Nucleic acid aptamer with high affinity to okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin
A technology of okadaic acid and nucleic acid aptamers, which can be applied in the fields of climate change adaptation, biochemical equipment and methods, and resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., and can solve problems such as the lack of sequence reports of various marine toxin aptamers. achieve good affinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1O
[0026] The optimization of embodiment 1OA original aptamer OA-1234
[0027] The DNA sequence of the original OA adapter OA-1234 is (as shown in SEQ ID NO.3):
[0028] 5'-GGTCACCAACAACAGGGAGCGCTACGCGAAGGGTCAATGTGACGTCATGCGGATGTGTGG-3', a total of 60 bases.
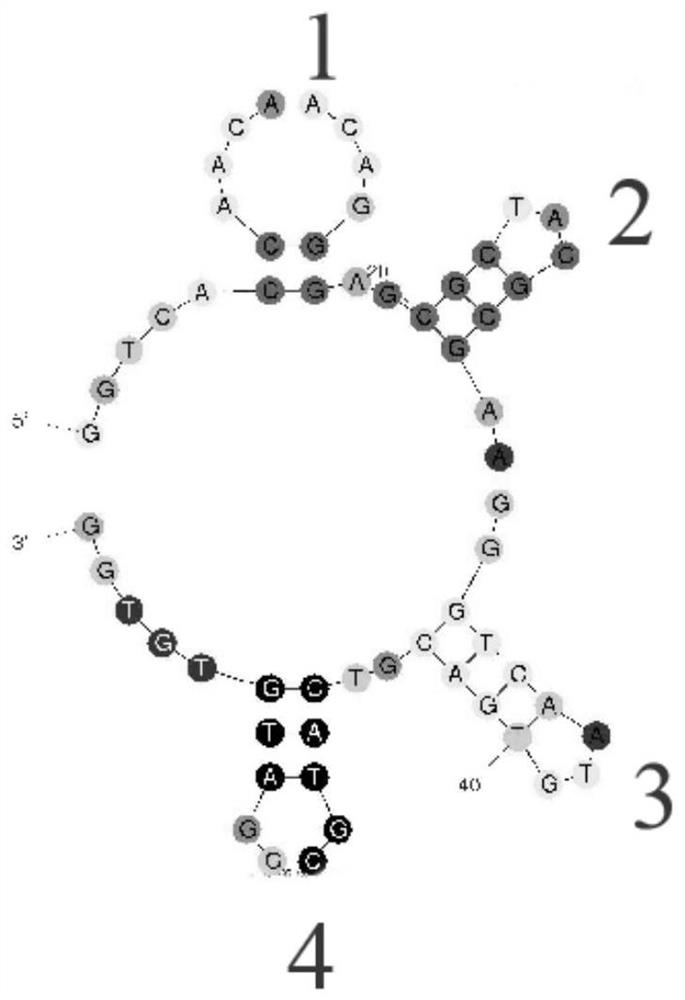
[0029] The secondary structure of the original aptamer OA-1234 was predicted by the online analysis tool the mfold web server, and it was found that the secondary structure contained 4 stem-loop structures, which were numbered sequentially from the 5' end, as shown in figure 1 shown.
[0030] The affinity constant (Kd) between the original OA aptamer OA-1234 and OA was 1.32 μM. In order to obtain a more optimized aptamer, the sequence of the aptamer was truncated and split.
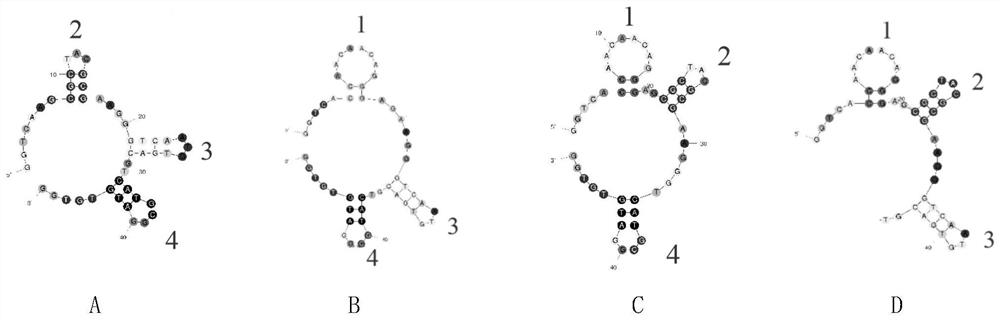
[0031] The stem-loop structure plays an important role in the combination of the aptamer and the target. According to the simulation of the secondary structure of the aptamer, one stem-loop was removed in turn, and the aptamers after removing the ste...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Aptamer DSP-134, DSP-1,34 specificity experiment
[0037] In order to verify the specificity of the modified aptamers DSP-134 and DSP-1,34, specificity experiments were performed with other toxin analogs that are easily enriched in shellfish.
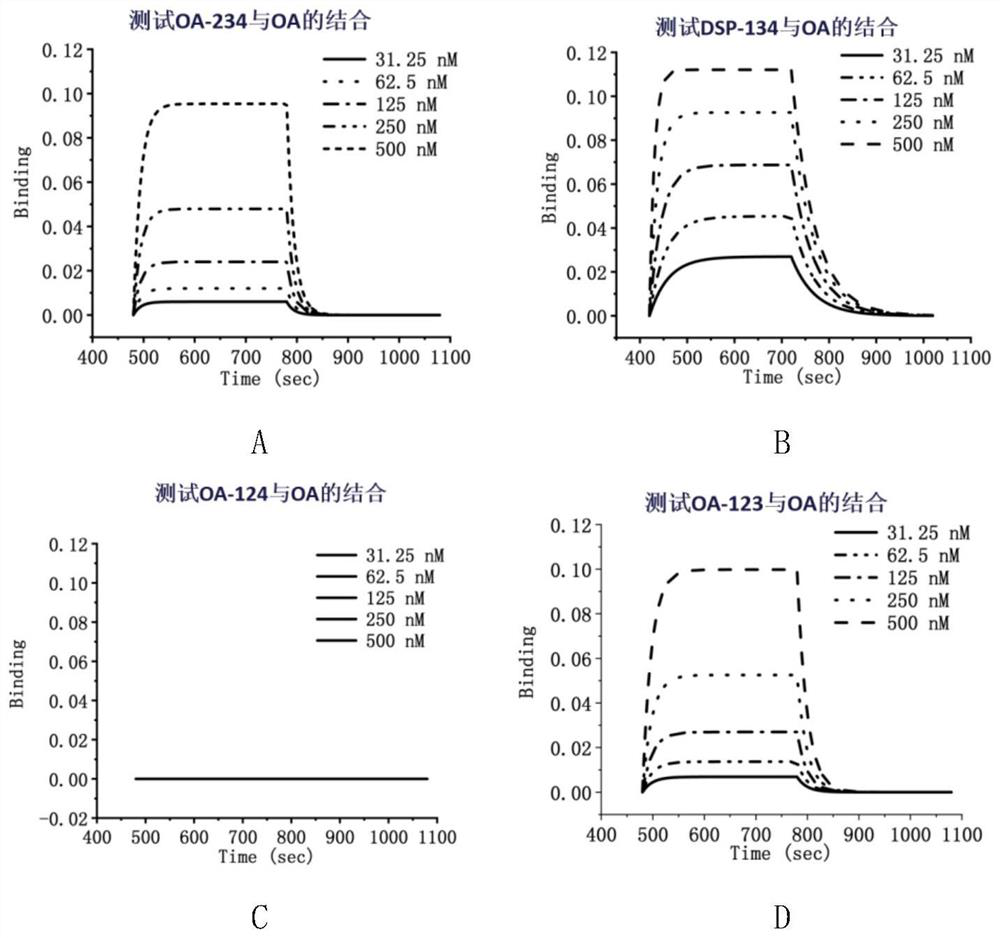
[0038] The modified aptamers DSP-134 and DSP-1,34 were tested by biomembrane interference molecular interaction instrument for STX, neo-STX, and GTX respectively, and the results showed that none of them could produce specific binding. The results are as follows: Figure 4 , Image 6 shown.
[0039] The aptamers DSP-134 and DSP-1,34 were tested by biomembrane interference molecular interaction instrument for DTX and OA respectively. Good affinity.
[0040] The specific information of DSP-134 and DSP-1,34 in this example is shown in Table 2.
[0041] Table 2 DSP-134 and DSP-1,34 specificity information
[0042] name target k DSP-134 STX - DSP-134 neo-STX - DSP-134 GTX - DSP...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com