Use of dehydroascorbic acid against nematode infection in plants
A technology for dehydroascorbic acid and nematode infection, applied in nematicides, plant growth regulators, botany equipment and methods, etc., capable of solving problems such as sugar beet yield damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
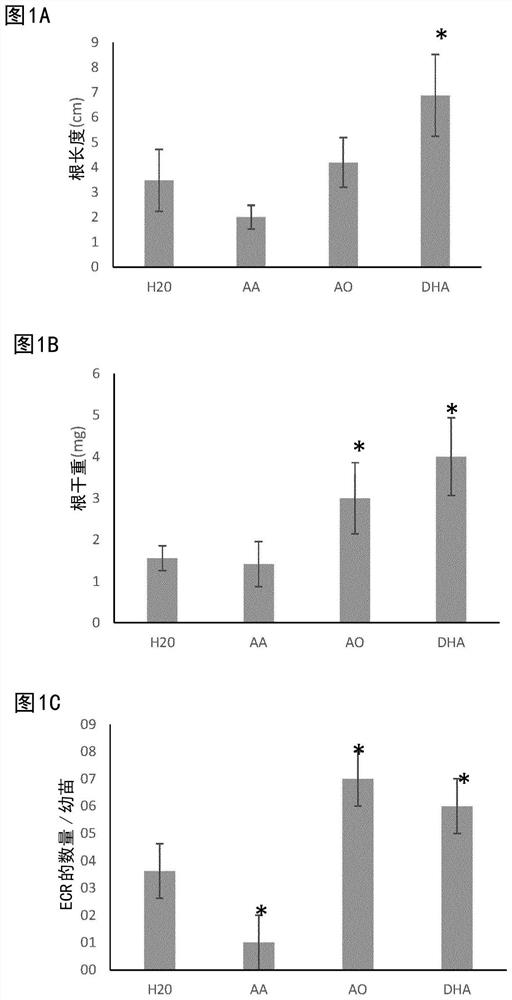
[0081] Example 1: DHA promotes root growth and embryo crown root formation in rice seedlings
[0082] Three days after germination, rice seedlings were watered with 1 mL of AA (reduced ascorbic acid, 20 mM), DHA (20 mM) or ascorbate oxidase (AO, 20 U / ml) or water as a control. Five days after this application, in DHA-treated seedlings, root length ( figure 1 A), root dry weight ( figure 1 B) and the number of embryo crown roots (ECR; figure 1 C) significantly higher. AA-treated seedlings had slightly shorter roots than control plants ( figure 1 A) and significantly less ECR ( figure 1 C), and seedlings generally appear stronger after DHA treatment. Although AO also had some positive effects on root dry weight and ECR, no root length effect was observed for this compound.
Embodiment 2
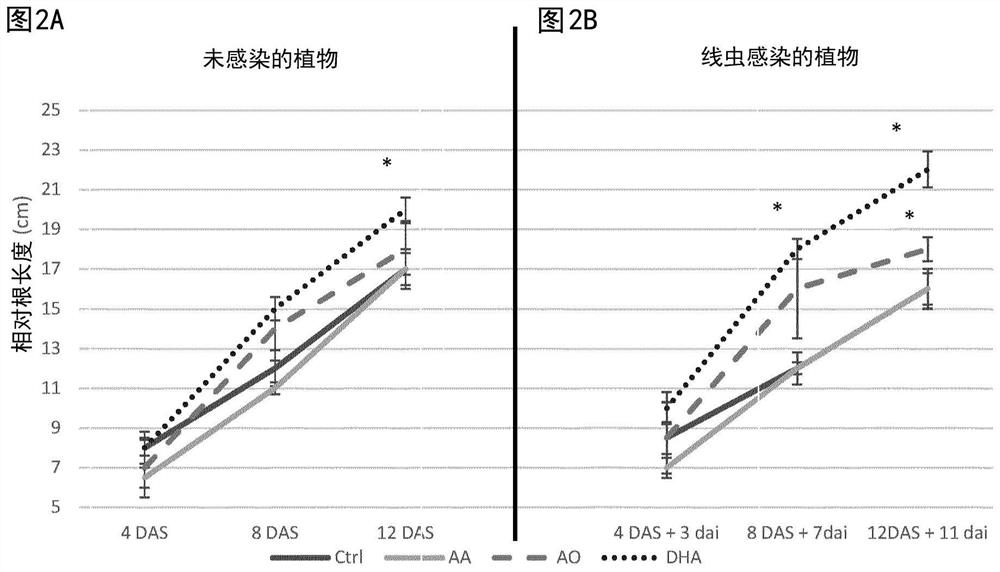
[0083] Example 2: DHA improves the tolerance of rice to root knot nematode infection
[0084] Use AA (20 mM), AO (20 U / mL), DHA (20 mM) or water (H 2 O) Foliar spraying on 14 day old rice plants. One day later, half of the plants were inoculated with 250 nematodes per plant, while the other half remained uninfected. Root length of all plants was monitored at three different time points: 4, 8 and 12 days after spraying (DAS). under uninfected conditions ( figure 2 A, left), DHA-only plants had significantly longer roots at 12DAS. Under nematode-infected conditions, AO-treated plants had slightly increased root length, while DHA-treated plants had the most significantly improved root length at both 8DAS (7 days after nematode inoculation) and 12DAS (11 days after nematode inoculation) ( figure 2 B).
Embodiment 3
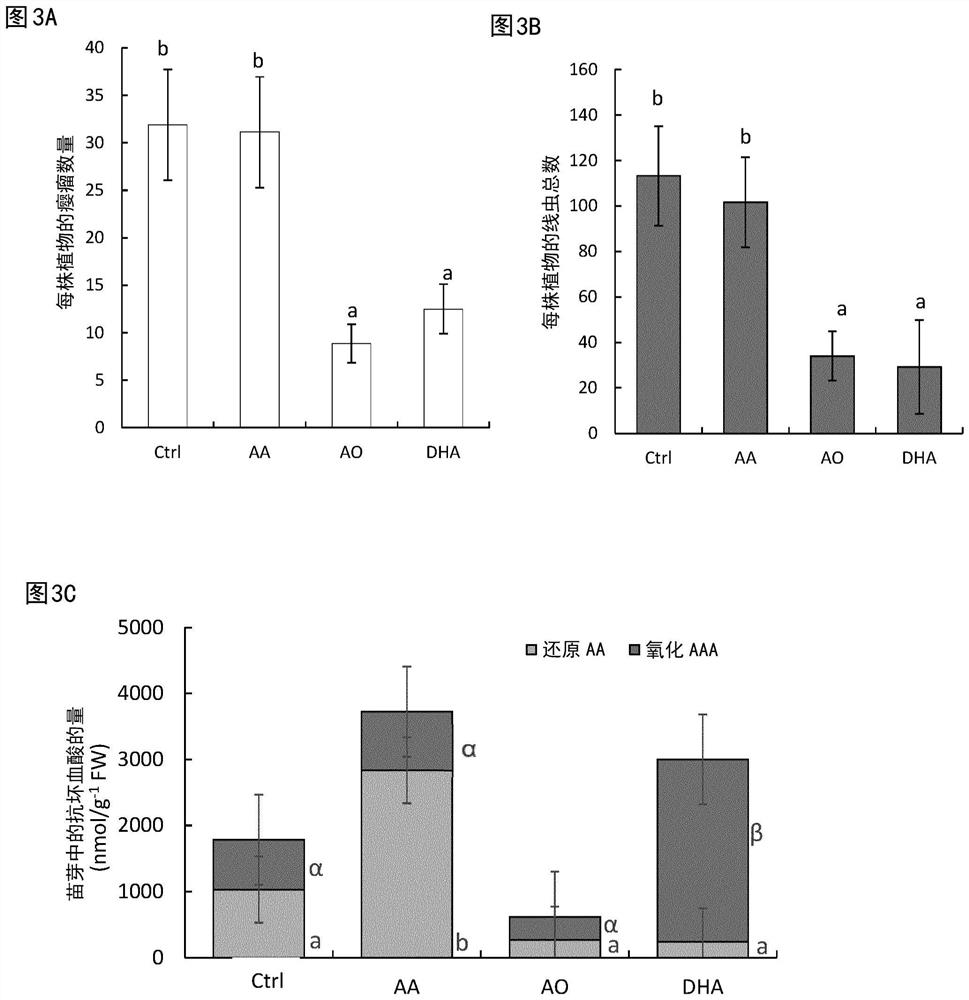
[0085] Example 3: Protection of rice from root-knot nematode infection by foliar spraying with DHA
[0086] Rice plants were foliar sprayed with AA (20 mM), DHA (20 mM) or ascorbate oxidase (AO, 20 U / ml) 24 h before nematode inoculation. We examined the effect of these treatments on gall numbers and nematode numbers at 12dai. There were no significant differences in the number of galls and the total number of nematodes between control plants and AA sprayed plants ( image 3 A and B), but significantly lower gall numbers were observed in rice plants sprayed with AO or with DHA ( image 3 A) and lower nematode numbers ( image 3 B).
[0087] We also evaluated the effect of foliar application of these chemicals (AA, AO and DHA) on exogenous reduced and oxidized AA (=DHA) levels 24 h after their application. The amount of reduced AA was significantly elevated in the shoots of AA-sprayed plants ( image 3 C), while no change was observed in the root ( image 3 D). After foli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com