Energy-saving effect evaluation method for marine wind power boosting rotor
An energy-saving effect and rotor technology, which is applied in computer-aided design, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as the reduction of the power of the main engine of the ship, the evaluation of the energy-saving effect of Class B energy-saving technologies by calculation results, and the unconfirmed detailed evaluation methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
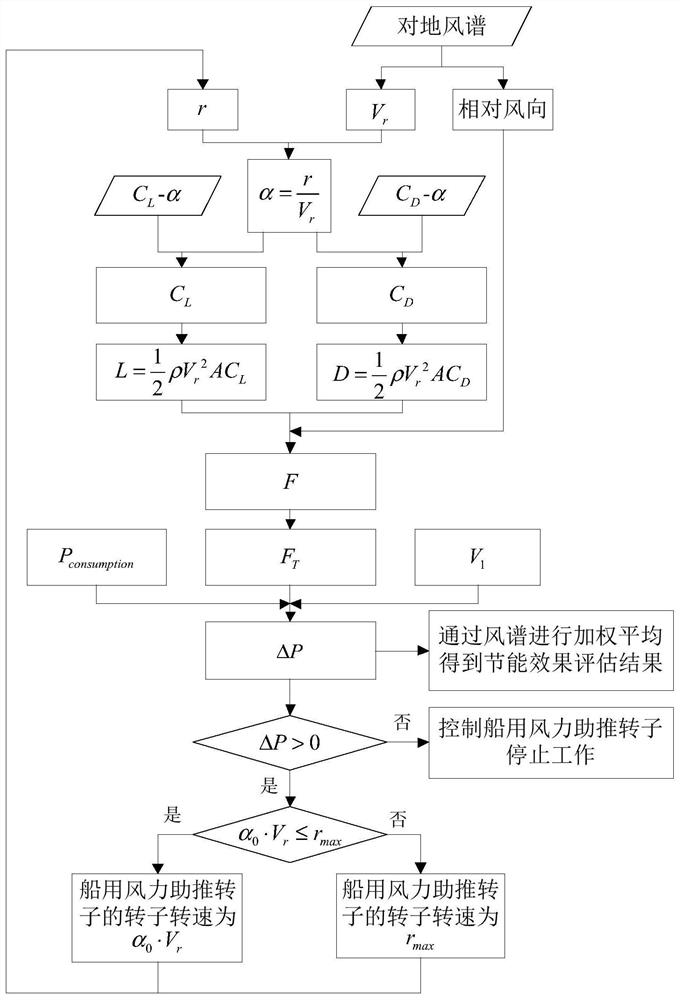
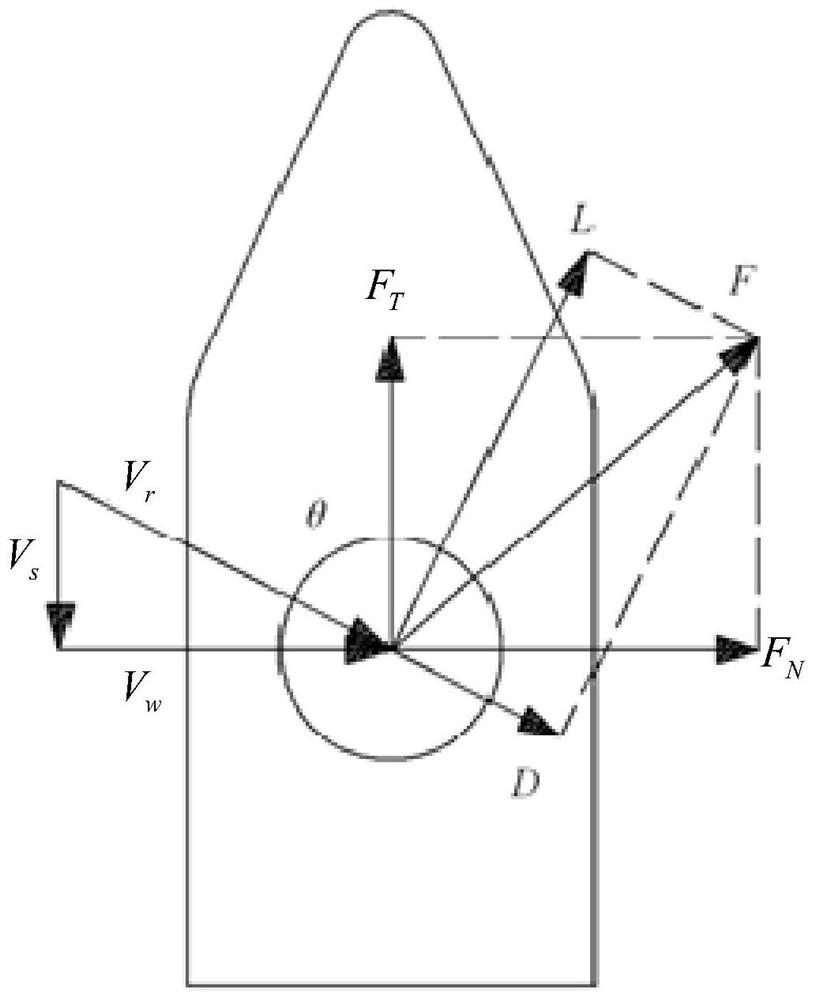
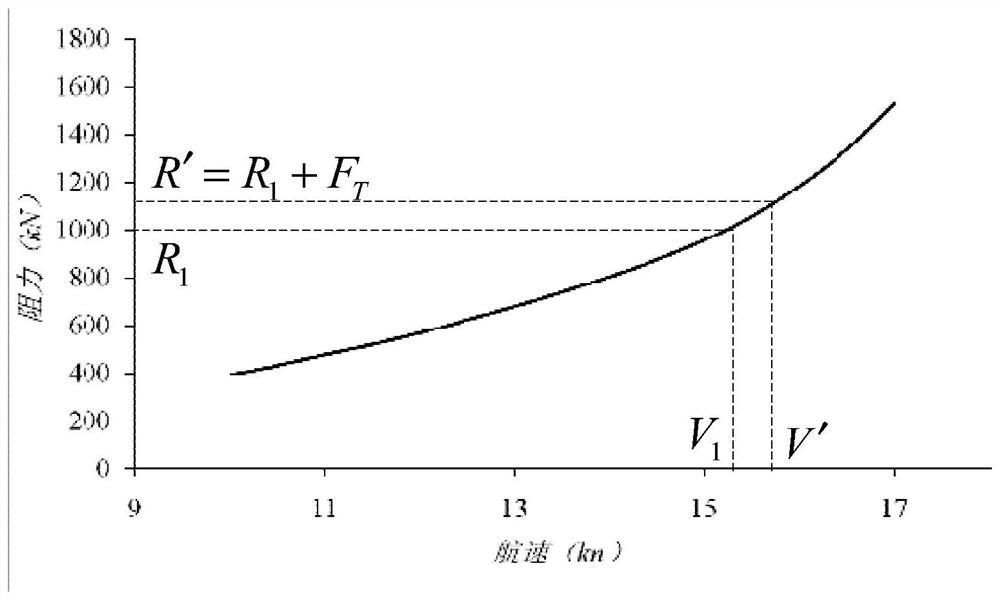
[0044] This application discloses a method for evaluating the energy-saving effect of a marine wind-assisted rotor. The method includes the following steps. Please refer to figure 1 :
[0045] 1. Determine the relative wind spectrum based on the ground wind spectrum. The relative wind spectrum includes the relative wind speed and relative wind direction in the on-board coordinate system. Probability values for absolute wind speed and absolute wind direction. Specifically, according to the course of the ship, the wind spectrum over the ground is mapped from the earth coordinate system to the on-board coordinate system, and the absolute wind speed V in the on-board coordinate system is obtained wAs well as the relative wind direction, the mapping relationship between the ship coordinate system and the earth coordinate system can be determi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com