Process for removing oxide skin on surface of forge piece
A technology of surface oxidation and scale, applied in the field of forging, can solve problems such as high cost, electrochemical corrosion of forgings, surface damage of forgings, etc., and achieve the effects of accelerating disintegration, ensuring disintegration and shedding, and accelerating removal of power.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] A process for removing scale on the surface of a forging, comprising the following steps:
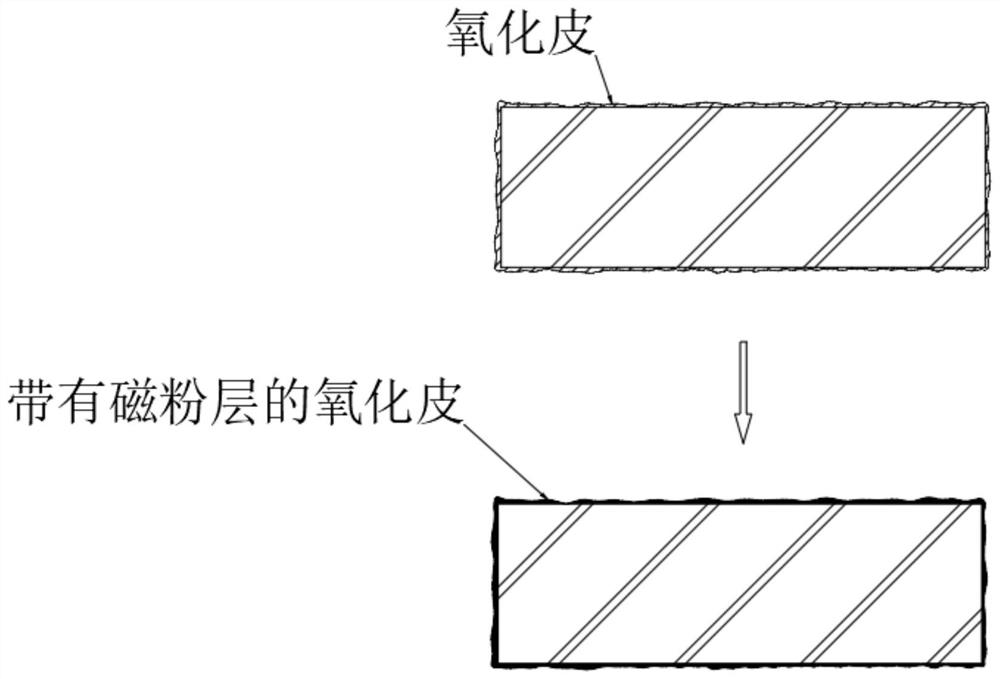
[0052] S1. First, knock the surface of the forging in a large range to break the scale and cracks, and then pretreat the forging to form a layer of magnetic powder in the scale;
[0053] see Figure 1-2 , the specific operation of preprocessing is:
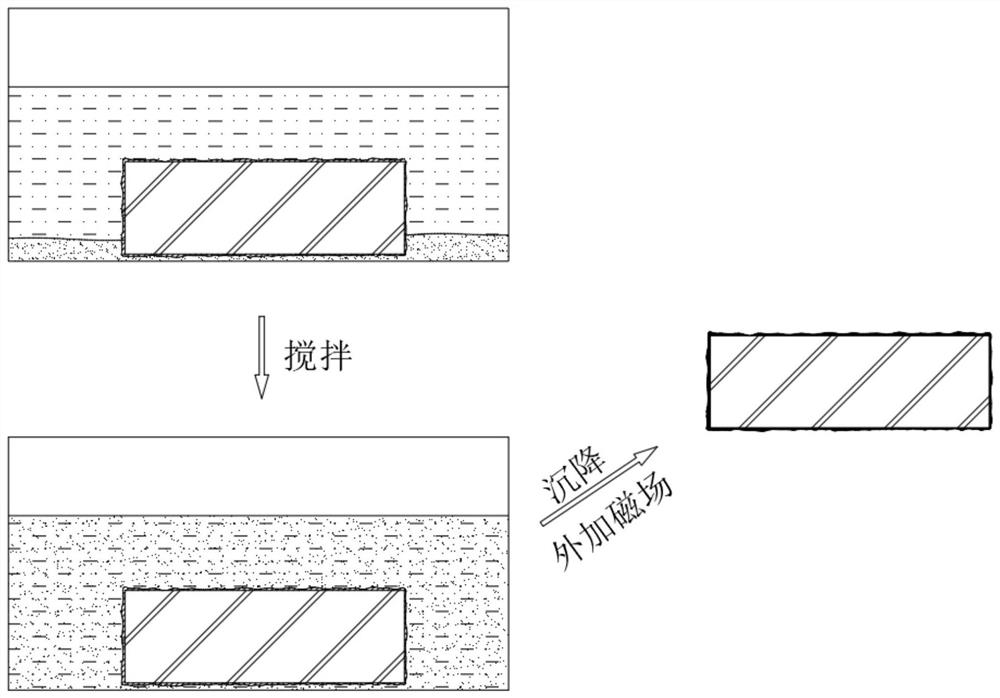
[0054] S11, first drop the knocked forging into nano magnetic water;
[0055] S12, then constantly stir the nano-scale magnetic water, so that the magnetic powder sinking to the bottom diffuses in the water;
[0056] S13, standing still, so that the magnetic powder continuously sinks and deposits on the surface of the forging, and at the same time penetrates into the middle oxide scale along the cracks of the oxide scale;
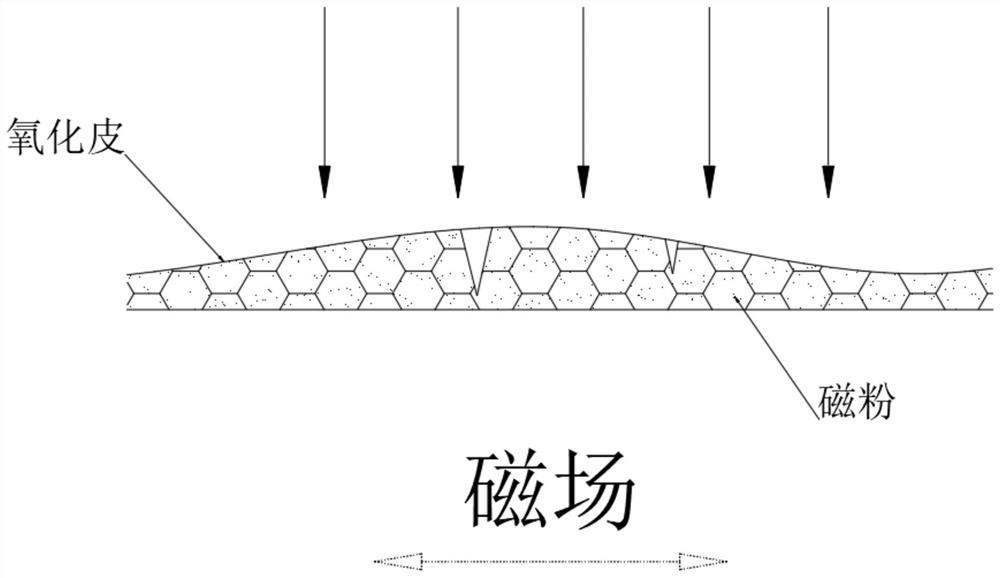
[0057] S14. Please refer to image 3 , when the magnetic powder is deposited, an external magnetic field is applied under the forging to guide the movement of the magnetic powder and improve the uniformity of ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] see Figure 7 , the pretreatment to the forging in step S1 is:
[0065] A plurality of magnetizing balls 1 are evenly laid on the surface of the scale, and then the multiple magnetizing balls 1 are squeezed and rubbed, so that the inner magnetic oil and water overflow, and the magnetic powder is infiltrated into the oxide scale, and then a magnetic field is applied. Improve the uniformity of magnetic powder distribution and form a magnetic powder layer.
[0066] Before the magnetizing ball 1 is laid on the oxide skin, it is soaked in water to hydrolyze the water-soluble material in the liquid guide channel 8 to facilitate the overflow of magnetic oil and water.
[0067] see Figure 8 The magnetic ball 1 includes a magnetic storage end 71 and a gas storage end 72 wrapped around the lower end of the magnetic storage end 71. The magnetic oil storage end 71 is filled with magnetic oil and water, which is a mixture of light oil and nano-scale magnetic powder. The gas stora...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com