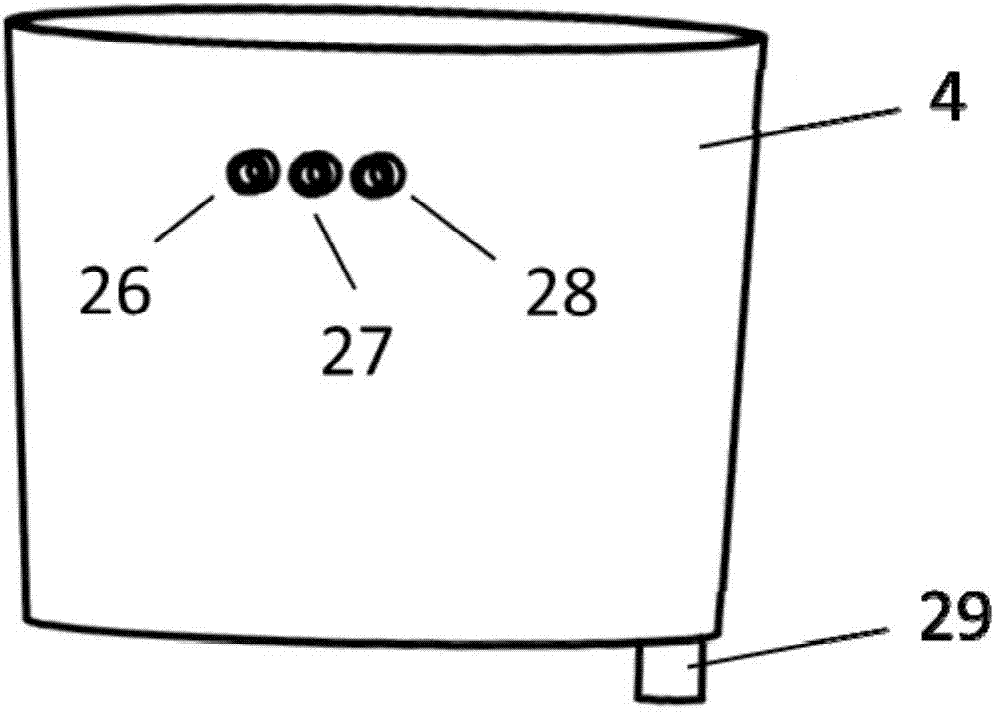
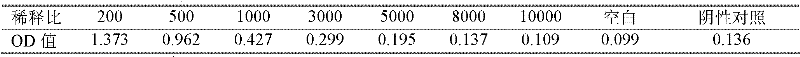Patents
Literature
51 results about "Paralytic shellfish toxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Saxitoxin (STX) is a potent neurotoxin and the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin, usually by consumption of shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms, is responsible for the human illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).
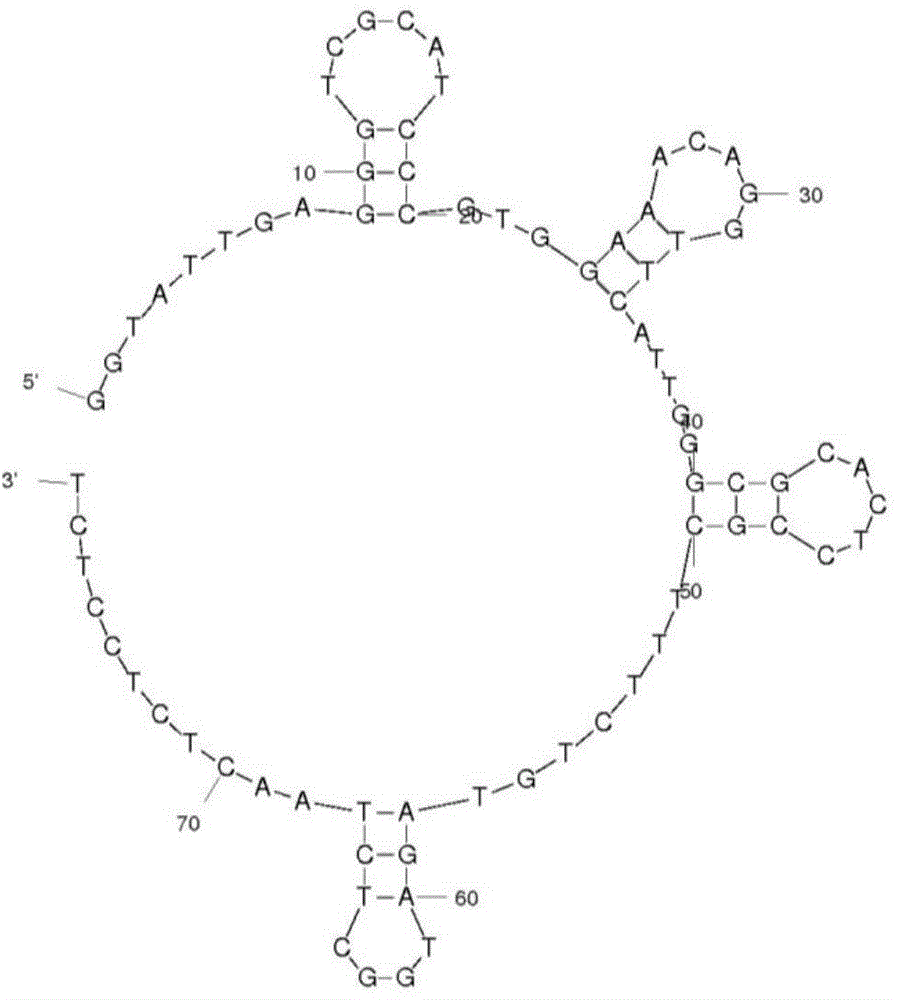
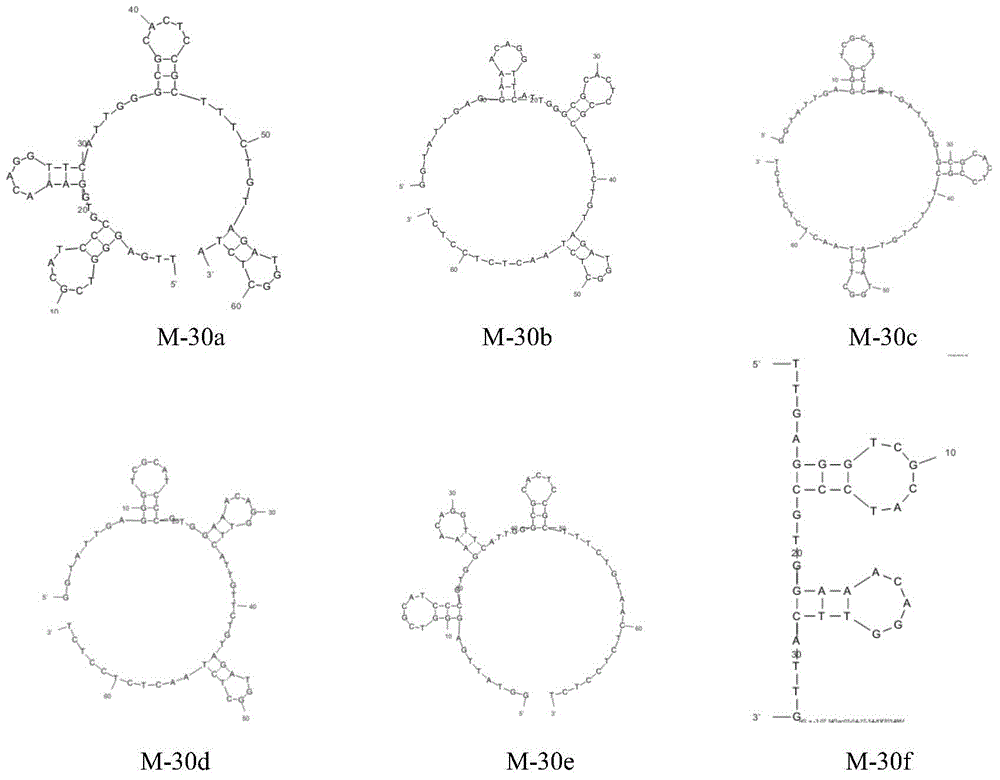
High affinity adapter body capable of specifically binding with saxitoxin acetate and application thereof
ActiveCN104894135AGreat potentialAntagonistic inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsSingle strand dnaBiology
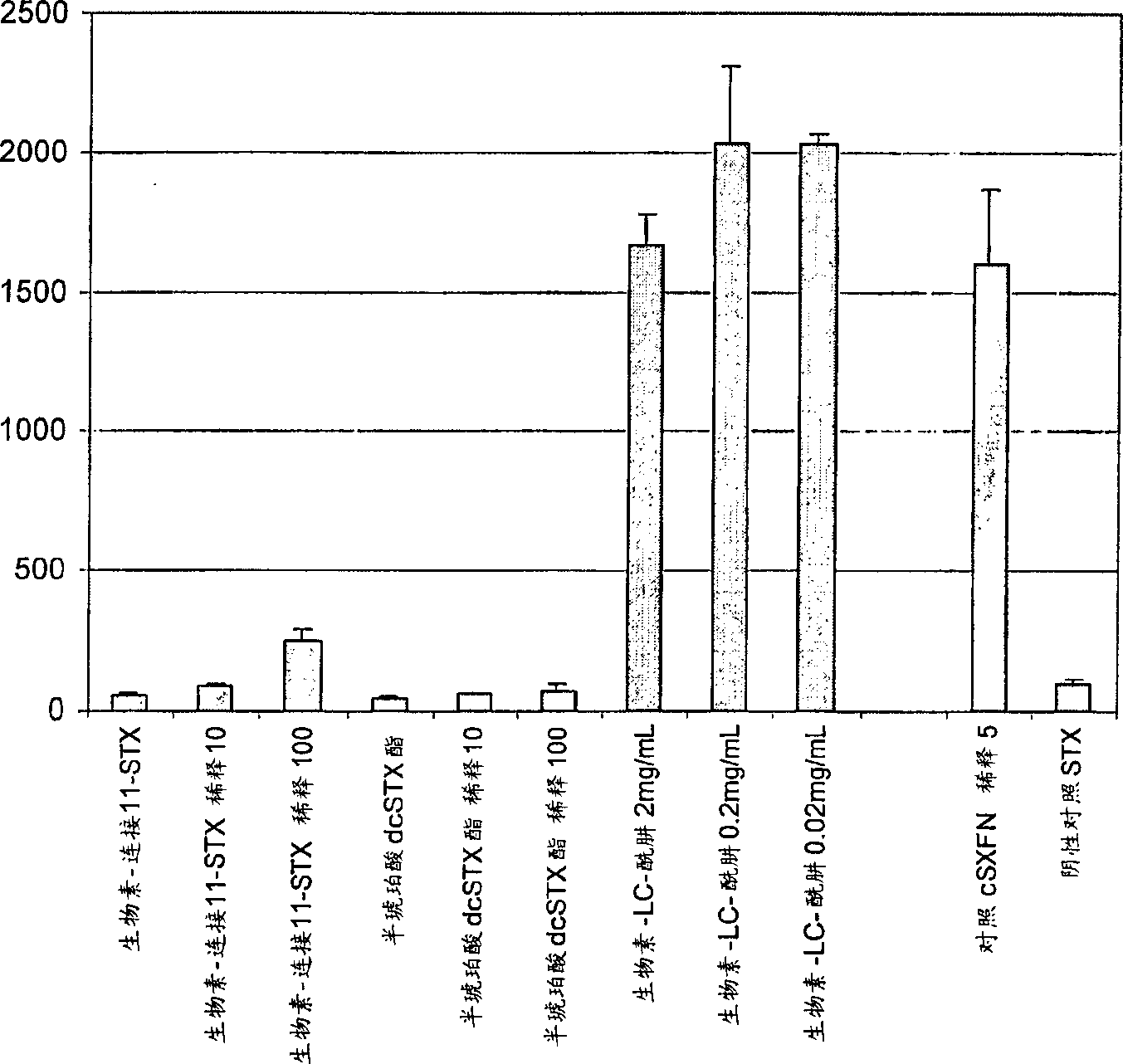
The invention relates to biological technical field, and provides a high affinity adapter body capable of specifically binding with saxitoxin acetate, and the sequence of single-stranded DNA adapter body as SEQ ID NO: 2. By mutation and truncation of an in vitro screened adapter body, a high affinity single-stranded oligonucleotide adapter body capable of specifically identifying the saxitoxin acetate can be obtained. The adapter body has a broad application prospect, and can be used for separation and enrichment of trace concentrations of STX (saxitoxin) in a sample, rapid detection of saxitoxin, and preparation of a drug for neutralization of saxitoxin sodium ion channel inhibition effect, and removal of toxins in water.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
High performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry detecting method of 16 fat soluble saxitoxins in shellfish meet
InactiveCN102928528AThe pre-processing process is simpleEasy to operateComponent separationOrganic solventQuantitative determination
The invention discloses a high performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry detecting method of 16 fat soluble saxitoxins in shellfish meet. The detecting method comprises the following steps of: processing a sample, purifying, testing the condition, qualitatively testing and quantitatively testing. According to the detecting method, methanol is adopted for extraction and a solid phase extraction column is adopted for purification so as to carry out the synchronous detection on the 16 fat soluble saxitoxins in the shellfish meet. The method is simple and convenient to operate, good in a purification effect, high in overall recycling rate and strong in reconstruction capability, and meanwhile an organic solvent and the processing time are saved, and the pretreatment process of the sample is simplified.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Immune colloidal gold test strip for rapidly detecting paralytic shellfish poison and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a detection device for detecting red tide virus. An immune colloidal gold test strip for rapidly detecting paralytic shellfish poison disclosed herein comprises a sample pad, a gold jed pad, a Sartorius NC film, an absorbent pad and a PVC backing, wherein, the sample pad, the gold jed pad, the Sartorius NC film, and the absorbent pad are attached to the PVC backing orderly, the gold jed pad is coated with a colloidal gold-labeled paralytic shellfish poison monoclonal antibody, and the Sartorius NC film is respectively coated with a detection line consisting of Saxitoxin-bovine serum albumin conjugate and a quality control line consisting of goat-anti-mouse antibodies. The test strip has the advantages of strong specificity, high detection sensitivity, rapid detection, simple pre-treatment, no need of any device, convenience in carrying, low cost of the detection, simple operation, no need of professional personnel to operate, convenient storage, good stability, and high accuracy and high precision of the detection result, and the test strip can be stored for at least 6 months at room temperature.
Owner:NATIONAL MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENTRE
Set of aptamers specifically recognizing three marine toxins
ActiveCN107541516ALow costShorten the production cycleDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationStructural homologySingle strand
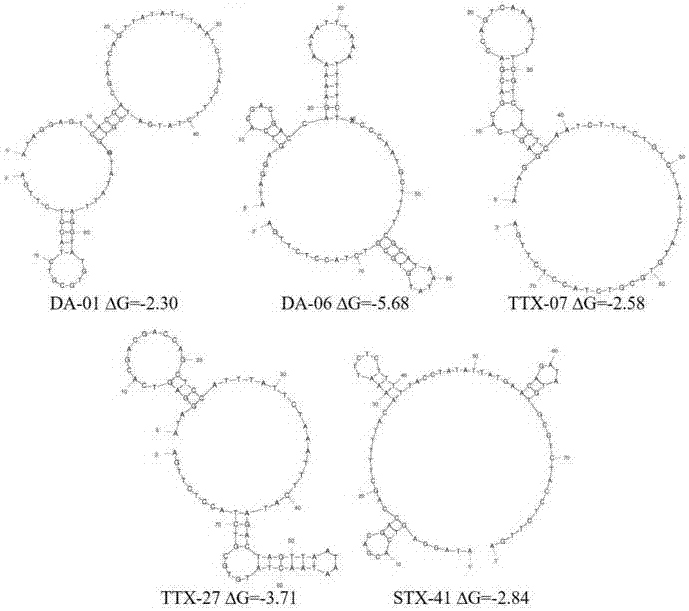
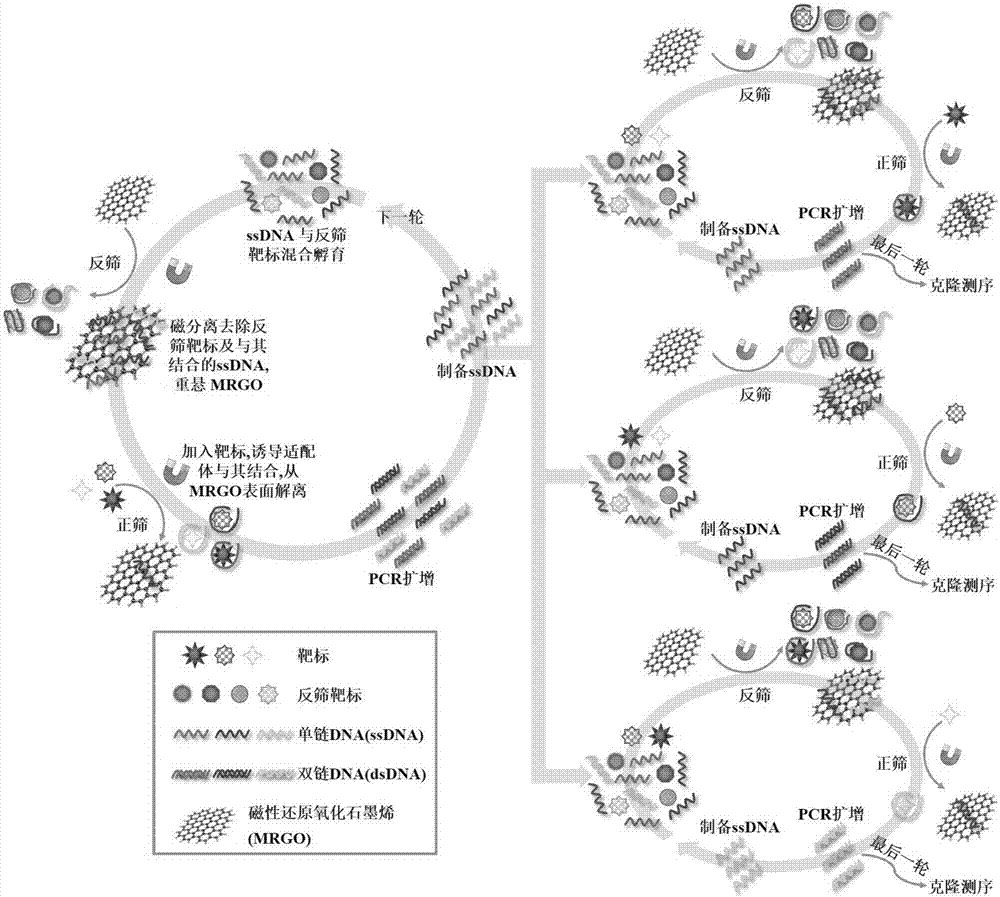
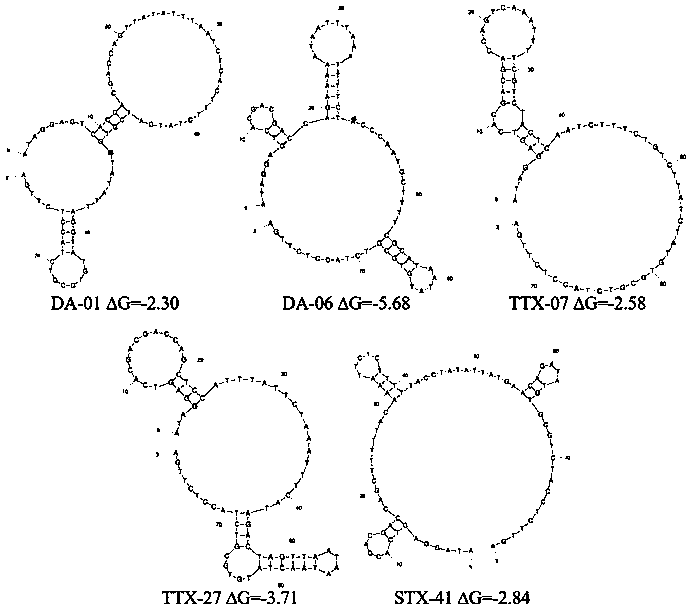
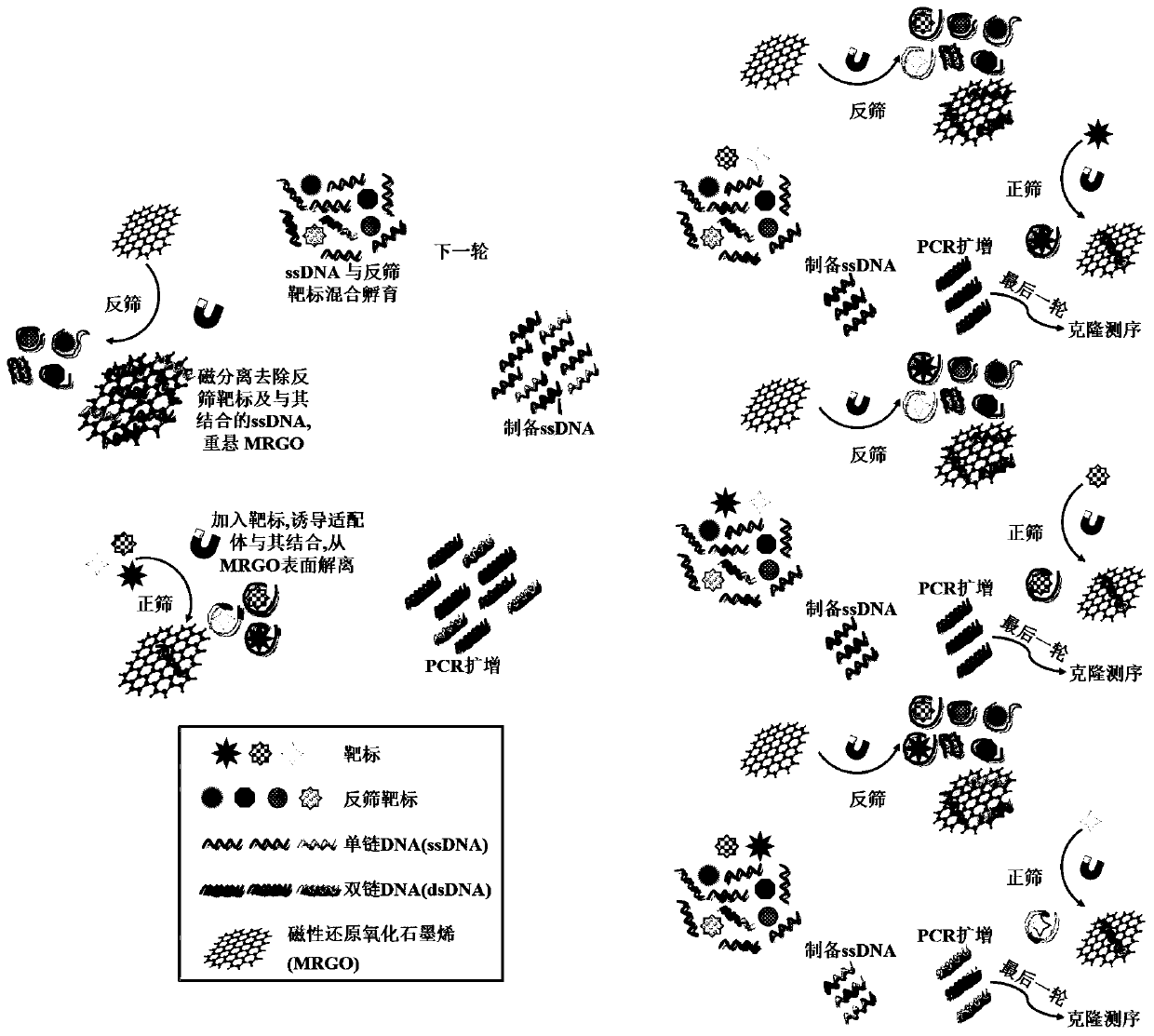
The invention provides a set of single stranded DNA (ssDNA) aptamers DA-01 and TTX-27 which can simultaneously recognize domoic acid (DA) and tetrodotoxin (TTX), including one ssDNA aptamer DA-06 which specifically recognizes DA, one ssDNA aptamer TTX-07 which can specifically recognize TTX, and one ssDNA aptamer STX-41 which can specifically recognize saxitoxin (STX). According to the invention,magnetic reduced graphene oxide (MRGO) is adopted to assist in separated systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX), properties of MRGO of being capable of adsorbing free ssDNA,but not adsorbing ssDNA combined with target molecules are utilized, and magnetic separation enrichment characteristics of MRGO are further used to separate ssDNA with affinity and without affinity to target toxins; primary structure homology and secondary structure similarity on obtained ssDNA are analyzed after 16 repeated rounds of incubation, separation, amplification and in-vitro screening for single-strand preparation, then the affinity and the specificity are measured, and finally one set of the aptamers with high affinity and specificity is obtained. The set of the aptamers has broadapplication prospects in the aspects of analysis, detection, separation, enrichment, removal and purification for DA, TTX and STX in aquatic products.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for removing saralytic saxitoxin
InactiveCN101367572AImprove adsorption efficiencyEasy to separateWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationMultistage water/sewage treatmentFiltrationParalytic shellfish toxin
The invention provides a removal method of paralytic shellfish poison, comprising the following steps: firstly, absorbent is distributed in embedding medium evenly; secondly, the embedding medium which contains the absorbent is solidified to form gel; thirdly, the solidified embedding medium which contains the absorbent is made into gel balls or blocks with uniform size; fourthly, the balls or the blocks are put in the solution which contains the paralytic shellfish poison, and the solution is then stirred for 5-30 minutes; and lastly, the gel is removed by filtration or centrifuge method to get the water which has removed the paralytic shellfish poison. The invention has the advantages that the absorbent which is treated by embedding can absorb the paralytic shellfish poison in the water. The absorption efficiency is higher than both pure absorbent and embedding medium. The embedded absorbent is comparatively big grain which is convenient to be separated from the system. The method can be used to remove the paralytic shellfish poison in the water, can be used for the enrichment and detection of positions, the purification of shellfish and so on, and can be used for the purification of other positions and pollutants in the environment after being improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Saxitoxin artificial antigen, anti-saxitoxin antibody prepared by the saxitoxin artificial antigen, and their preparation methods and application
The invention relates to a saxitoxin artificial antigen, an anti-saxitoxin antibody prepared by the saxitoxin artificial antigen, and their preparation methods and application. Through carbodiimide method, amino groups in saxitoxin (STX) are connected with carboxyl groups in ovalbumin (OVA) as a carrier protein. A high purity saxitoxin immunization antigen STX-OVA is obtained through dialysis utilizing a gradient method. The prepared high purity saxitoxin artificial immunization antigen STX-OVA is utilized for preparation of a polyclonal antibody and the polyclonal antibody is utilized for preparation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit utilized for detecting saxitoxin. In the invention, saxitoxin artificial antigens of STX-OVA and STX-BSA are synthesized successfully to immunize BALB / c mice and then a polyclonal antibody with high titer and strong singularity is obtained. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit prepared by an established enzyme-linked immunoassay can be utilized for the rapid detection of saxitoxin.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
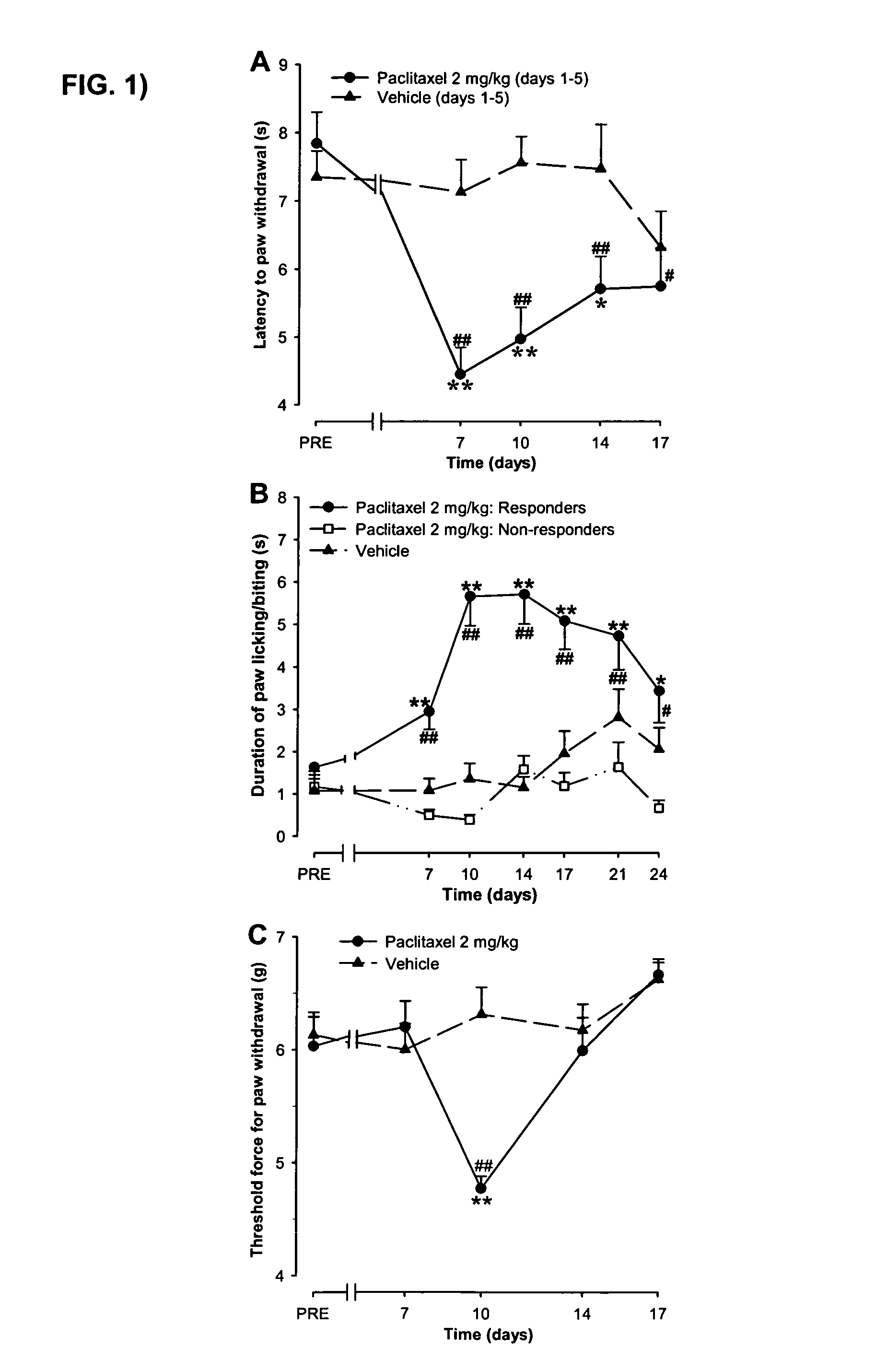
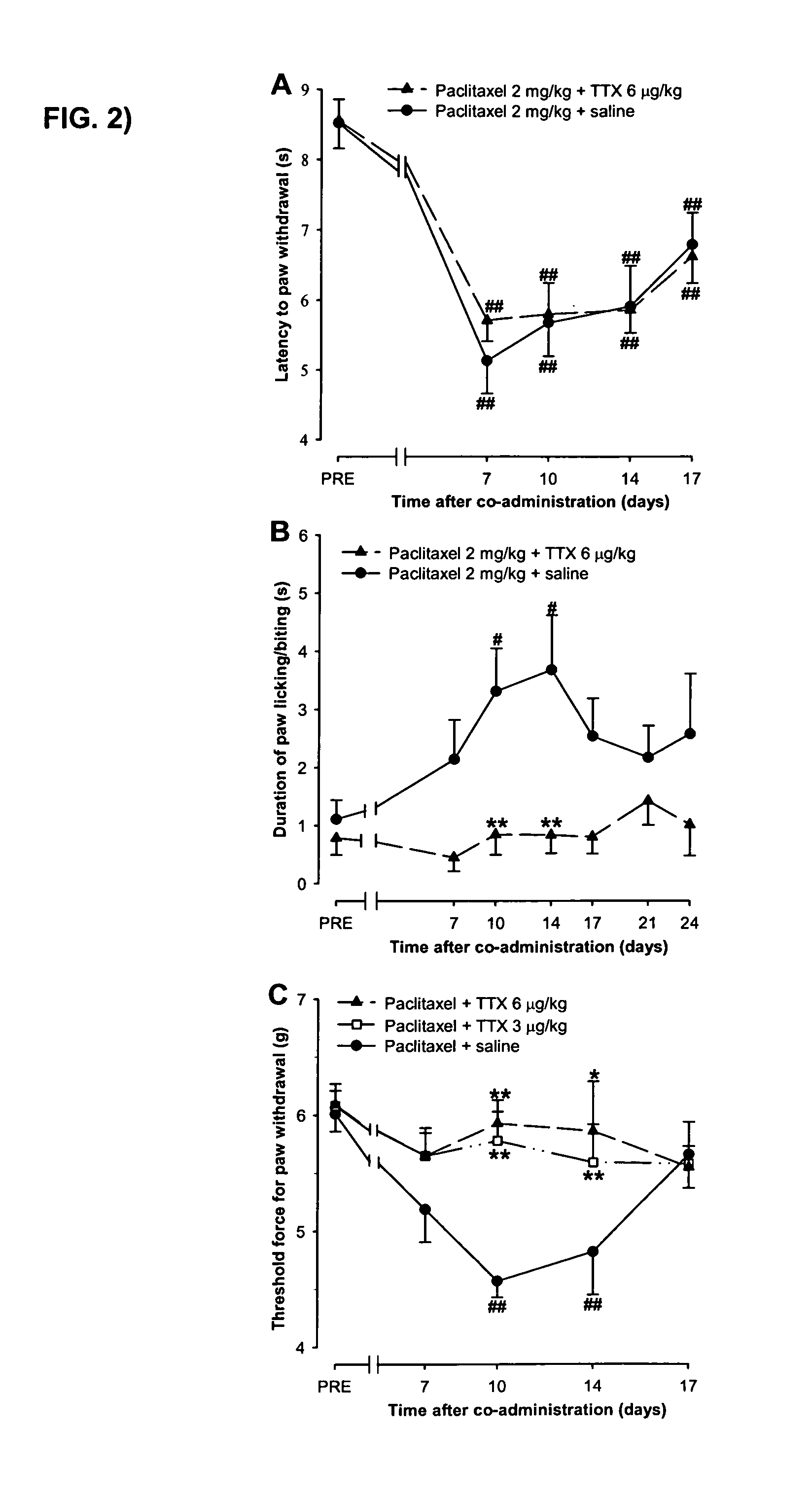
Tetrodotoxin And Its Derivatives For The Treatment Of Central-Nervously Derived Neuropathic Pain
The present invention refers to the use of a sodium channel blocker such as tetrodotoxin or saxitoxin, their analogues and derivatives as well as their physiologically acceptable salts, in medicinal products for human therapeutics for the treatment of central-nervously derived neuropathic pain.
Owner:WEX PHARMA
Microfluidic chip for rapid detection of saxitoxin and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101839913APreparing sample for investigationBiological testingControl layerDimethyl siloxane
The invention belongs to the technical field of biologic analysis and detection, and in particular relates to a microfluidic chip for rapid detection of saxitoxin and a method for preparing the same. The chip is made of the material such as optically transparent dimethyl silicone polymer by the molding method and mainly comprises a sample reaction micro-channel layer, a valve control layer and a substrate layer. The chip comprises a sample enrichment and immunity analysis module and a signal acquisition module, wherein each module consists of a plurality of paralleled immunity chromatographiccolumn micro analysis chambers of nanoliter volume; and saxitoxin antibody protein or antigen is fixed in each analysis chamber so as to realize rapid on-site detection of the saxitoxin in the sample. The chip can perform automatic signal acquisition, remote transmission and signal analysis due to the characteristics of high speed, high efficiency, convenient carrying, low cost and easy automation control and is suitable for on-site rapid detection of the saxitoxin in the water environment and remote detection in a large range.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
The detection and identification of saxiphilins using saxitoxin-biotin conjugates
The present invention relates to a method for capturing saxiphilin so as to detect, characterize, separate and / or purify said saxiphilin or its ligand, the method comprising: (1) providing a PST conjugate , the PST conjugate includes a PST part, which is directly or indirectly bound to the biotin part through a linker and through a non-binding site of saxitoxin; (2) exposing the PST conjugate for a sample assumed to contain said saxiphilin, to generate a reaction mixture, and expose to (strep)avidin; and (3) allow binding to saxiphilin via the PST moiety, and via This biotin moiety binds to (streptavidin) to form the captured PST complex.
Owner:CLEVELAND BIOSENSORS PYT LTD
Preparation method of saxitoxin molecularly-imprinted nano fluorescent material and application
ActiveCN106832296AReduce usageSolve the problem of high consumption of expensive templatesOther chemical processesFluorescence/phosphorescenceCross-linkMethacrylate
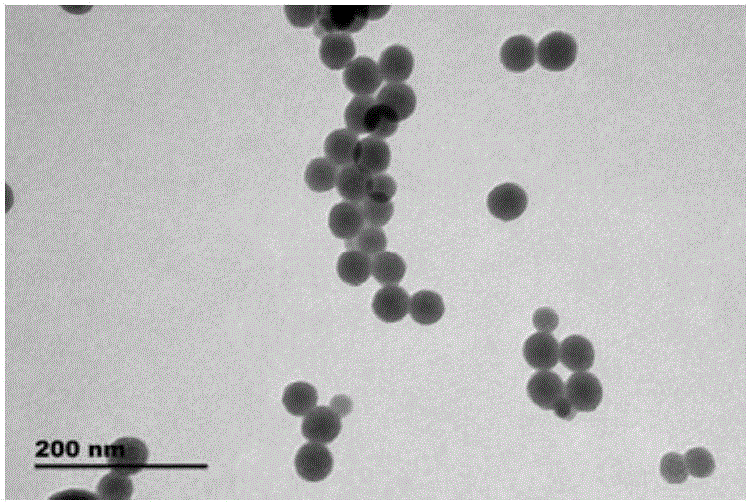
The invention discloses a preparation method of a saxitoxin molecularly-imprinted nano fluorescent material and an application. The preparation method comprises the steps of taking saxitoxin as a template molecule and adding a quantum dot fluorescent nanomaterial; and initializing polymerization in the presence of a cross-linking agent tetraethylortho silicate and a functional monomer 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane or 3-(tri(trimethsilyl)silyl)propyl methacrylate, and then removing the template molecule in the obtained polymer by adopting an ultrasonic-assisted extraction method to obtain the saxitoxin molecularly-imprinted nano fluorescent material capable of specifically identifying the saxitoxin. The saxitoxin molecularly-imprinted nano fluorescent material can be used for detecting the content of the saxitoxin in a shell sample, and has the advantages of uniform particle sizes, good selectivity and excellent fluorescent stability; and fast and high-sensitivity detection of the saxitoxin in the shell sample can be achieved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Use of sodium channel blockers for the treatment of neuropathic pain developing as a consequence of chemotherapy
ActiveUS20100215771A1Improve stabilityAvoid separationHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideChemotherapy inducedNeuropathic pain
The present invention refers to the use of sodium channel blockers such as tetrodotoxin or saxitoxin, its analogues / derivatives as well as their acceptable salts, for the production of a medicament for the treatment of neuropathic pain resulting from chemotherapy.
Owner:WEX MEDICAL LTD
Use of sodium channel blockers for the treatment of neuropathic pain developing as a consequence of chemotherapy
The present invention refers to the use of sodium channel blockers such as tetrodotoxin or saxitoxin, its analogues / derivatives as well as their acceptable salts, for the production of a medicament for the treatment of neuropathic pain resulting from chemotherapy.
Owner:WEX MEDICAL LTD
Methods and compositions for studying, imaging, and treating pain
InactiveCN102459273AEfficiently provideCompounds screening/testingCosmetic preparationsDiseaseWrinkle skin
Saxitoxin analogue compounds, compositions, pharmaceutical compositions, methods of synthesis of saxitoxin analogues, methods of imaging, methods of treatment, including methods of treating pain, are provided. Saxitoxin (STX), gonyautoxin (GTX), and zetekitoxin, and variant STX compounds bind to sodium channels and are effective to reduce or block flow of sodium ions through such channels. Such channel block affects nerve and muscle action, and may be effective to reduce or block pain sensations, relax muscles, reduce muscle spasm, and reduce wrinkles. STX analogue binding to sodium channels may also be useful to locate, image, or mark sodium channels, and so be useful in studying sodium channels and sodium channel disorders, and in the diagnosis and treatment of patients suffering from sodium channel disorders. In embodiments, the variant STX compounds include conjugates having increased serum half-life as compared to STX when administered to a subject. In embodiments, the present disclosure provides a method for alleviating pain in a subject in need of treatment, the method comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of a saxitoxin analogue compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, isomer, tautomer or prodrug thereof, whereby pain in said subject is alleviated.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for extracting paralytic shellfish toxins from shell raw materials
InactiveCN104876939AHigh extraction rateReduced loss of biological activityOrganic chemistryRetention timeImpurity
The invention discloses a method for extracting paralytic shellfish toxins from shell tissues. The method comprises the following steps: 1, mixing shell raw materials with acetic acid until the pH value of the obtained mixture is 2-4, carrying out ultrasonic crushing, heating the crushed mixture in boiling water for 5-10min, cooling, filtering, and collecting the obtained filtrate; 2, carrying out reduced pressure concentration on the filtrate, freezing, centrifuging, taking the obtained supernatant, extracting the supernatant by using trichloromethane, uniformly mixing the obtained upper layer extract liquid with ethanol, stirring at room temperature for 20-24h, carrying out secondary centrifuge, collecting the obtained new supernatant, carrying out reduced pressure concentration, drying, dissolving the obtained dried material in acidic methanol, filtering, collecting the obtained new filtrate, drying, dissolving the dried new filtrate in an aqueous acetic acid solution with the pH value of 2-4, adding the obtained sample to a gel column, carrying out column chromatography, and collecting the fraction with the retention time of 160-250min. The method maximally improves the extraction rate of the paralytic shellfish toxins, can effectively remove fats, proteins, carbohydrates and other impurities in the tissues, and maximally reduces the bioactive loss of the toxins.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Automatic pretreatment device for processing paralytic shellfish toxin samples
InactiveCN104777018AFully automatedNo special requirementsPreparing sample for investigationPulp and paper industryFilter paper
The invention discloses an automatic pretreatment device for processing paralytic shellfish toxic samples. The device comprises a controller, a motor with a large torque force, a cutter head, a grinding cavity, a first suction connecting pipe, a filter upper cover, a filter paper bag, a filter paper sheet, a filter lower cover, a second suction connecting pipe, a suction filter, and a collecting bottle. The cutter is arranged on the large torque force motor and forms an enclosed space with the grinding cavity. The grinding cavity is connected to the filter upper cover through the first suction connecting pipe. The filter upper cover and the filer lower cover are connected to form an enclosed filter. In the filter, the filter paper bag and the filter paper sheet are arranged in sequence from top to bottom, the filter lower cover is connected to the top end of the second suction connecting pipe in the filter, and the controller is individually connected to the grinding cavity, the filter, and the suction filter though air pipes or liquid pipes. The provided device can automatically process shellfish meat samples before experiments for detecting the paralytic shellfish toxin, the pretreatment operation is simplified, and the pretreatment efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nucleic acid apt (aptamer) biosensor for rapidly detecting STX (saxitoxin) and preparation method of nucleic acid apt biosensor
ActiveCN109593764AEasy to operateUltra sensitive implementationColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAptamerColorimetric analysis
The invention discloses a nucleic acid apt (aptamer) biosensor for rapidly detecting STX (saxitoxin) and a preparation method of the nucleic acid apt biosensor. The apt sequence of STX is 5'SH-(CH2)6-CCGTGGAAACATGTTCATTGGGCGCACTCCGCTTTCTGT-3'. According to the biosensor, STX detecting sensitivity is improved, and STX at a minimum of 0.05 ng / mL can be detected. The advantages of fastness and ultra-sensitivity of colorimetric analysis are closely combined with the characteristics of high affinity and high selectivity of the nucleic acid apt, the biosensor has the characteristics of being simpleto operate and portable of sensors, and the requirements of ultra-sensitivity, high specificity, rapid detection and on-site detection of STX in a seawater shellfish complex matrix can be met. Research results can provide technical support for research and development of rapid detection technology and equipment for shellfish toxins in seawater shellfish, and have great scientific research significance and market value.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV +1
Method for detecting paralytic shellfish poisoning
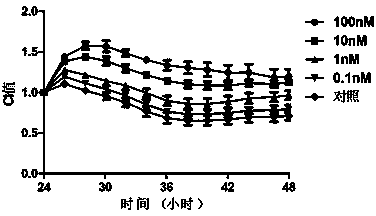
The invention discloses a method for detecting paralytic shellfish poisoning. The method is implemented on a mouse neuroma cell impedance sensor. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating neuro2a cells to sensor chip cell culture holes for culturing; respectively adding a to-be-detected solution into cell culture holes a solution containing ouabain and veratridine; and detecting a CI value of each cell culture hole after the to-be-detected solution is added, and judging the content of the paralytic shellfish poisoning in the to-be-detected solution according to change of the CI value. According to the method, cells are directly taken as detection carriers, the operation is simple, and the cost is low. According to the method, the detection limit of saxitoxin is low to 0.9ng / ml and has obvious progress compared with the detection limit (160ng / ml) of mouse bioassay in a current national standard detection method. In addition, the method is slightly influenced by interference effect of shellfish meat matrixes and reliable in data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Detection of saxitoxin-producing dinoflagellates
The current disclosure generally relates to the field of saxitoxins and the identification of microorganisms capable of producing them. In particular, the saxitoxin A (sxtA) gene comprising catalytic domain sequences saxitoxin A1 (sxtA1) and saxitoxin A4 (sxtA4) is identified in a number of dinoflagellate species. The disclosure relates to methods of detection of saxitoxin-producing dinoflagellates by amplification and detection of the sxtA gene (in particular by PCR) and kits and primers for use in the method are also disclosed. Saxitoxin-producing dinoflagellate genera detected by the method include Alexandrium, Pyrodinium or Gymnodinium.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD +1
Method to enhance production of paralytic shellfish toxins from dinoflagellate cultures
InactiveUS20090291484A1Slow growth rateControl is possibleFermentationChemical cell growth stimulationBiological bodySolid phase extraction
Owner:SELANDER ERIK +1
The invention also discloses application of three-dimensional fluorescence spectrometry in identification of paralytic shellfish toxin-producing microalgae
ActiveCN111912824AImprove the accuracy of discriminationReduce mistakesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescence spectrometryRed tide
The invention discloses an application of a three-dimensional fluorescence spectrometry in identification of paralytic shellfish toxin-producing microalgae. The method comprises the following steps: extracting three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum information of PSP-producing algae and PSP-non-producing algae growing under different environmental conditions, extracting characteristic peaks of experimental algae by using a Coif2 wavelet function, performing clustering analysis by using a system clustering method, removing abnormal spectrums, and screening standard spectrums to obtain a Coif2fluorescence characteristic standard spectrum library; when the discriminating function established according to the fluorescence characteristic standard spectrum library is used for discriminating the PSP-producing algae and the PSP-non-producing algae, the discriminating correct rates are respectively 77.3% and 84.5%, the correct rates are very high, and the purpose of quickly and accurately identifying the toxin-producing algae is basically achieved. The invention provides a research result of the application of the three-dimensional fluorescence spectrometry in identification of paralyticshellfish toxin-producing microalgae for the first time, and the three-dimensional fluorescence spectrometry can be applied to the aspects of red tide algae identification sensors or portable algae fluorescence identification instruments and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN LIGHTSUN TECH CO LTD +1
Paralytic shellfish toxin cell detection method based on alpha-enolase
ActiveCN105785002AEasy to handleLow detection limitBiological material analysisAlpha-enolaseFood safety
The invention provides a paralytic shellfish toxin cell detection method based on alpha-enolase.The detection method comprises the following steps: S1, sample treatment; S2, cell explosure and protein sample extraction; S3, detection, wherein an alpha-enolase ELISA test kit is used for detecting the content of alpha-enolase in the protein sample, standard curves are established, the content of alpha-enolase is calculated through the OD value, and then the content of paralytic shellfish toxin is obtained.The detection method belongs to the technical field of food safety testing.The cell detection method has the advantages that sample treatment is easy, limit of detection is low, repeatability is high, and cross reactions are avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Method for quickly screening and identifying various paralytic shellfish toxins in red tide algae
InactiveCN107102081ARapid identificationFast and accurate screening and identificationComponent separationSolventCrusher
The invention relates to a method for quickly screening and identifying various paralytic shellfish toxins in red tide algae. The method comprises the following steps: weighing a certain quantity of red tide algae samples, putting into a centrifugal tube, adding a certain quantity of extracting solvents, crushing by adopting a cell crusher or an algae grinding method, then extracting the various paralytic shellfish toxins and combining into an extracting solution; performing centrifugal separation to remove a precipitate, absorbing supernatant liquid, filtering through a micro-porous filtering membrane and injecting into a sample bottle for later use; performing separation analysis on the paralytic shellfish toxins in the red tide algae crude extracting liquid by adopting a high-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry; through comparing information related to the accurate molecular weight of the common paralytic shellfish toxins in the red tide algae, the quick identification on the various common paralytic shellfish toxins in the red tide algae is realized. The method provided by the invention can be used in a department of marine environmental management to quickly determine whether the paralytic shellfish toxins are contained in the red tide algae or not and is further used for judging the influence of the marine shellfish toxins on aquatic products to ensure the consumption safety of the aquatic products.
Owner:连云港市海洋环境监测预报中心
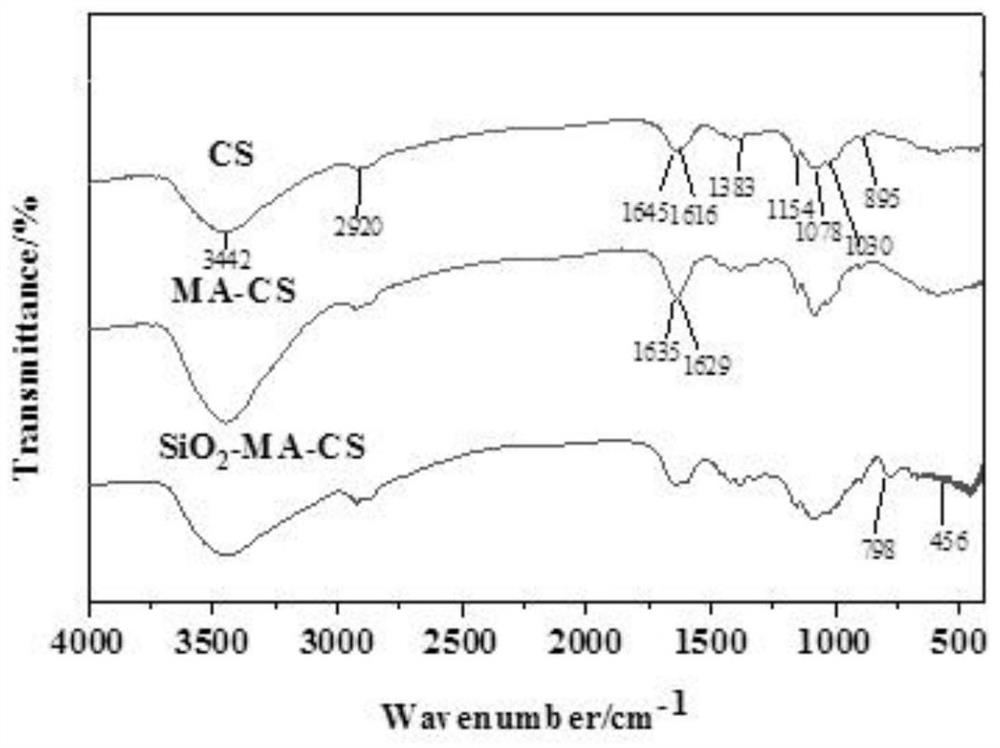
Malic acid-chitosan nanopore hydrogel microspheres as well as preparation method and application thereof
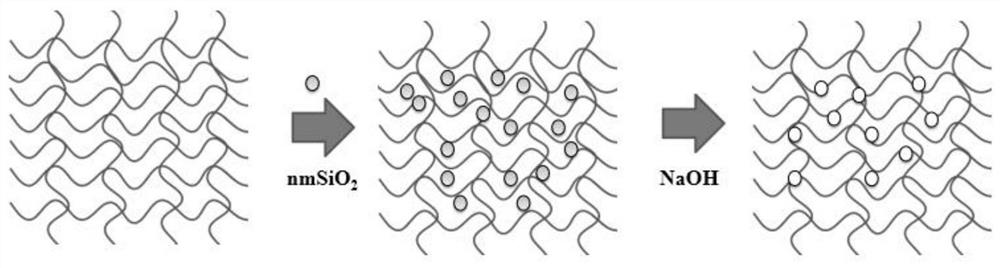
PendingCN112915974AGood detox effectEasy to prepareOther chemical processesSpecific water treatment objectivesChitosan malateFreeze-drying
The invention discloses malic acid-chitosan nanopore hydrogel microspheres as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of guaranteeing the safety of aquatic food and preparing paralytic shellfish toxin bio-adsorbents. The invention discloses a preparation method of malic acid-chitosan nanopore hydrogel microspheres. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: preparing malic acid and chitosan into hydrogel; preparing a malic acid-chitosan nano-pore hydrogel microsphere, adding nano-silica and glycerin into the prepared hydrogel, adding sodium hydroxide, completely dissolving the nano-silica under an alkaline condition to form uniformly distributed nano-pores, performing washing, performing freeze-drying, and performing grinding and sieving to obtain the malic acid-chitosan nano-pore hydrogel microsphere. The malic acid-chitosan nanopore hydrogel microspheres prepared by the invention can be used as an efficient adsorbent for adsorbing and removing paralytic saxitoxin in a water body. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, convenient to use and easy to store after being dried, and has great application significance on shellfish toxin pollution and improvement of product safety.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Modifier capable of reducing saxitox
InactiveCN105029514AMeet safety requirementsCause substitution effectFood preparationOrganic compound food ingredientsFlavorFood safety
The invention provides a modifier capable of reducing saxitoxin. The modifier capable of reducing saxitoxin is characterized by comprising the following components in parts by weight: 10-100 parts of garlicin, 10-200 parts of astaxanthin, 10-200 parts of beta-cyclodextrin, 10-200 parts of quercetin, 500-1000 parts of ethanol and 500-1000 parts of water. The modifier is capable of filling up the blank in the industry; the modifier which utilizes garlicin and astaxanthin as main components is capable of reducing the saxitoxin in food by no less than 50%, and does not cause substitutability influence on original flavor of the food; furthermore, the modifier adopts natural components and conforms to the food safety requirement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Determination method of lipid soluble saxitoxin in long-term-preserved oyster sample
InactiveCN107024547AAccurate shellfish toxin contentData information is accurateComponent separationLipid formationGas phase
The invention discloses a determination method of lipid soluble saxitoxin in a long-term-preserved oyster sample, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) sample pretreatment; (2) extracting of free fatty acids in the sample; (3) boron trifluoride methyl esterification of the free fatty acids, and gas chromatography detection; and (4) result correction. The determination method uses a corrected boron trifluoride methyl esterification method for corrected detection of the lipid soluble saxitoxin the preserved oyster sample, and a method for obtaining the accurate content of toxins in an original production sample by detection of the saxitoxin in the preserved oyster sample is provided. Through effective correction, a real-time detection value can accurately reflect the original content of the saxitoxin in the preserved oyster sample, accurate data information can be obtained, and the retrospective study can be supported.
Owner:徐静 +3
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection method for paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish
PendingCN112379015AReduce consumptionEasy to eluteComponent separationUltrafiltrationSample purification
The invention provides a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection method for paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish. The method comprises the following steps: 1.1, performing sample extraction: adding a formic acid solution into a shellfish sample, carrying out ultrasonic extraction and centrifuging, taking the supernatant, and fixing the volume to obtain a sample extracting solution; 1.2, performing sample purification: adding dichloromethane into the sample extracting solution, uniformly performing mixing, performing centrifuging, taking supernatant, adding the supernatant into an activated C18 solid-phase extraction column, performing eluting, collecting effluent and eluent, performing combining, fixing the volume, performing standing, performing centrifuging, and taking a supernatant filter membrane to obtain a sample detection solution; and 1.3, performing sample detection: taking the sample detection solution, carrying out liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection, and performing quantifying by an external standard method. The method belongs to the technical field of food safety detection, simplifies the operation, reduces the consumption of anorganic solvent, has a good sample purification effect, does not need an ultrafiltration step, realizes effective separation and detection of partial structural analogues in PSTs, and widens the detection variety of the PSTs.
Owner:SHENZHEN CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION +1
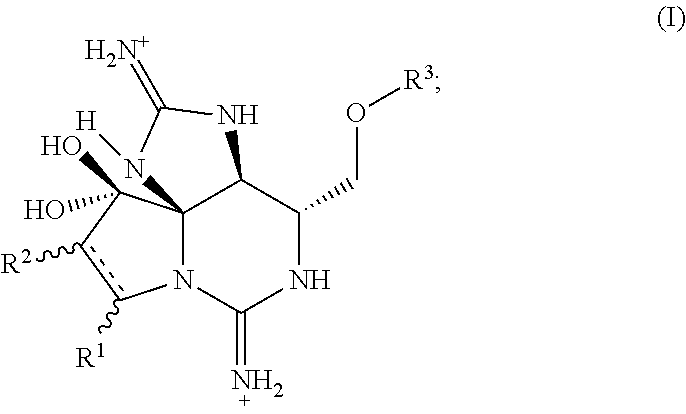
10′,11′-modified saxitoxins useful for the treatment of pain
Provided herein are compounds, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions in treating conditions associated with voltage-gated sodium channel function, for example conditions associated with pain. The compounds are 10′,11′-modified saxitoxins. The compounds are optionally additionally modified at carbon 13. In certain embodiments, the 10′,11′-modified saxitoxins are of Formula I: where R1, R2 and R3 are as described herein. Also provided herein are methods of treating pain in a mammal comprising administering an effective treatment amount of a 10′,11′ modified saxitoxin or composition to a mammal. In an embodiment, the mammal is a human.
Owner:SITEONE THERAPEUTICS +1
Model for detecting cell density of microalgae producing paralytic saxitoxin and as establishment method and application of model
ActiveCN113673090AImprove stabilityImprove analytical performanceClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationStepwise regressionZoology
The invention discloses a model for detecting the cell density of microalgae producing paralytic shellfish toxin and an establishment method and application of the model. According to the method, three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum information of algae producing paralytic shellfish poison or algae not producing paralytic shellfish poison under different environmental conditions is extracted, a characteristic spectrum of the density of the algae producing the poison is extracted through a Db7 wavelet function, and the quantitative model of the algae producing the paralytic shellfish poison is established by adopting a stepwise regression analysis method based on the characteristic spectrum of the density of the algae producing the paralytic shellfish poison. The fluorescence characteristic standard spectrum library can be used for quantitatively analyzing the cell density of the microalgae producing paralytic saxitoxin. According to the invention, a paralytic shellfish producing quantitative model is established by a stepwise regression analysis method according to component fluorescence characteristic spectrums of a second scale and a third scale of a Db7 wavelet function, when toxic dinoflagellate is mixed with non-toxic dinoflagellate as a dominant species, the accuracy rates of density testing of the toxic dinoflagellate at high, medium and low concentrations are 98%, 67% and 90% respectively, and the aim of quantitatively analyzing the cell density of the toxin-producing algae is fulfilled.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
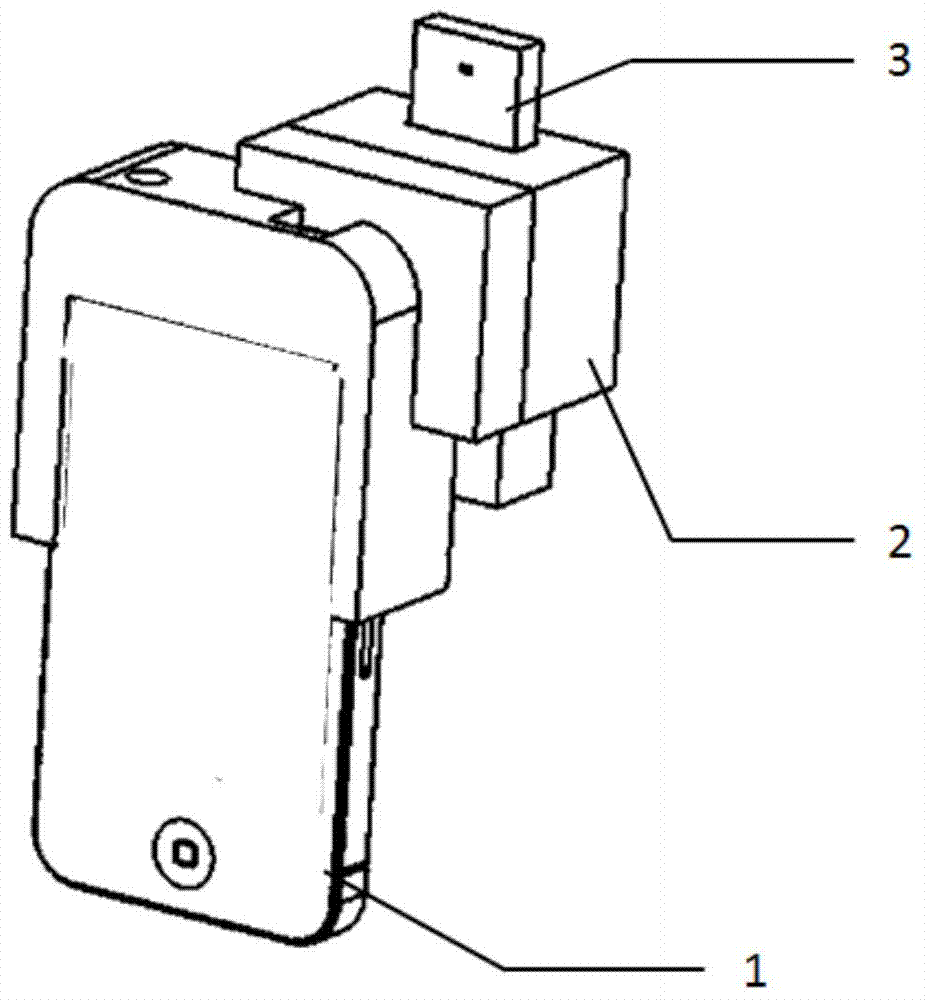
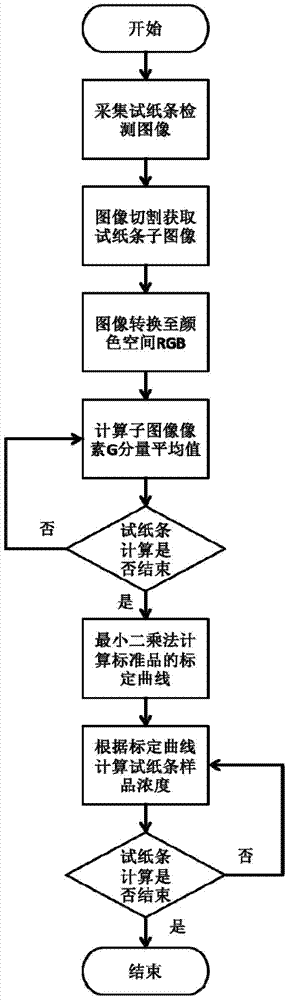
Detection method of shellfish paralytic toxin based on image analysis
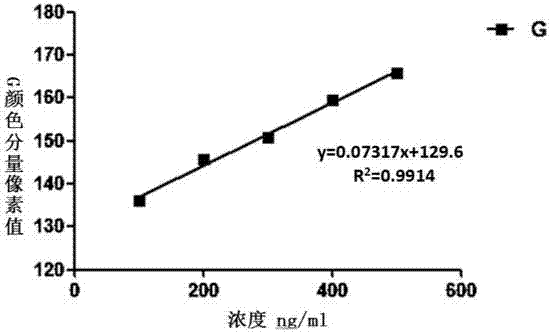
InactiveCN104777159BQuick checkSimple and fast operationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor imagePattern recognition
The invention discloses a method for detecting shellfish paralytic toxin based on image analysis. The method first performs sample pretreatment to prepare a sample solution of shellfish paralytic toxin to be tested; then prepares a standard solution and uses a test strip; Through detection image acquisition, image analysis, calculate the pixel value of the G component in the RGB space of the color image of the detection test strip, and then fit the calibration curve of the test strip to detect shellfish paralytic toxin by the least square method; by analyzing the sample to be tested The sub-image G component pixel values of the control line and detection line of the solution on the test strip are brought into the calibration curve, and then the shellfish paralytic toxin concentration of the sample solution to be tested is calculated. The invention realizes the quantitative detection of shellfish paralytic toxin, and has the advantages of simple operation steps, rapid detection, adaptability to on-site detection and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A group of nucleic acid aptamers that specifically recognize three marine toxins
ActiveCN107541516BLow costShorten the production cycleDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerStructural homology
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com