Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on electro-copper-based mofs sensitive membrane modified electrode and preparation method and detection method thereof
A technology of molecular imprinting and modified electrodes, which is applied in the field of electrochemical sensing, can solve the problems of shape, unclear crystal form, and unclear explanation of influence, etc., and achieve the effects of good conductivity, time saving and high stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1. a molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor of an electro-copper-based MOFs sensitive membrane modified electrode, comprising a working electrode, characterized in that, outside the working electrode, Cu-MOF sensitive membrane, chitosan membrane, cross-linking agent are successively connected The insulating layer with the target protein and the polypyrrole molecular imprinting layer, the polypyrrole molecular imprinting layer has imprinted holes of the target protein.
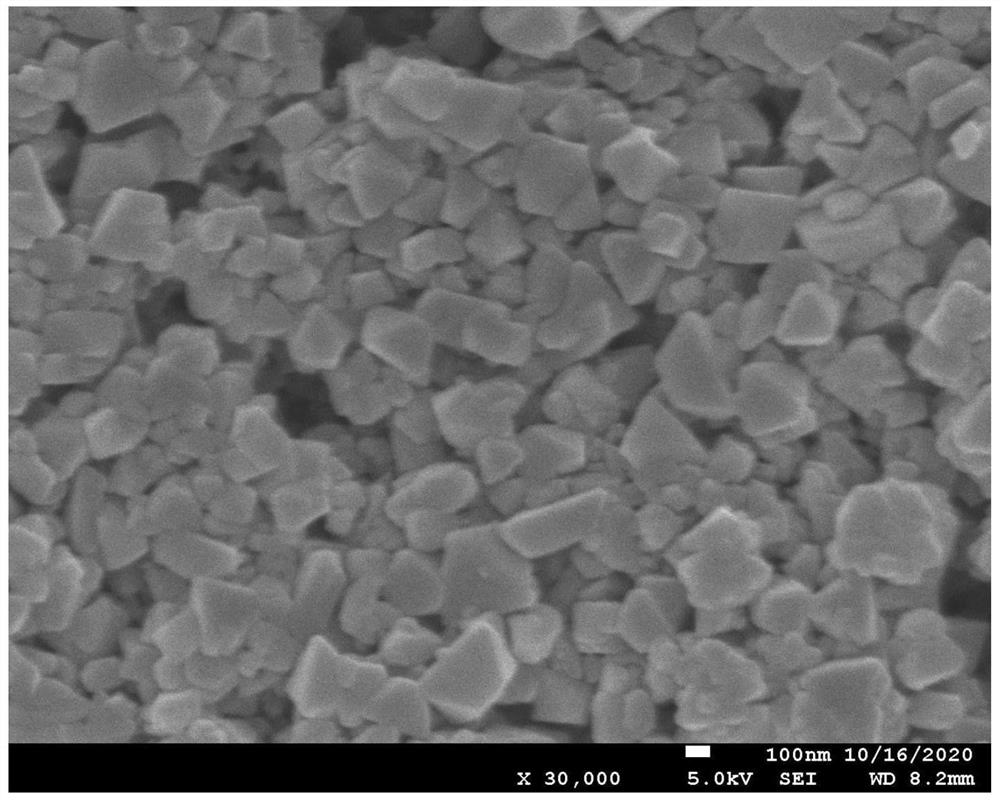
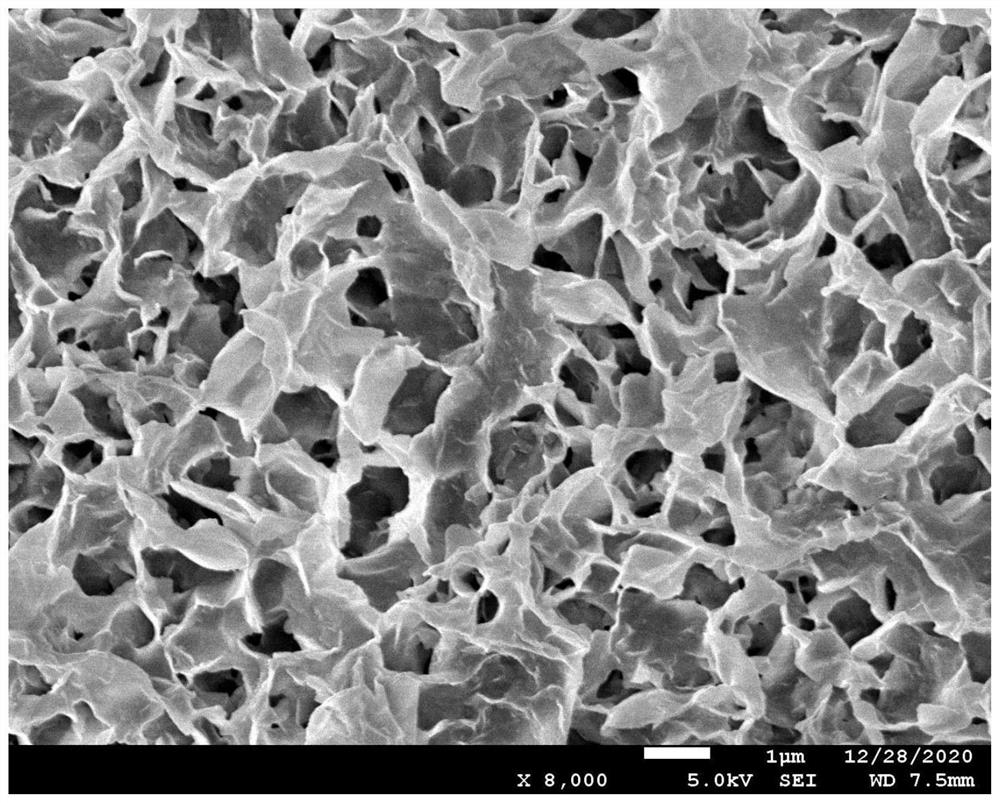
[0040] 2. The working electrode is a glassy carbon electrode, and the electro-copper-based MOF sensitive membrane is a modified electrode, which is a new type of highly ordered porous material with the advantages of large specific surface area, porosity and adjustable function. The surface film is formed by the accumulation of 100nm MOFs, and the surface is relatively dense. MOFs were directly electrodeposited on the conductive substrate through electrochemical reduction process, and the layered st...
Embodiment 2
[0047] 1) Weigh 10 mmol of copper nitrate trihydrate (Cu(NO) 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O), 15mmol 1,3,5- trimesic acid (H 3 BTC) and 10 mmol triethylamine hydrochloride (Et 3 NHCl) was dissolved in 50 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF);
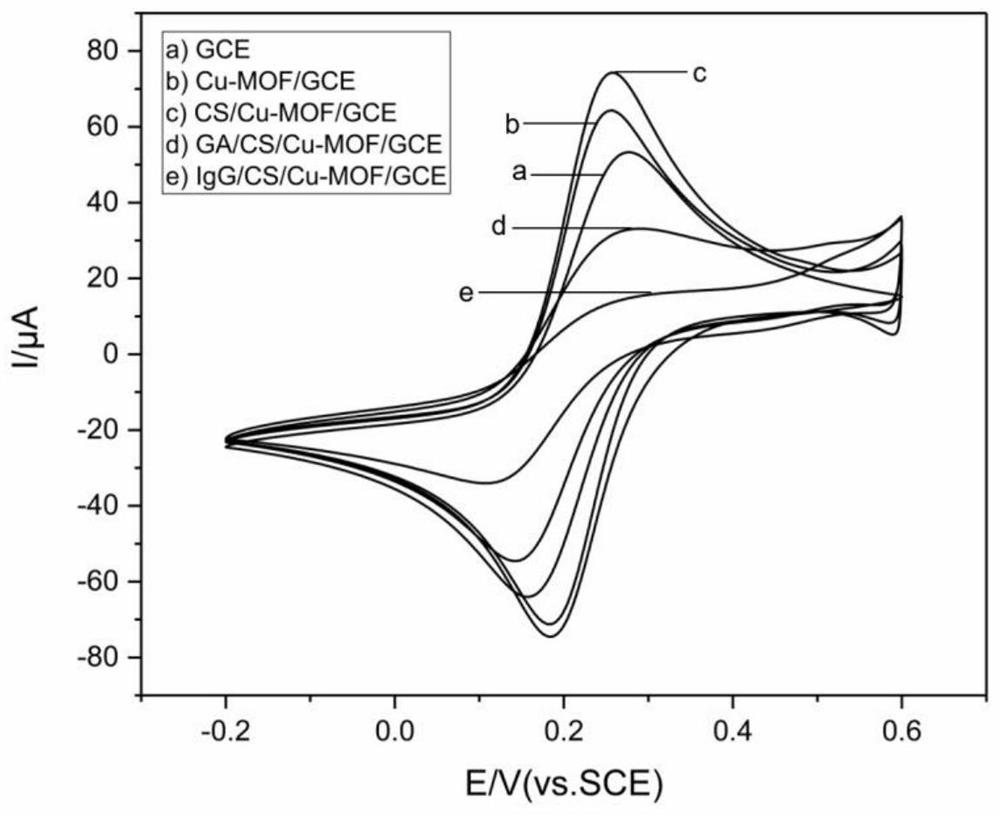
[0048] 2) Cu-MOF was deposited on the surface of glassy carbon electrode by electrodeposition method. The electrodeposition process was carried out in potentiostatic mode, with -1.3V electrodeposition for 5 minutes. After the end, the electrode was quickly taken out from the deposition bottom solution and dried for later use. The prepared electrode was named Cu-MOF / GCE.
[0049] The specific steps of preparing the human immunoglobulin G molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor in the present invention are as follows:
[0050] 3) Weigh 3 μL of 0.25 mg / mL (in 0.02 mol / L acetic acid) chitosan solution dropwise onto the electrode surface, dry at room temperature and name it CS / Cu-MOF / GCE.
[0051] 4) Drop 10 μL of 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution on the...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Detection based on the molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor prepared in Example 2:
[0058] 1) Immerse the modified electrode to 50mmol / l[K 3 Fe(CN) 6 ] in 1 mol / l KCl solution, each modified electrode was then scanned by electrochemical voltammetry and measured by AC impedance method, and the corresponding cyclic voltammetry (CV) and AC impedance (EIS) maps were obtained after scanning.
[0059] 2) The prepared electrochemical sensor was immersed in a standard solution of human immunoglobulin G containing 0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5 ng / mL, and measured by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) to dissolve Degrees are plotted against DPV response values.
[0060] 3) Lysozyme, Human Serum Albumin and Bovine Serum Albumin were selected as the structural analogs of human immunoglobulin to determine the selectivity of MIP / CS / Cu-MOF / GCE.
[0061] as attached Figure 4 As shown, the peak current value and IgG concentration showed a good linear relationship ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com