Torque characteristic improvement method under short-circuit fault of five-phase permanent magnet motor
A short-circuit fault and torque characteristic technology, which is applied in the direction of motor, motor control, AC motor control, etc., can solve problems affecting the operating characteristics of multi-phase permanent magnet motors, and achieve the effect of improving torque output characteristics and torque characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
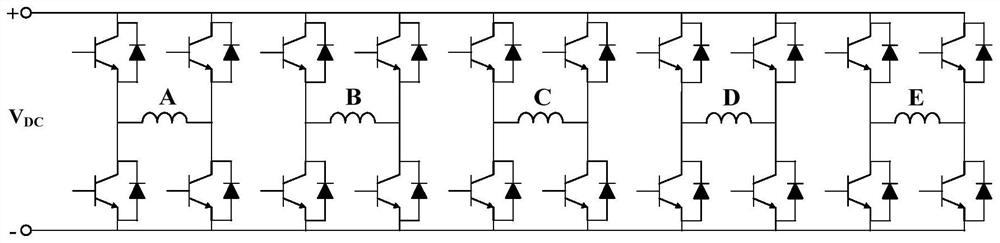
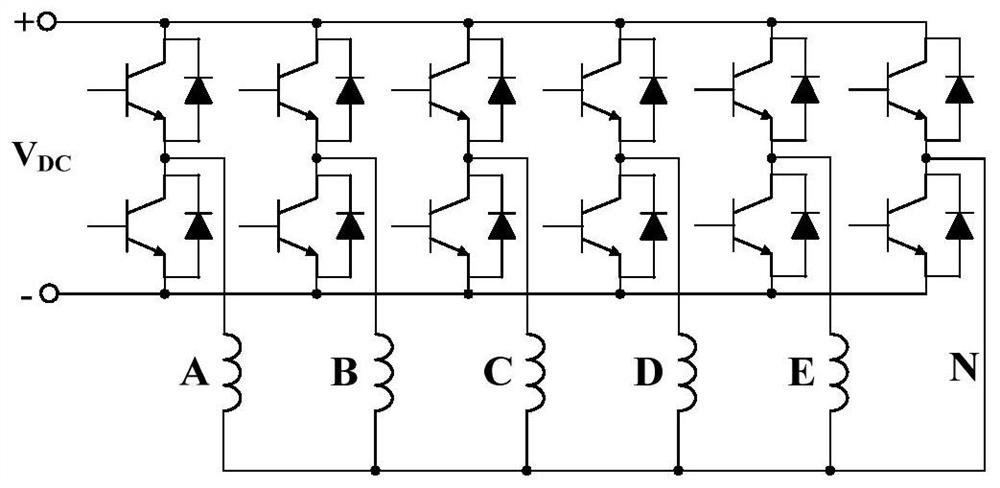
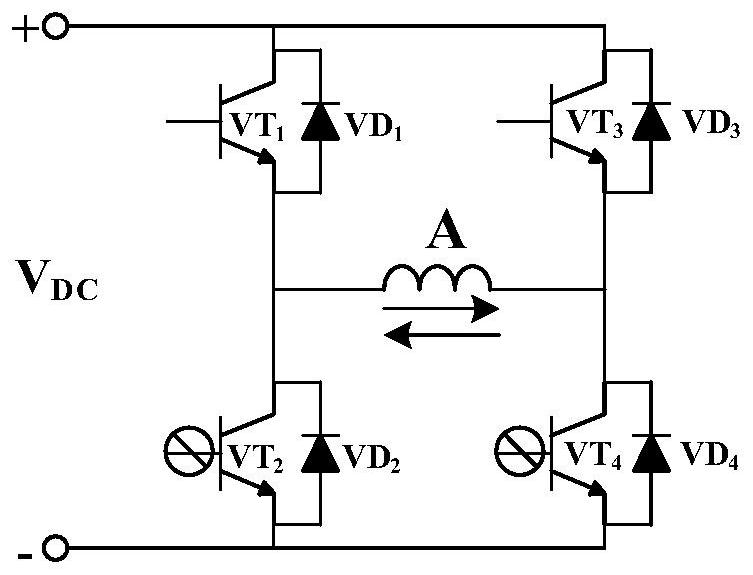
[0070] Specific embodiment one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 4 This embodiment will be described. The method for improving torque characteristics of a five-phase permanent magnet motor under short-circuit faults described in this embodiment is the same as the method for improving torque characteristics under short-circuit faults at the ends of windings of any phase A, B, C, D, and E. A Taking the short circuit at the end of the phase winding as an example, the fault-tolerant control method of the five-phase permanent magnet motor when the end of any phase winding is short-circuited is as follows:
[0071] When the end short-circuit fault occurs in the A-phase winding, the main component expression of the A-phase winding short-circuit current is:
[0072]
[0073] In the formula, i Ashort is the short-circuit current of the A-phase winding, I As1 and I As3 are the fundamental and third harmonic current amplitudes in the short-circuit current of the A-pha...
Embodiment
[0111] Embodiment: A specific embodiment of a five-phase permanent magnet motor in the case of a short-circuit fault at the end of a phase winding of a five-phase permanent magnet motor is given below.
[0112] Taking a five-phase permanent magnet motor with 15 slots and 12 poles as an example, the output torque characteristics of the five-phase permanent magnet motor in the normal state, the short-circuit state at the end of the one-phase winding, and the method of the present invention are respectively given, such as Table 1 shows the advantages of the method of the present invention.
[0113] Table 1 Comparison of torque characteristics under normal state and A-phase terminal short-circuit fault state
[0114] working status normal status A phase end short circuit (uncontrolled) A-phase terminal short circuit (fault-tolerant control) Output torque (N m) 62.8 44 31.9 Torque ripple (%) 0.5 62.6 21.4
[0115] It can be seen that using the m...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0116] Specific embodiment two: the following combination image 3 and Figure 4 This embodiment is described. This embodiment further describes Embodiment 1. The short-circuit fault covers the end short circuit and partial turn short circuit of the winding, and one of the situations where the switch tube short circuit occurs in the bridge arm of the inverter where the winding is located. its combination.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com