Fruit yield estimation method and application thereof
A technology of fruit yield and fruit quantity, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of large yield prediction error, large workload, low accuracy, etc., and achieve the effect of fast statistical speed, high accuracy, and reduced error rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
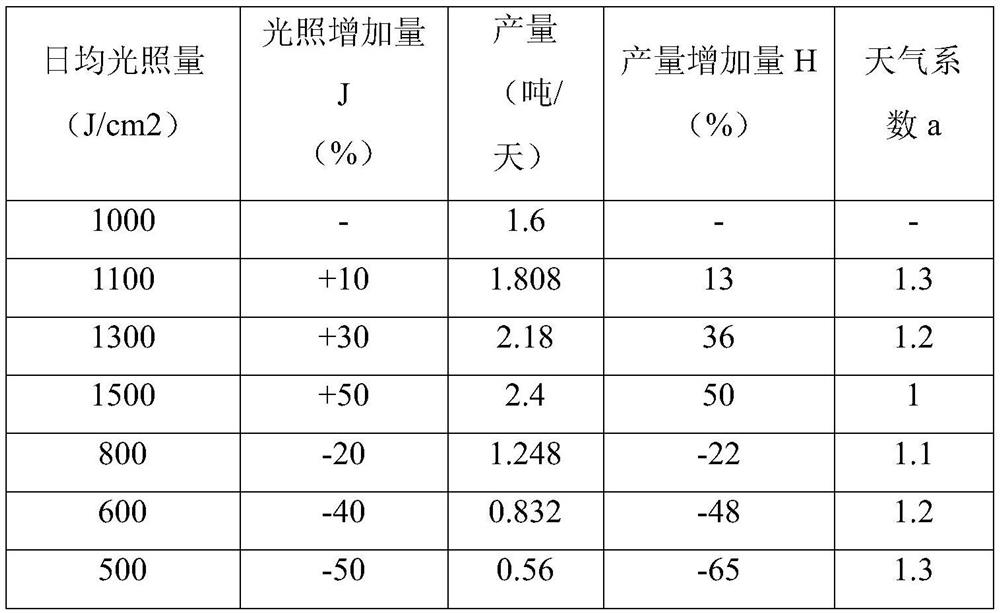
[0051] Establish a database of weather coefficient a
[0052] This application has established a database of weather coefficient a, and the specific methods are as follows:
[0053] (1) Take the red bunched small tomato plant as an example, collect the yield data of tomato under different average daily light levels; set the daily average basic light level of the tomato plant to 1000J / cm 2 ;
[0054] (2) Taking the daily average light amount as the abscissa and the tomato yield as the ordinate, establish the relationship curve between the daily average light amount and the tomato yield, and define the slope of the curve as the weather coefficient a.
[0055] In this preparation example, in order to describe the changing trend of the weather coefficient a, some representative data are selected from the weather coefficient a database (the illumination coefficient is 1000J / cm, respectively). 2 , 1100J / cm 2 , 1300J / cm 2 , 1500J / cm 2 , 800J / cm 2 , 600J / cm 2 , 500J / cm 2 The t...
Embodiment 1-4
[0062] Embodiments 1-4 provide a method for estimating fruit yield, respectively. In the above-mentioned method for estimating fruit yield, the fruit is a small red bunch harvested tomato.
[0063] The difference of the above-mentioned embodiment is: the season (month) of tomato yield estimation, specifically as shown in Table 2.
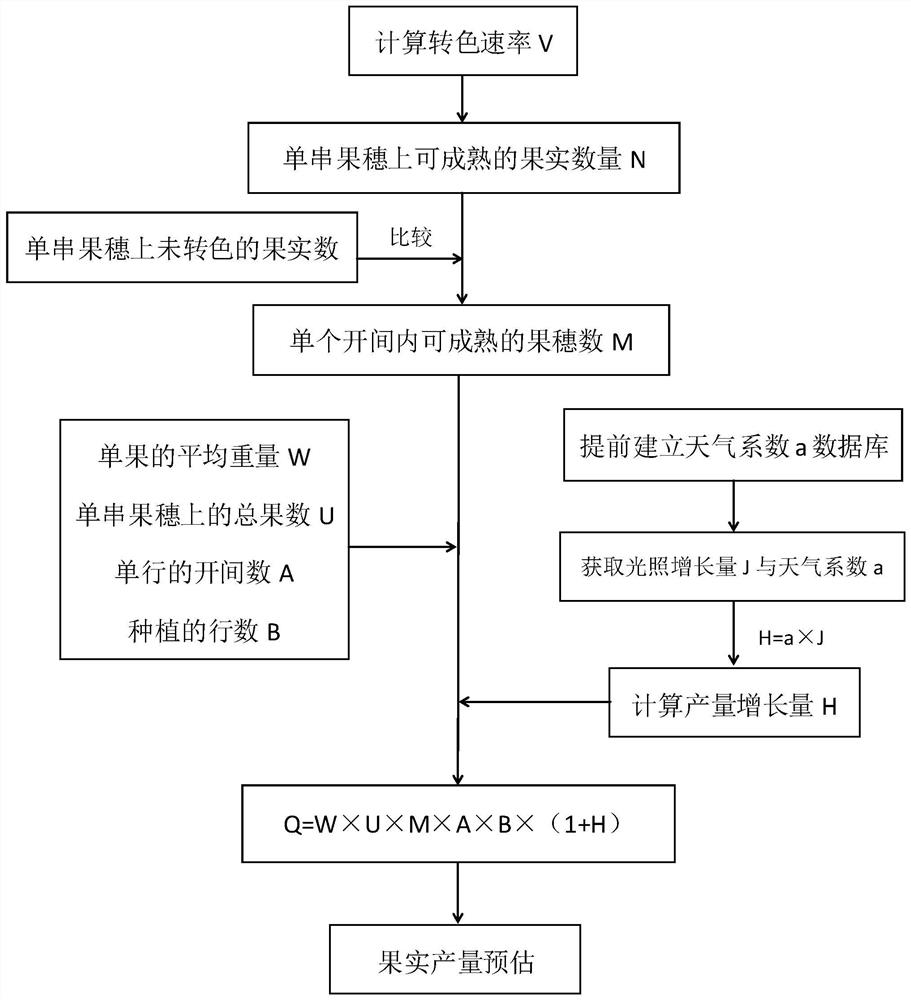
[0064] (1) Calculation of color change rate V: First, a light detection device is established to detect the daily average cumulative amount of light radiation received before and after tomato color change, and the time required for tomato color change in different seasons (months) is obtained, and then the color change rate V is calculated. ; The formula for calculating the rate of color change V is: rate of color change V = the number of tomatoes on a single bunch of fruit ears Y / the number of days T for color change.
[0065] (2) According to the color change rate V, calculate the number N of tomatoes that can be ripened on a single bunch of frui...
Embodiment 5-6
[0075] Embodiment 5-6 provides a kind of fruit yield estimation method.
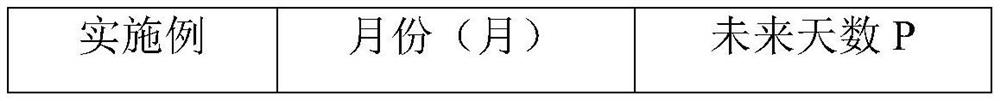
[0076] The difference between above-mentioned embodiment and embodiment 3 is: the estimated time of tomato yield; that is, the number of days P in the future, specifically as shown in Table 3.
[0077] The time that tomato yield is estimated in the fruit yield estimation method that table 3 embodiment 3, embodiment 5-6 provide
[0078]
[0079]
[0080] In the fruit yield estimation method that embodiment 5-6 provides, the concrete steps that step (3) counts the number of fruit ears M that can be ripened in a single bay are: when the number of days in the future P is 14 days or the number of days in the future P is the tomato of 21 days When estimating the yield, it is necessary to estimate the number of fruit ears M that can be ripened in a single bay with a future number of days P of 7 days or a future number of days of P of 14 days.
[0081] When the number of days P in the future is 7 days, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com