Dynamic allocation method and system for satellite bandwidth management
A technology of bandwidth management and dynamic allocation, applied in the field of satellite bandwidth management, to achieve the effect of improving operating income, saving maintenance and upgrading costs in the later stage, and balancing bandwidth usage requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
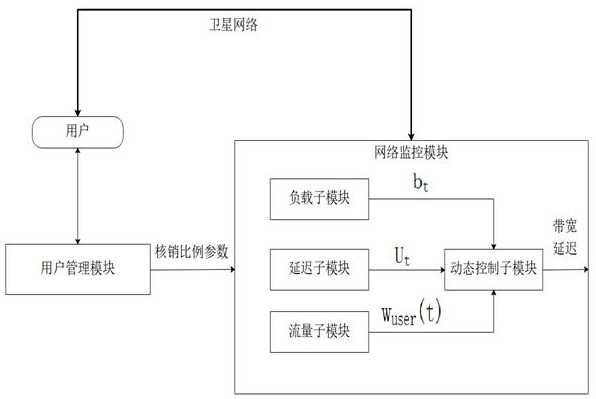
[0051] A dynamic allocation method for satellite bandwidth management, the allocation method comprising performing the following steps:
[0052] Create an account for the user's allocation of points;
[0053] Users submit network usage requirements to the distribution system;
[0054] The distribution system analyzes the user's network usage requirements, and establishes a user's demand model;
[0055] Based on the demand model, the user enters into a bandwidth allocation agreement with the allocation system, and determines multiple write-off ratio parameters of the write-off function p;
[0056] The allocation system monitors the bandwidth usage of the user according to the bandwidth allocation protocol, and writes off the allocation points of the user according to the write-off function p;
[0057] The user adjusts one or more of the set write-off ratio parameters according to the value of the write-off function p and the requirements of its own satellite network usage con...
Embodiment 2
[0101] This embodiment should be understood as including at least all the features of any one of the foregoing embodiments, and further improved on the basis thereof;
[0102] For users with strong application scenarios, the network traffic-time relationship function changes periodically; as shown in the appendix image 3 is the statistical curve of a user's traffic-time function within a week; the user's traffic-time function is counted through big data, and a traffic model q(t) is established, which can be used to estimate the user's traffic at a certain time t. traffic consumption rate;
[0103] Further, by integrating the time through the flow model q(t), Q can be calculated user (t), that is:
[0104] , Formula 5;
[0105] Then according to the calculation method of formula 3, when the actual consumption flow of the user is greater than its theoretical consumption value, then the flow function W user (t) The corresponding increase will speed up the consumption of th...
Embodiment 3
[0107] This embodiment should be understood as including at least all the features of any one of the foregoing embodiments, and further improved on the basis thereof;
[0108] Further, in order to give the user of the satellite network greater flexibility in use, the user is allowed to adjust the write-off ratio parameter k according to the actual application situation. 1 , k 2 , k 3 one or more of the values;
[0109] In one implementation, the user is allowed to adjust the write-off ratio parameter within a certain range of values; for example, under some temporary requirements, the user needs to temporarily increase the upper limit value of the bandwidth, and improve the allocation system for its the priority of the bandwidth response; in this case, the user adjusts the parameter k by 1 to a higher value, so as to obtain high bandwidth requirements for this temporary period; and after these temporary requirements are over, the parameter k can be reset 1 The value range ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com