Damage positioning imaging method and system based on non-linear Lamb wave zero frequency component
A zero-frequency component, damage localization technology, used in the analysis of solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, measurement devices, etc. Problems such as detection and complex operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
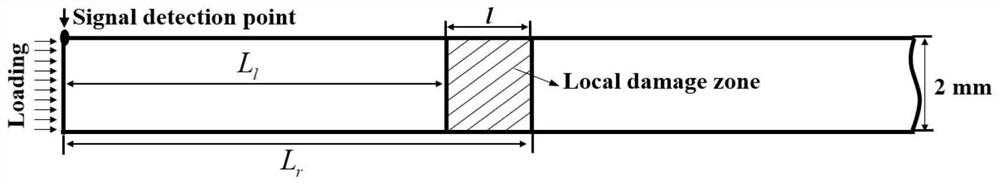
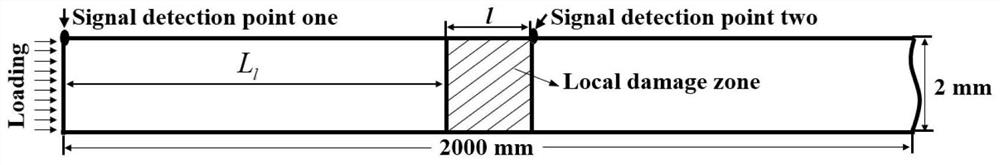
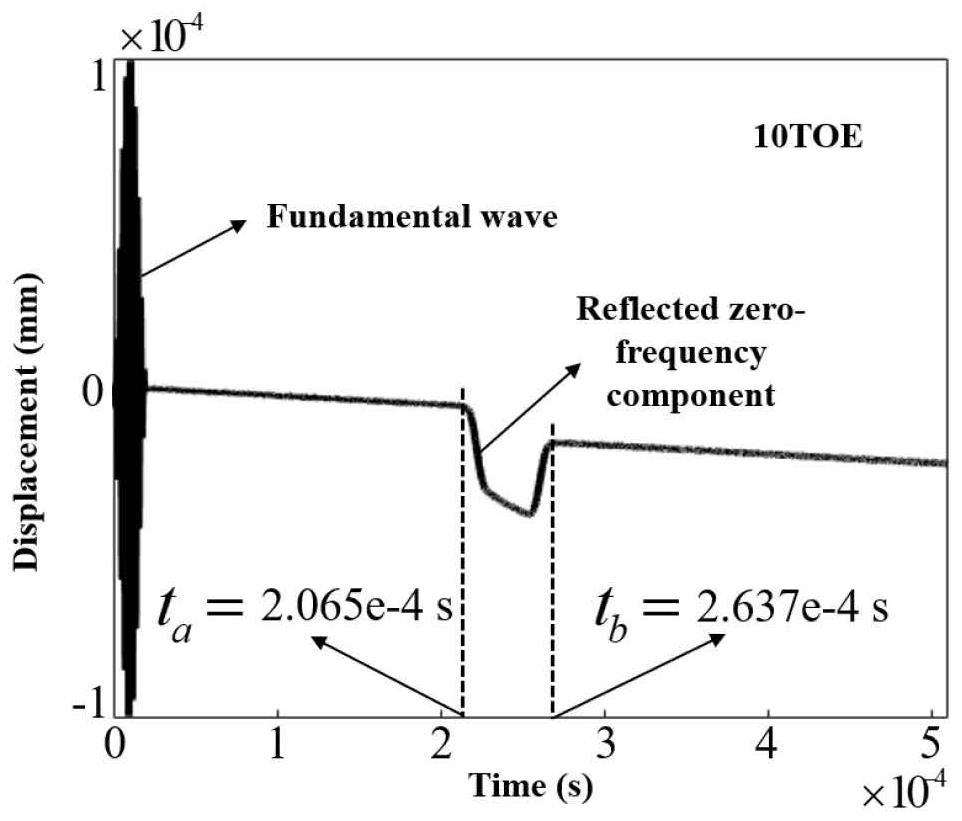
[0034] Such as figure 1 Shown, L l The distance from the left boundary of the local damage to the signal excitation point, v is the fundamental wave phase velocity, v 0 is the zero-frequency phase velocity, t a is the arrival time of the zero-frequency signal received by the signal receiving point (also the signal transmitting point), there is
[0035]
[0036] L r is the distance from the right boundary of the local damage to the signal excitation, t l is the departure and end time of the zero-frequency signal received by the signal receiving point (also the signal transmitting point), Δt is the width of the zero-frequency signal generated in the local damage area, and
[0037]
[0038] The width of the local damage area is
[0039] l=L r -L l (3)
[0040] According to the inventors in the document "SUN X Q, LIU H J, ZHAO Y X, et al. The zero-frequency component of bulk waves in solids with randomly distributed micro-cracks [J]. Ultrasonics, 2020, 107: 106172."...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the ultrasonic probe in this embodiment (mainly referring to the receiving point) includes: a housing 1, a CMUT sheet 4, an acoustic lens 3 and a controller; the CMUT sheet 4 includes multiple a CMUT element; the acoustic lens 3 is located on the surface of the CMUT sheet 4; the bottom surface of the CMUT sheet 4 is provided with a liner layer 7, the liner layer 7 is bonded to the CMUT sheet 4, and the liner layer 7 and the acoustic lens 3 are respectively Located at the top and bottom of the CMUT sheet 4; the CMUT sheet 4 is connected to the flexible substrate 2 through a wire; the flexible substrate 2 is electrically connected to the controller (the flexible substrate 2 is also connected to the controller with an external power lamp and other equipment); the housing 1 is provided with a piezoelectric ceramic sheet 5, and the piezoelectric ceramic sheet 5 is provided with an electrode 6 with opposite polari...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com