Threshold signature method, system, device and storage medium based on aggregated multi-signature
A threshold, signature public key technology, applied in transmission systems, digital transmission systems, secure communication devices, etc., can solve problems such as long transaction confirmation time and high transaction costs, reduce transaction costs, improve signature efficiency, and improve The effect of privacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
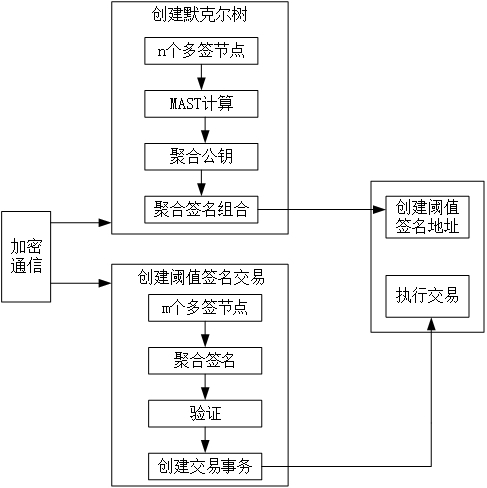
[0069] The present invention proposes a threshold signature method based on aggregated multi-signature, and provides a threshold signature method in the architecture block chain based on sr25519 protocol (for example, Substrate supports sr25519 and Schnower's multi-signature, but does not support threshold signature), and its overall structure flow Such as figure 1 As shown, the threshold signature is completed on the basis of aggregated multi-signatures combined with the Merkle tree structure of the MAST structure, where n signature nodes are deployed in the blockchain network for multi-signature transactions on the chain, and m is The threshold of the supported threshold signature, where n≥m; each signature node among the n signature nodes generates a pair of public-private key pairs for transaction signature, and the private key is used as its second random private key; the public key is used as the second signature public key.
[0070] The specific steps are as follows: ...
Embodiment 2
[0087]In this embodiment, the threshold signature method of the present invention is described from the specific implementation method, specifically as follows:
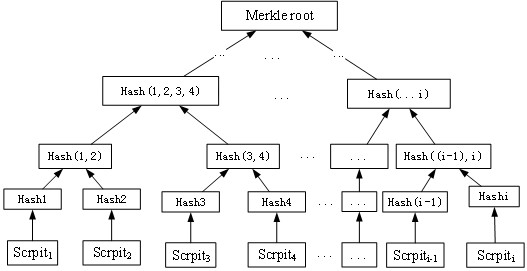
[0088] (1) Create a Merkle tree structure of the MAST structure and create a threshold signature address:
[0089] To create a multi-signature with a threshold of m in n signature nodes (n≥m), first calculate the second aggregated public key C formed by n signature nodes:
[0090] C = hash(L,PK 1 ’) PK 1 ’+…+ hash(L,PK i ’) PK i ’+…+ hash(L,PK n ’) PK n ');
[0091] Where L is the list of public keys: L={PK 1 ’,…,PK i ’, …,PK n ’} represents an ordered set of all public keys involved in the signature process;
[0092] Second signature public key PK i '=sk i ’·G (G is the base point of the unified elliptic curve); sk i ’ is the second random private key of the signing node; i is any one of the n signing nodes.
[0093] In order to realize a multi-signature with a threshold of m among n nodes, the public ...
Embodiment 3
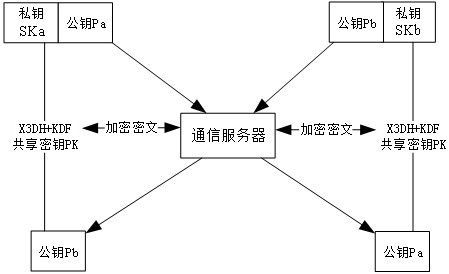
[0121] In this embodiment, the signing public key and temporary public key are sent between the signing nodes involved in generating the aggregated public key and the signature generated by the signing public key is sent between the signing nodes involved in the aggregated signature process. The transmission is encrypted using an encrypted communication protocol, and a communication server is set up between each signing node to store the updated shared key and transmit the encrypted message ciphertext:
[0122] Such as image 3 As shown, the signature public key of the signature node is used as the initial key. For example, the signature public key or the signature transaction is sent between the signature nodes a and b. The private key of node a is Ska, and the corresponding signature public key is Pa. Node The private key of b is Skb, and the corresponding signature public key is Pb. Node a uses the X3DH algorithm to generate the shared key PK of both signing nodes, and uses...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com