Knee joint MRI bone structure segmentation method based on 2D-3D feature fusion
A 2D-3D, feature fusion technology, applied in image analysis, neural architecture, image enhancement, etc., can solve the problems of low segmentation accuracy, irregular bone boundaries, narrow gaps at joint joints, etc., to improve practicability and segmentation accuracy. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
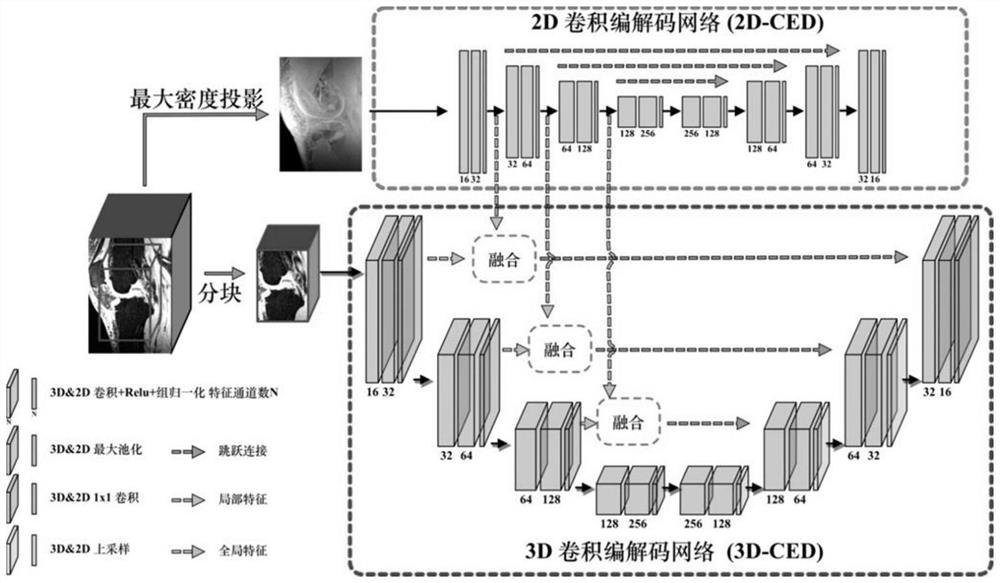
[0030] The overall structure of the method of the present invention is as follows figure 1 As shown, unlike the previous deep learning-based methods, in order to efficiently and accurately segment the bone structure of the knee joint, we propose a new segmentation network architecture based on 2D-3D feature hierarchical fusion.
[0031] 1. Segmentation network based on 2D-3D feature level fusion
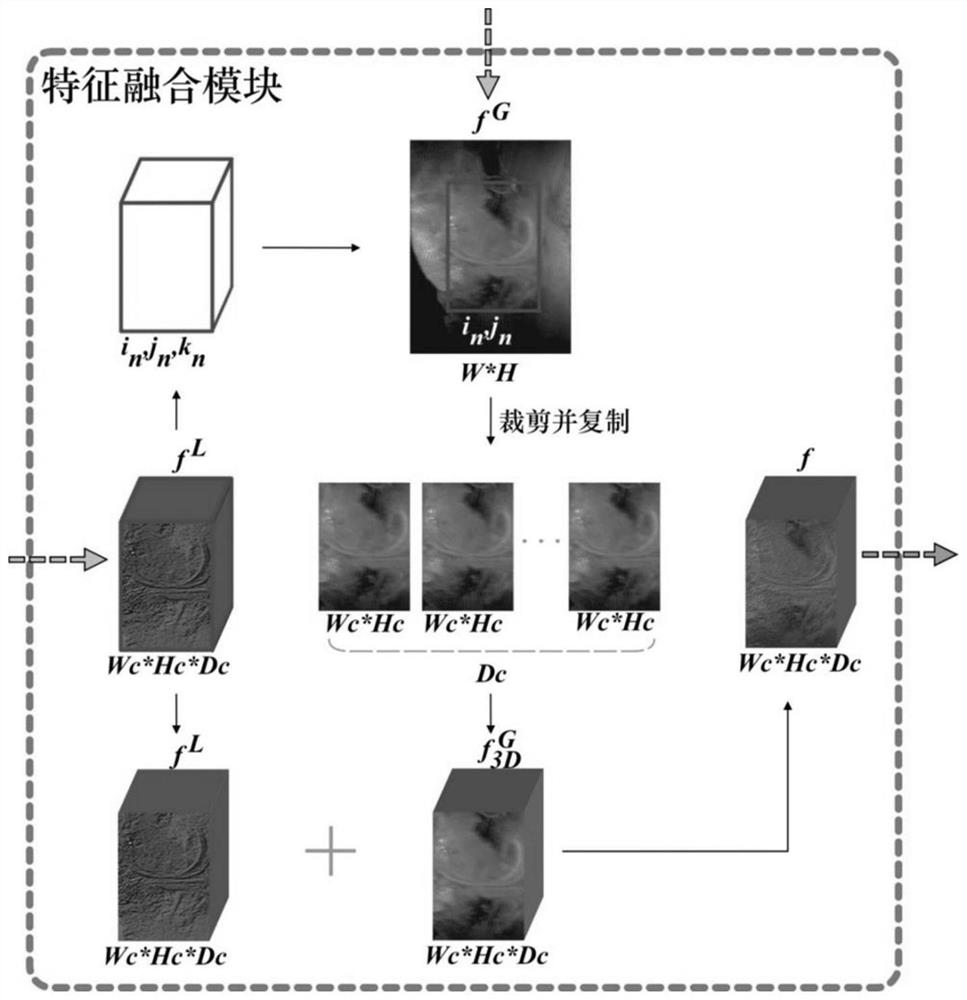
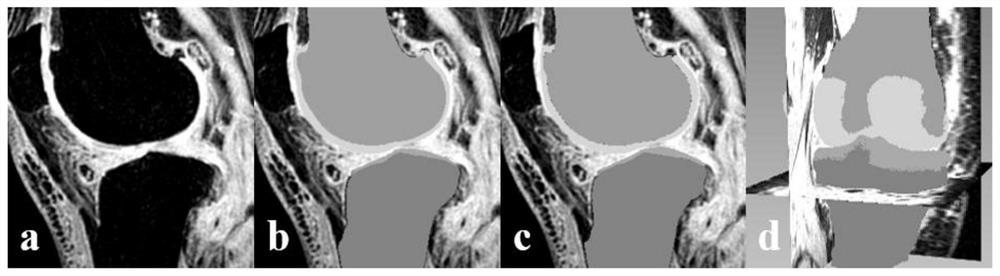
[0032] Previous deep learning-based knee bone structure segmentation methods were mainly based on 2D convolutional neural networks, 2D or 3D network hybrid cascades, and neural network segmentation methods combined with anatomical prior information. The new network is a segmentation network based on the features of 2D network and 3D network after hierarchical fusion. The detailed structure is as follows: figure 1As shown, the input of the network is the MR image of the 3D knee joint part, and the output is the segmentation result of the corresponding femur, femoral cartilage, tibia,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com