Power failure event quasi-real-time monitoring method and system based on edge calculation
An edge computing, quasi-real-time technology, applied to electrical components, measuring electronics, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as false positives and negative negatives, and low computing efficiency, so as to reduce computing pressure, improve real-time performance, and reduce false alarm rates and the effect of false negative rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
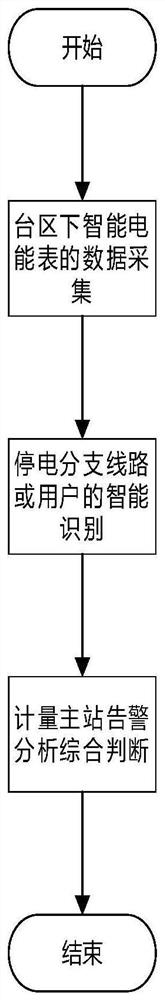
[0040] A quasi-real-time monitoring method for power outage events based on edge computing, including the following steps:
[0041] Step S1: Data collection of smart energy meters in the station area:
[0042] Periodically collect the voltage data of the smart electric energy meters in the station area according to the time interval, and use the collected voltage data for analysis, and eliminate the data of the smart electric energy meters in the non-local area
[0043] Step S2: Intelligent identification of power outage branch lines or users:
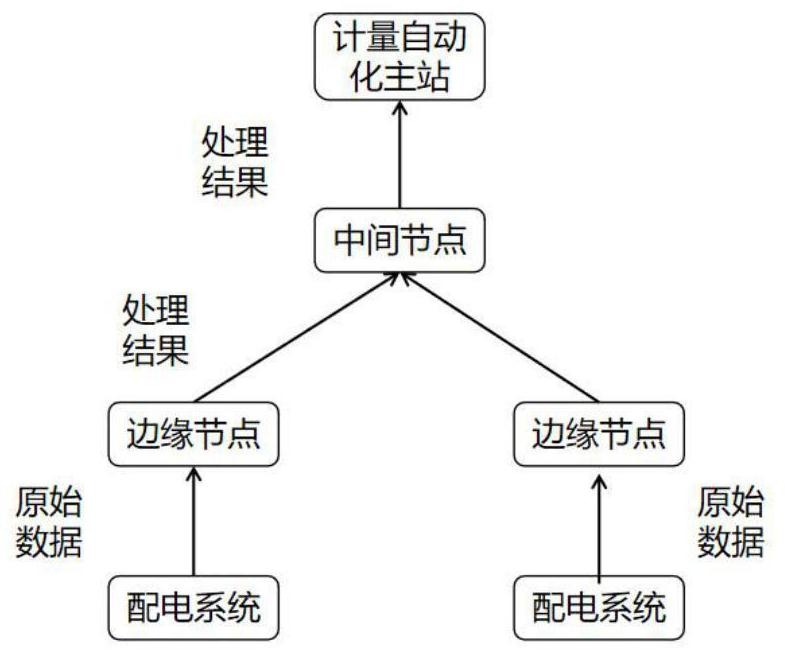
[0044] The smart metering terminal on the edge side receives the active power outage reporting event of the smart energy meter in real time, and collects the voltage data of the smart energy meter in real time after data analysis; if the voltage data returned by the smart energy meter cannot be received within a certain period of time or the voltage data is lower than the limit , it is judged that the household has a power outage;
...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A quasi-real-time monitoring method for power outage events based on edge computing, including the following steps:
[0050] Step S1: Data collection of smart energy meters under the station area:
[0051]Periodically collect the voltage data of the smart electric energy meters in the station area according to the time interval, and use the collected voltage data for analysis, and eliminate the data of the smart electric energy meter in the non-local area;
[0052] Step S2: Intelligent identification of power outage branch lines or users:
[0053] The smart metering terminal on the edge side receives the active power outage reporting event of the smart energy meter in real time, and collects the voltage data of the smart energy meter in real time after data analysis; if the voltage data returned by the smart energy meter cannot be received within a certain period of time or the voltage data is lower than the limit , it is judged that the household has a power outage; ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The quasi-real-time monitoring method for blackout events based on edge computing is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0064] Step S1: Data collection of smart energy meters in the station area:
[0065] Periodically collect the voltage data of the smart energy meters in the station area according to the time interval, and use the time and space of the voltage data to eliminate the data of the smart energy meters in the non-local area;
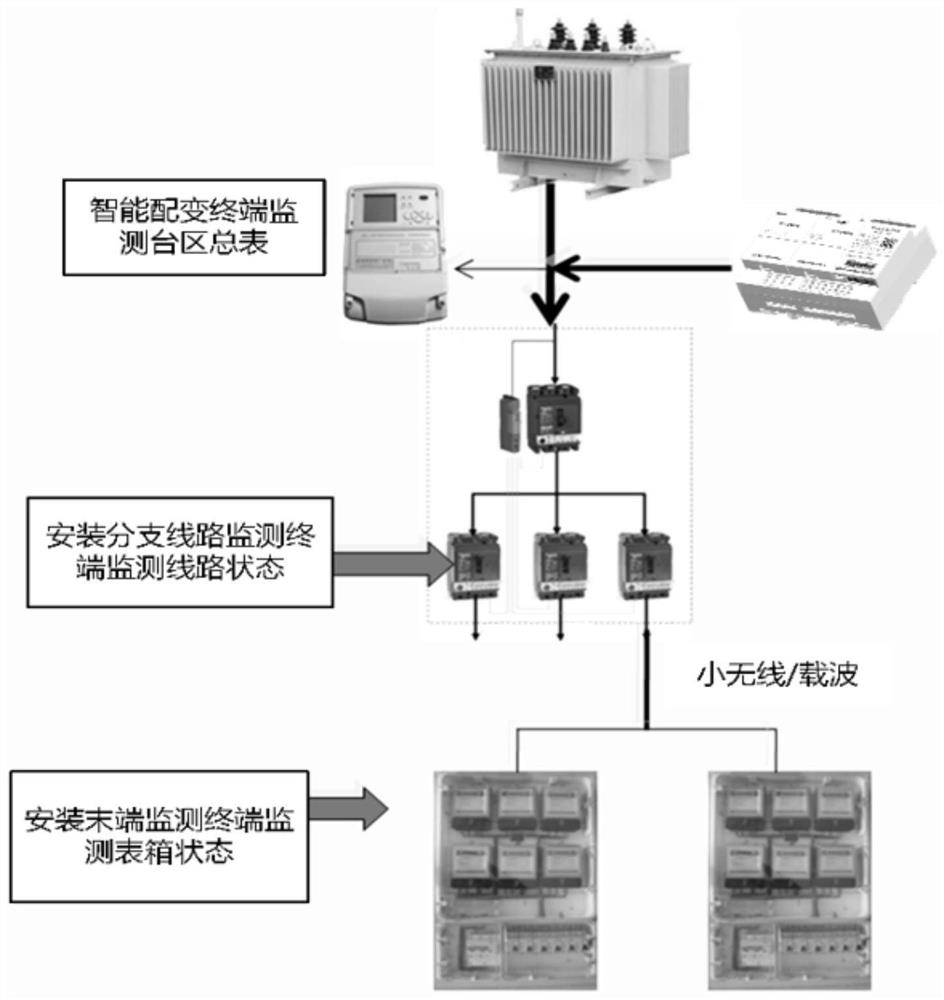
[0066] (1) The edge-side smart metering terminal periodically collects smart voltage data under the station area;
[0067] (2) Through the collected voltage data, analyze the voltage data collected by the smart energy meter in the station area within a period of time (15s), and the voltage change trend in the same station area should be the same;
[0068] (3) Dynamically judge the electric energy meters under the station area, and eliminate the data of the smart electric energy meter in the non-local area;
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com