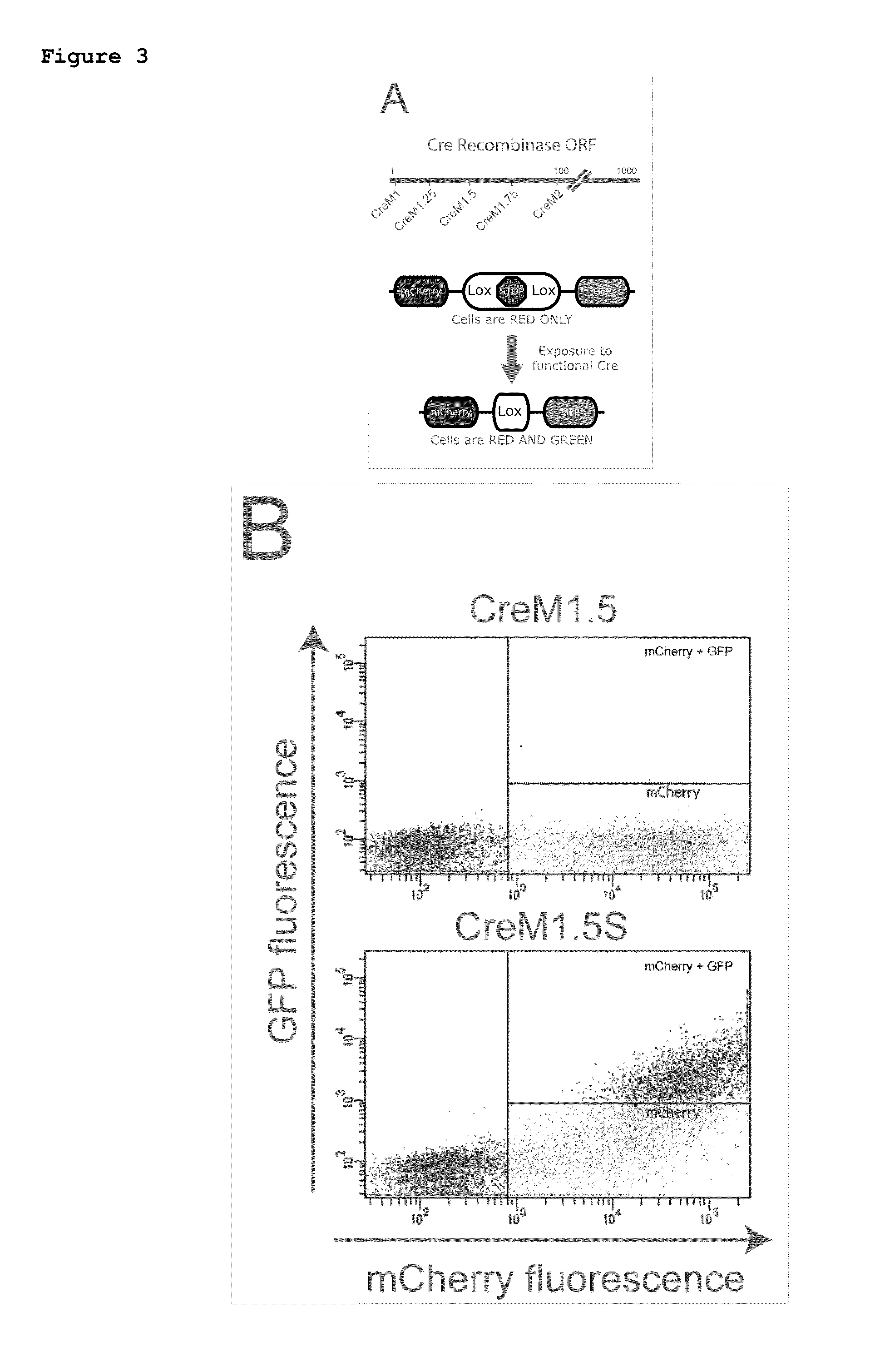
Trans-splicing ribozymes and silent recombinases
The present invention provides a trans-splicing ribozyme comprising i) a targeting nucleotide sequence that is complementary to a target nucleotide sequence within a mRNA that is expressed in a cell; contiguous with ii) a catalytic RNA sequence; contiguous with iii) a donor transcript, which donor transcript comprises at least a nucleotide sequence that encodes a trans-activator, wherein when the trans-splicing ribozyme is expressed in a cell, the catalytic RNA sequence cleaves the mRNA and ligates the donor transcript to the mRNA to generate a spliced mRNA which comprises the donor transcript, such that the donor transcript is translated as part of the spliced mRNA in the cell, as well as methods of using the trans-splicing ribozyme. The present invention also provides variants of Cre and other recombinases, as well as method of using the variants.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com