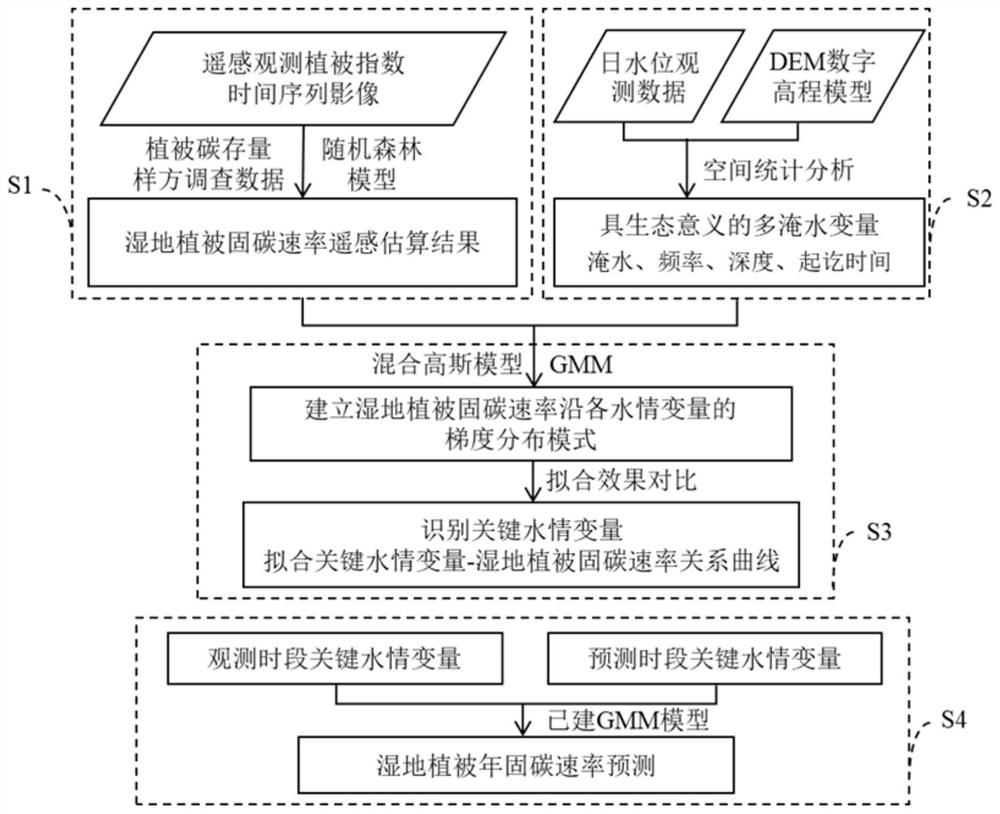
Wetland vegetation carbon sequestration rate prediction method based on relation between key water regimen variables and vegetation carbon sequestration rates
A wetland vegetation and prediction method technology, applied in the direction of prediction, probability CAD, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve the problems of estimating the carbon sequestration rate of wetland vegetation and the difficulty of using remote sensing methods, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Take Poyang Lake Wetland, a typical wetland ecosystem, as an example.
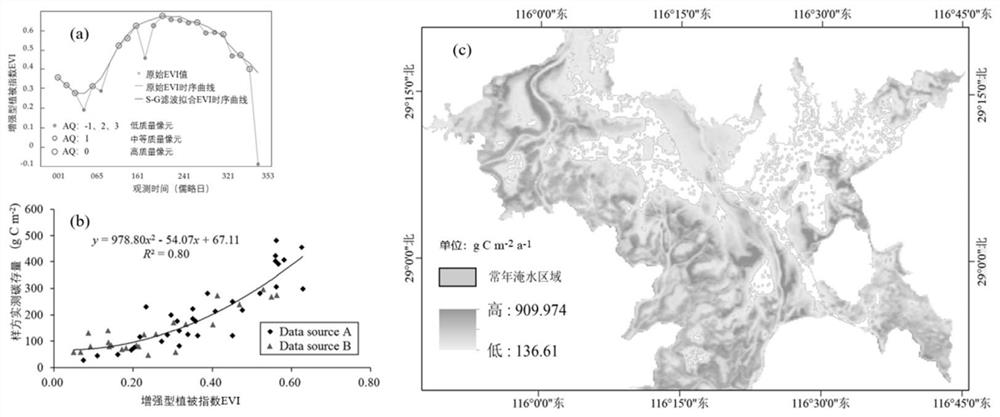
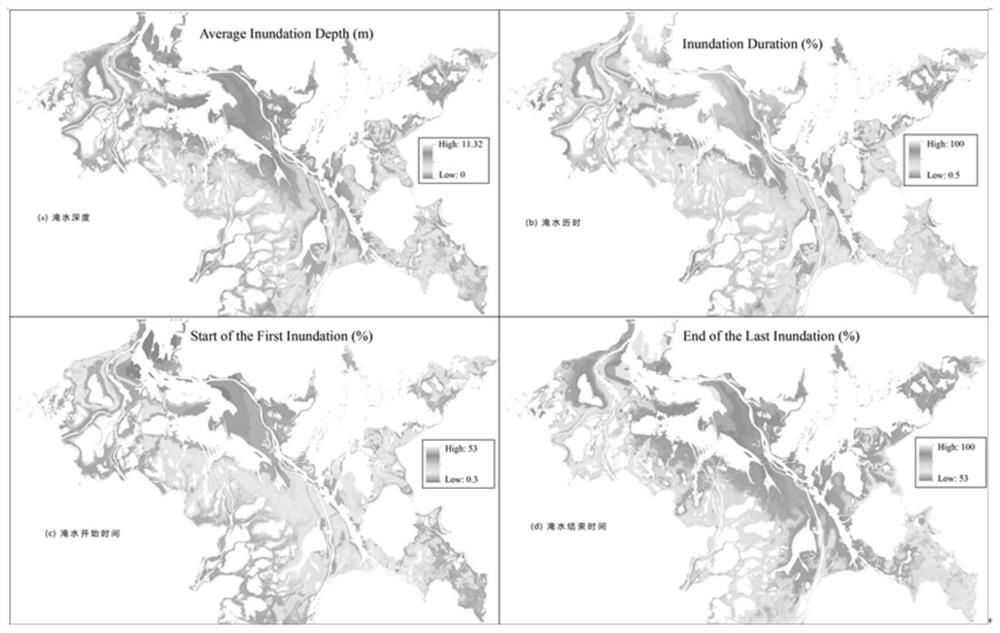
[0053] figure 2 Schematic diagram for estimating carbon sequestration rate of Poyang Lake wetland vegetation based on time-series images of vegetation index observed by remote sensing. The specific steps include ① based on the AQ value (AncillaryQuality value, AQ) of the generalized quality layer (Band Pixel Reliability), delete the low-quality pixels with AQ of -1, 2 and 3, and only keep the middle and high-quality pixels ; Fit the EVI time series curve with S-G filter, and complete the interpolation for eliminating abnormal values ( figure 2 a); ②Establish the functional relationship between measured wetland vegetation carbon stock and EVI index based on the binomial, and establish a remote sensing inversion model for wetland vegetation carbon stock ( figure 2 b) Use it to invert the carbon stock of wetland vegetation corresponding to the remote sensing images of each period, and use the cu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com