Method for enriching a biomass with proteins
A biomass and protein technology, applied in the field of enriching biomass with protein, can solve problems such as inapplicability of biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0086] Materials and methods
[0087] cracking biomass
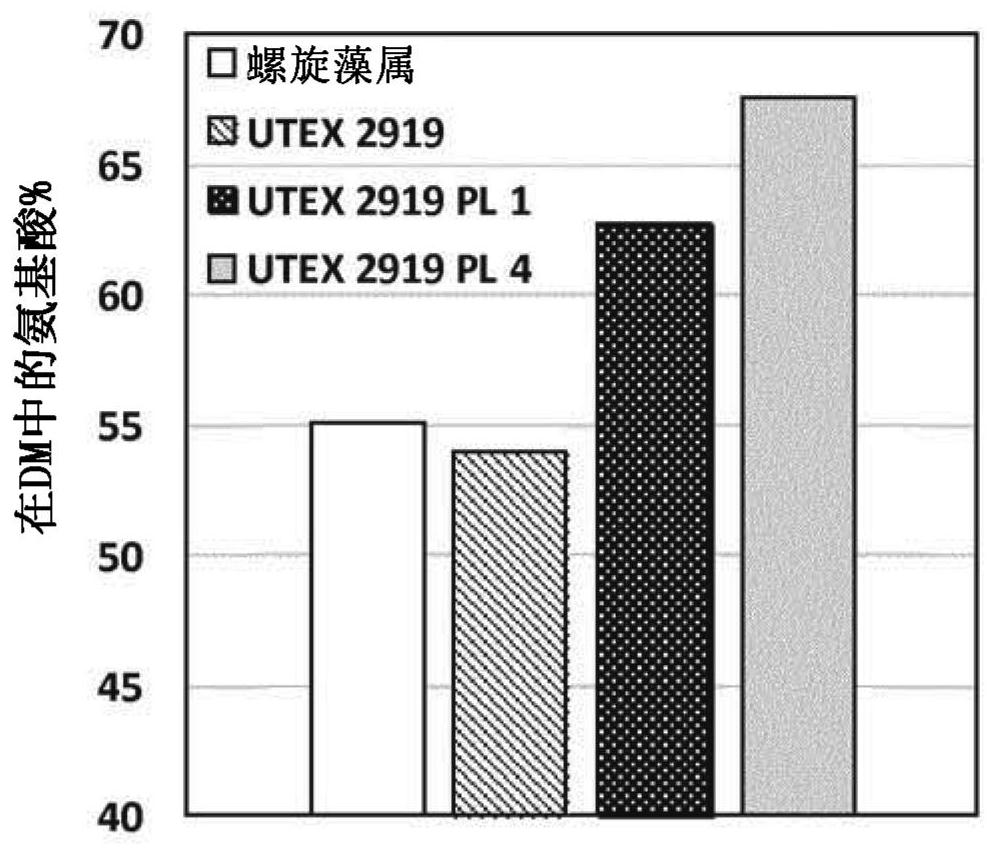
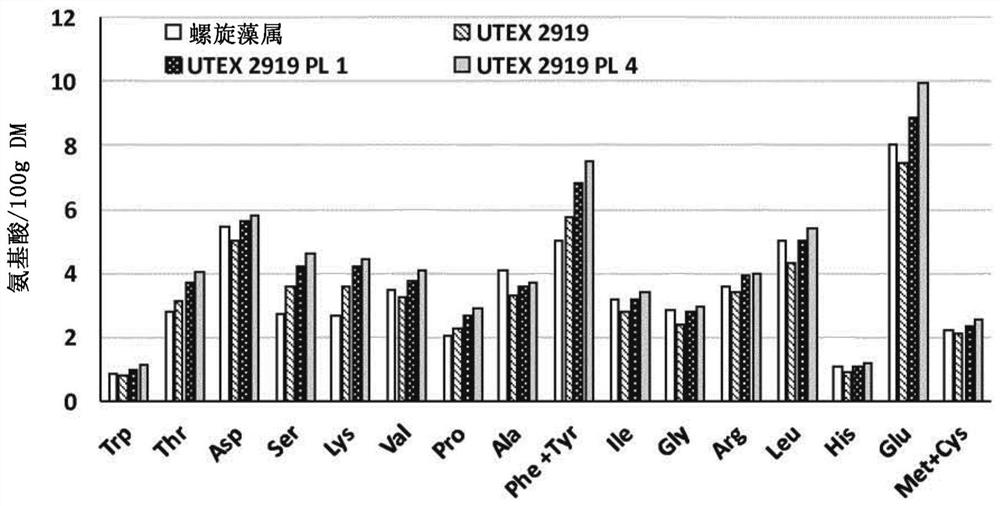
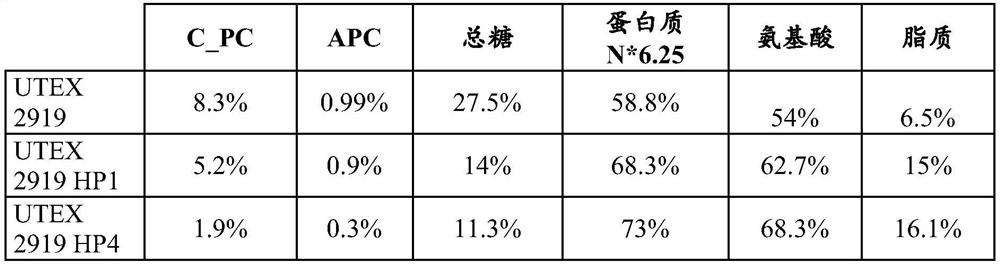
[0088] The biomass treated by the method according to the invention is that of the Spirulina genus (Arthrospira platensis) and the Rhodophylla thiaphila Galtieria strain UTEX 2919 cultivated according to the usual methods for cultivating these strains (UTEX Algae Culture Center, 205 W. 24th Street, Biological Labs 218, University of Texas at Austin (A6700), Austin, Texas 78712 USA).
[0089] Lysed biomass has 95% lysed cell content
[0090] 10% dry matter content
[0091]operating procedures
[0092] The enrichment process is carried out by repeatedly rinsing the ground biomass pellet under acidic pH conditions. For this, the operation involved the use of a centrifuge, described here by using a Sorvall RC5B plus and a Sorvall SLA3000 fixed angle rotor. The ground biomass was centrifuged at 12000 x g for 15 min to maximize the sedimentation of the insoluble fraction. The "soluble fraction" supernatant was removed an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com