Branching macromolecule entanglement processing method and coarse graining simulation method
A technology of processing method and simulation method, applied in computational theoretical chemistry, instrumentation, informatics, etc., can solve difficult problems such as the study of rheological properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
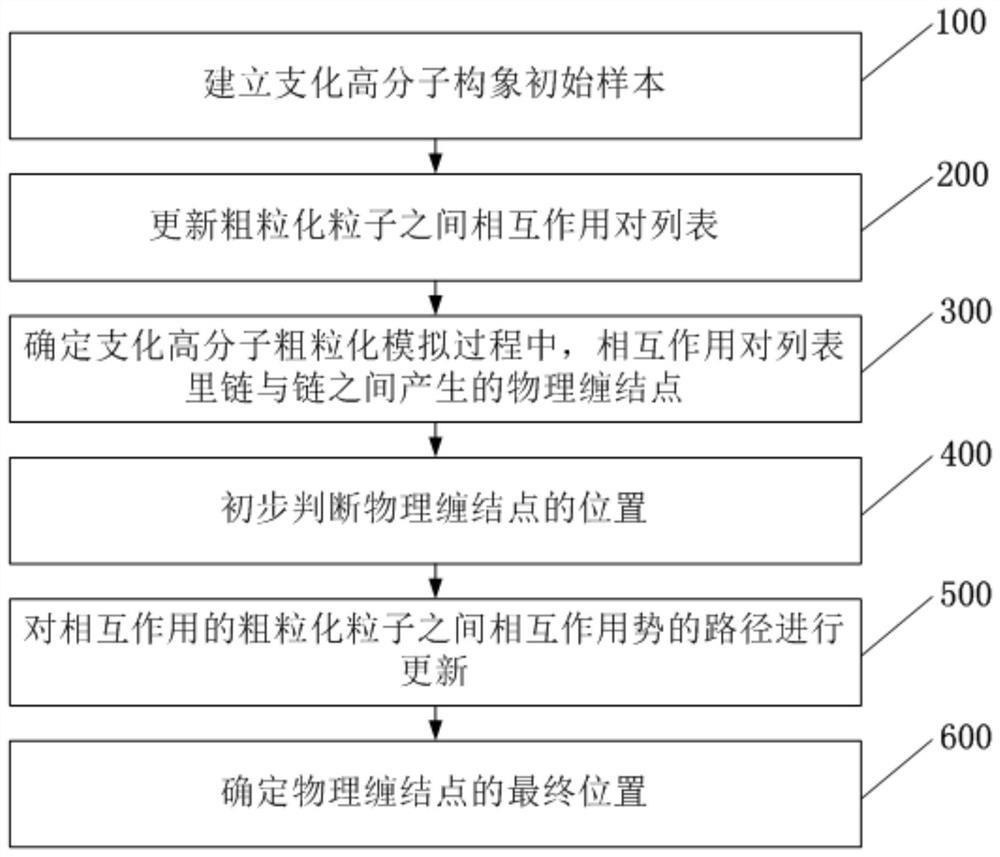
[0054] Such as figure 1 As shown, a branched polymer entanglement processing method provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0055] Step 100, establishing an initial sample of the branched polymer conformation.
[0056]In this step, the initial sample is based on Brownian dynamics, and the coarse-grained particles make the system reach an equilibrium state through the interaction of forces within a long period of time in each step. The initial sample is, for example, a three-arm symmetric star-branched polyethylene molecule, which can also be used in the coarse-grained simulation of branched polymer systems with other topological structures, for example, by changing the molecular weight of one of the side arms of the three-arm star polymer , the polymer topology gradually transitions from symmetric star to asymmetric star.
[0057] Step 200, updating the list of interaction pairs between coarse-grained particles.
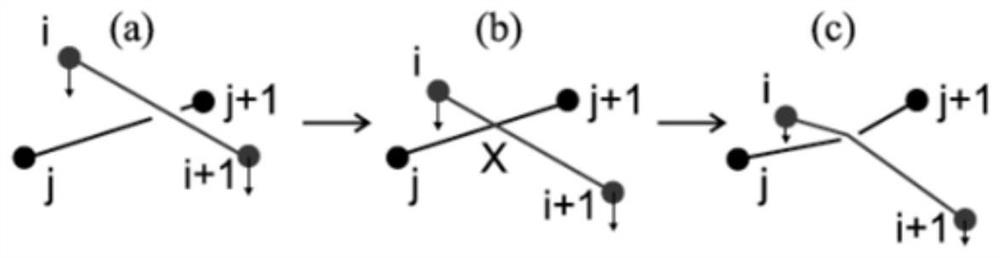
[0058] Step 300, determining the phys...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Such as image 3 As shown, a branched polymer coarse-grained simulation method provided in an embodiment of the present invention includes: the branched polymer entanglement processing method provided in any embodiment of the present invention, after step 600, further includes:
[0081] Step 700, calculate the average force field and entanglement force, and use the first-order Langevin equation to describe and update the position of the sample; each step completes coordinate update and boundary condition inspection, and finally completes the loop output.
[0082] Among them, the cyclic output includes: the coordinates of each coarse-grained particle, the position of the entanglement point and the labels of the intertwined coarse-grained particles, and the force and velocity of each coarse-grained particle. After completing the cycle output, record the simulated sample conformation and force.
[0083] Step 800, using the information obtained from the loop output to anal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com