Bolt connection structure of wind turbine generator, blade root structure, wind turbine blade, and wind turbine generator
A technology for wind turbines and connection structures, which is applied to the bolt connection structure of wind turbines, blade root structure, wind power blades and units, can solve the problems of easy fatigue fracture of blade bolts, difficult design life requirements, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
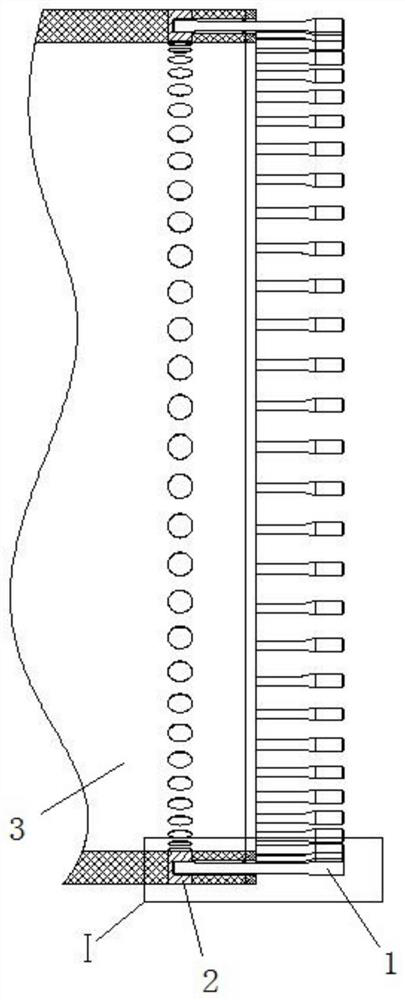
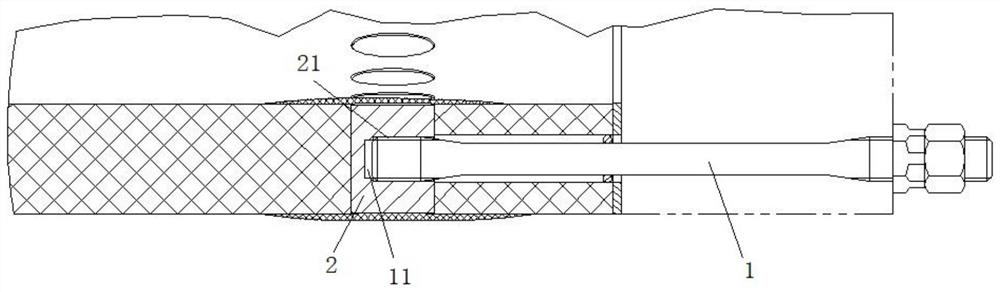
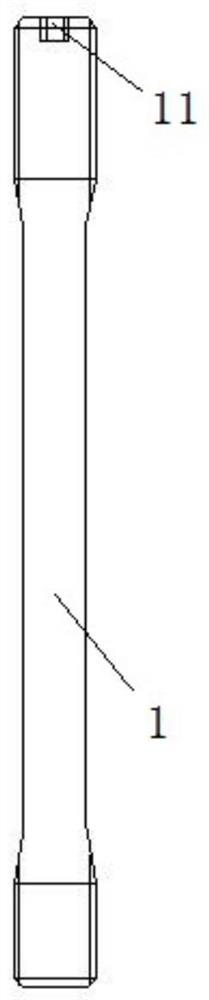
[0037] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, a bolted connection structure of a wind turbine includes a first bolt 1 and a second bolt 2 matched with the first bolt 1. One end of the first bolt 1 is provided with a male thread 11. On the second bolt 2 A female thread 21 that cooperates with the male thread 11 is provided, and the root fillet radius of the male thread 11 is twice or more than that of other bolts with the same bolt diameter.
[0038] The fillet radius of the bottom of the male thread 11 is twice or more than that of other bolts with the same diameter, which can effectively reduce the stress concentration at the bottom of the thread, thereby significantly improving the fatigue resistance. The range of fatigue stress that the first bolt 1 can bear increases, and it can bear a large fatigue load that fluctuates periodically for a long time. Thereby improving the fatigue life of the bolt.
[0039] It is worth noting that the specific connection structure of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, as a further optimization of Embodiment 1, this embodiment includes all the technical features of Embodiment 1. In addition, this embodiment also includes the following technical features:
[0050] A wind turbine blade root structure includes the above-mentioned wind turbine bolt connection structure.
[0051] As a preferred technical solution, the second bolt 2 is arranged at the root of the blade of the wind turbine.
[0052] This is beneficial to the fixed installation of the blade root of the wind turbine, which is convenient for use.
[0053] A wind turbine blade of a wind turbine comprises the above-mentioned bolt connection structure of the wind turbine.
[0054] As a preferred technical solution, the second bolt 2 is arranged at the root of the blade of the wind turbine.
[0055] A wind turbine, comprising a bolt connection structure of the wind turbine.
[0056] As a preferred technical solution, the second bolt 2 is ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 5As shown, a bolted connection structure of a wind turbine, the first bolt 1 on the blade 3 adopts a larger thread bottom fillet, which can improve the stress concentration of the thread bottom. Only 0.125P (P is the pitch), taking a bolt with a nominal diameter of 36mm as an example, the root fillet radius of the ordinary threaded bolt is 0.5, while the radius of the top and bottom fillet of the first bolt 1 external thread can reach 1.5 mm, which is three times the fillet radius of the common thread bottom. If the fillet radius of the tooth bottom is large, the stress concentration at the thread part is small, so the stress at the first bolt 1 is small. At the same time, due to the increase of the fillet radius of the bottom of the tooth, the corresponding small diameter of the thread increases, and the load that the first bolt 1 can bear increases. Under the same load, the stress of the first bolt 1 is smaller, so that the first bolt 1 can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com