Graph data deleting method and system based on MapReduce
A deletion method and graph data technology, applied in the field of big data, can solve problems such as the influence of subjective factors, achieve the effect of improving data processing efficiency and reducing network overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 6 As shown, this example discloses a specific implementation of a MapReduce-based graph data deletion method (hereinafter referred to as "method").
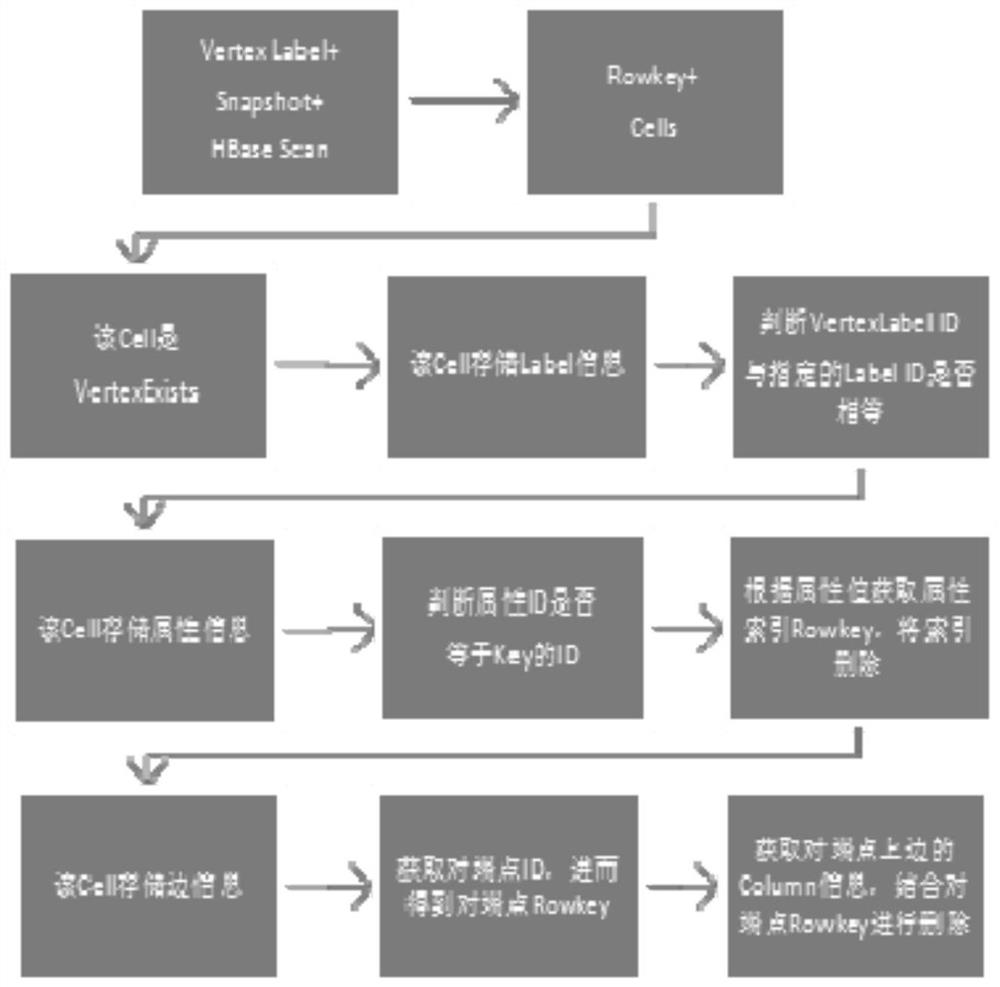
[0073] Specifically, when performing data operations on HBase, it is necessary to understand the data storage structure of JanusGraph in HBase. In JanusGraph, the point is the center and the data is stored in the form of edge cutting. The ID of the node is used as the Rowkey of HBase, and each attribute and each edge on the node is used as an independent Cell of the Rowkey, that is, each attribute , Each edge is an independent KCV structure (Key-Column-Value). JanusGraph defines each element in the graph as a RelationType, and assigns it an id, including whether there are marker points (VertexExists), point Label points (VertexLabel), attribute points, edge Label points (EdgeLabel), etc. JanusGraph assigns each point an ID called RelationTypeId. JanusGraph also defines three directions: PROP...
Embodiment 2
[0125] In combination with the MapReduce-based graph data deletion method disclosed in Embodiment 1, this embodiment discloses a specific implementation example of a MapReduce-based graph data deletion system (hereinafter referred to as "system").
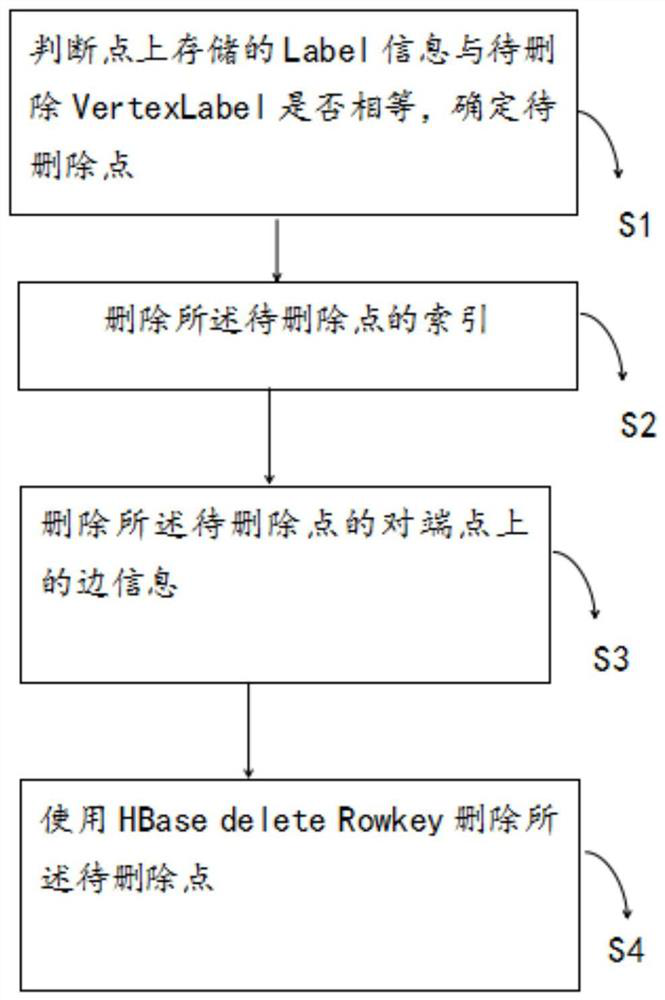
[0126] refer to Figure 7 As shown, the system includes:
[0127] Judging module 10, whether the Label information stored on the judging point is equal to the VertexLabel to be deleted, determines the point to be deleted;
[0128] The index deletion module 20 deletes the index of the point to be deleted;
[0129] The opposite end point deletion module 30, deletes the side information on the opposite end point of the point to be deleted;
[0130] The point deletion module 40 uses HBase delete Rowkey to delete the point to be deleted.
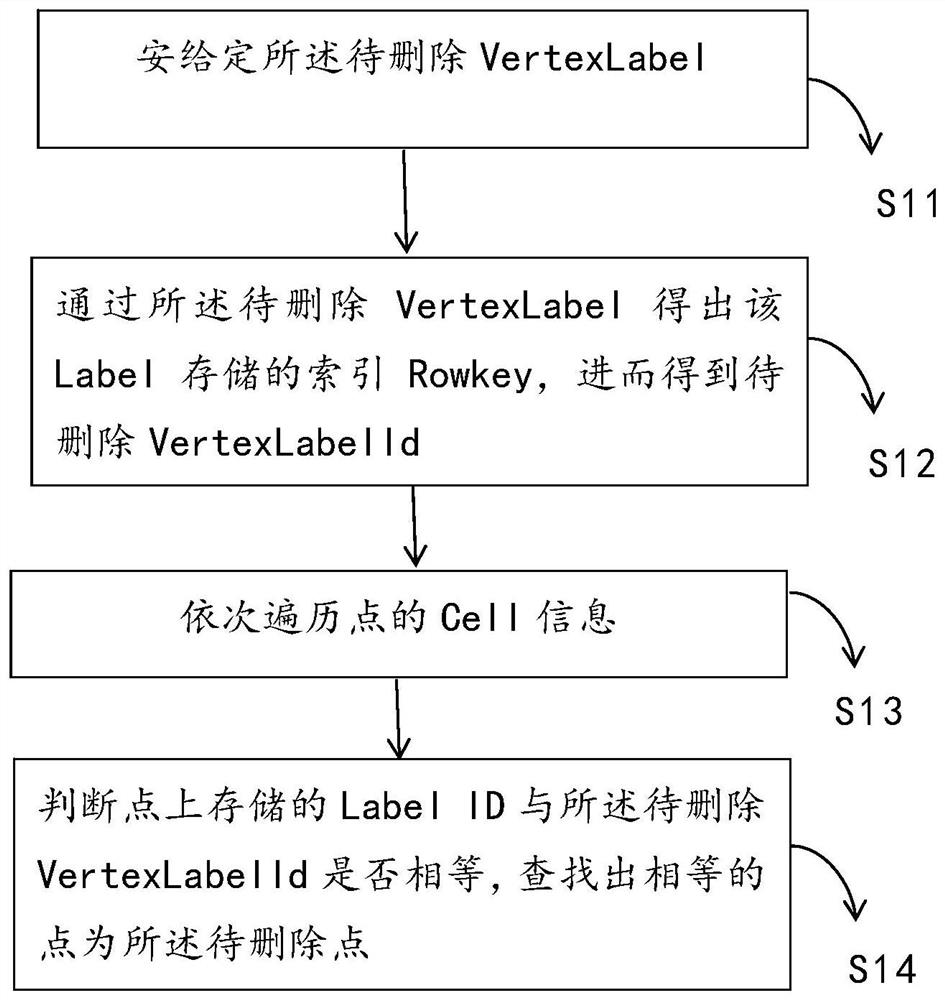
[0131] Specifically, in some of these embodiments, the judgment module 10 specifically includes:
[0132] Given unit 11, given the VertexLabel to be deleted;
[0133] VertexLabelId acquisition un...
Embodiment 3
[0151] combine Figure 8 As shown, this embodiment discloses a specific implementation manner of a computer device. The computer device may comprise a processor 81 and a memory 82 storing computer program instructions.
[0152] Specifically, the processor 81 may include a central processing unit (CPU), or an Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC for short), or may be configured to implement one or more integrated circuits in the embodiments of the present application.
[0153] Among them, the memory 82 may include mass storage for data or instructions. For example without limitation, the memory 82 may include a hard disk drive (Hard Disk Drive, referred to as HDD), a floppy disk drive, a solid state drive (SolidState Drive, referred to as SSD), flash memory, optical disk, magneto-optical disk, magnetic tape or universal serial bus (Universal Serial Bus, referred to as USB) drive or a combination of two or more of the above. Storage 82 may comprise removable or non-r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com