Intraoperative dynamic path optimization method and device for tumor thermal ablation
A technology of dynamic paths and optimization methods, applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve problems such as time-consuming and resource-consuming, inability to match the motion of organs, and poor accuracy of respiratory motion models.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
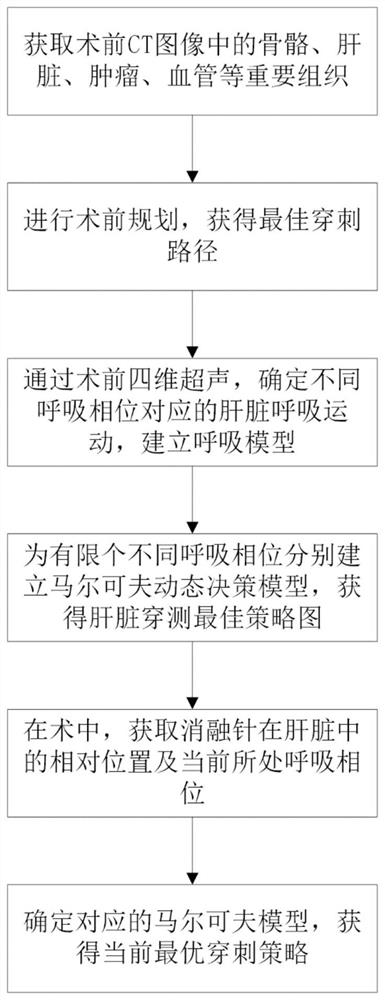
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, this intraoperative dynamic path optimization method for tumor thermal ablation includes the following steps:
[0021] (1) Obtain the segmentation results of the liver, tumors on the liver, blood vessels inside the liver, and important tissues and organs near the liver from the preoperative CT images;
[0022] (2) Obtain the puncture area of the liver according to the size of the important tissue, and construct the optimal needle path L before operation on this basis;
[0023] (3) According to the preoperative four-dimensional ultrasound image, the liver motion deformation field and the corresponding respiratory signal are obtained, and the respiratory model is constructed to match the liver motion and the respiratory phase. Different respiratory frequencies cause different changes in liver motion, so the respiratory signal is discretized into k phase segment;
[0024] (4) For each phase segment, build a Markov decision model on the preope...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com