Optical allocation for dynamic gain balancer and adder-subtractor
A technology of optical equipment, light beams, applied in the field of optical configurations including diffraction gratings, capable of solving problems such as inability to realize advantages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
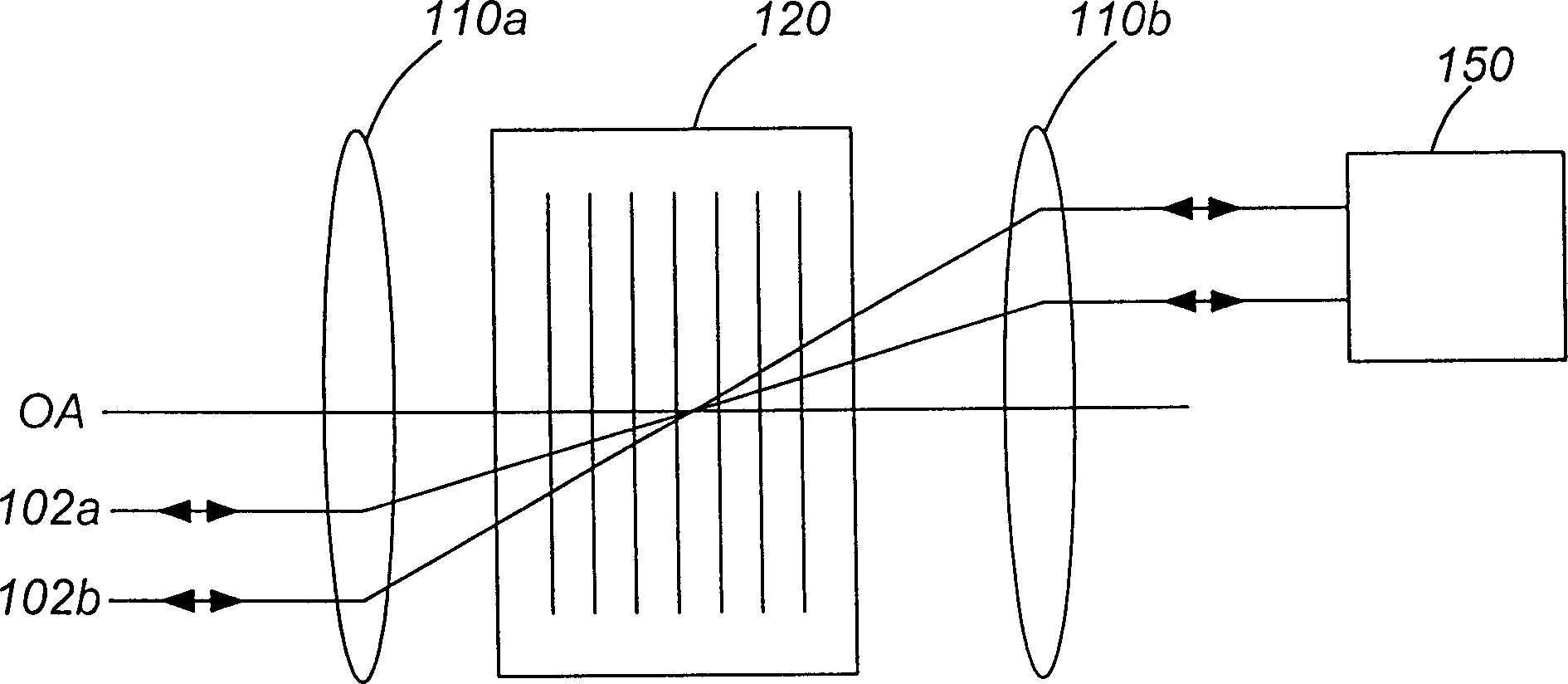
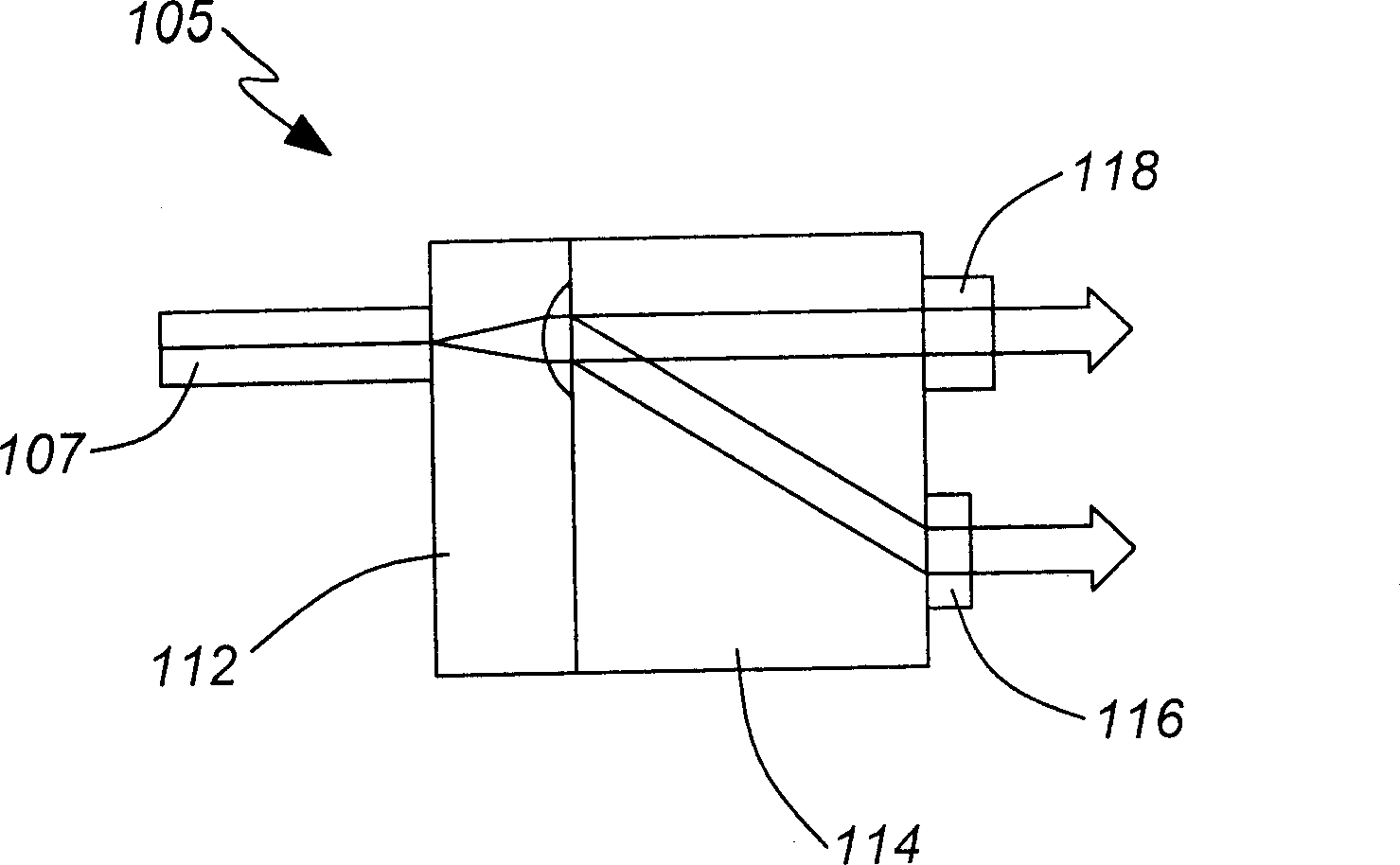
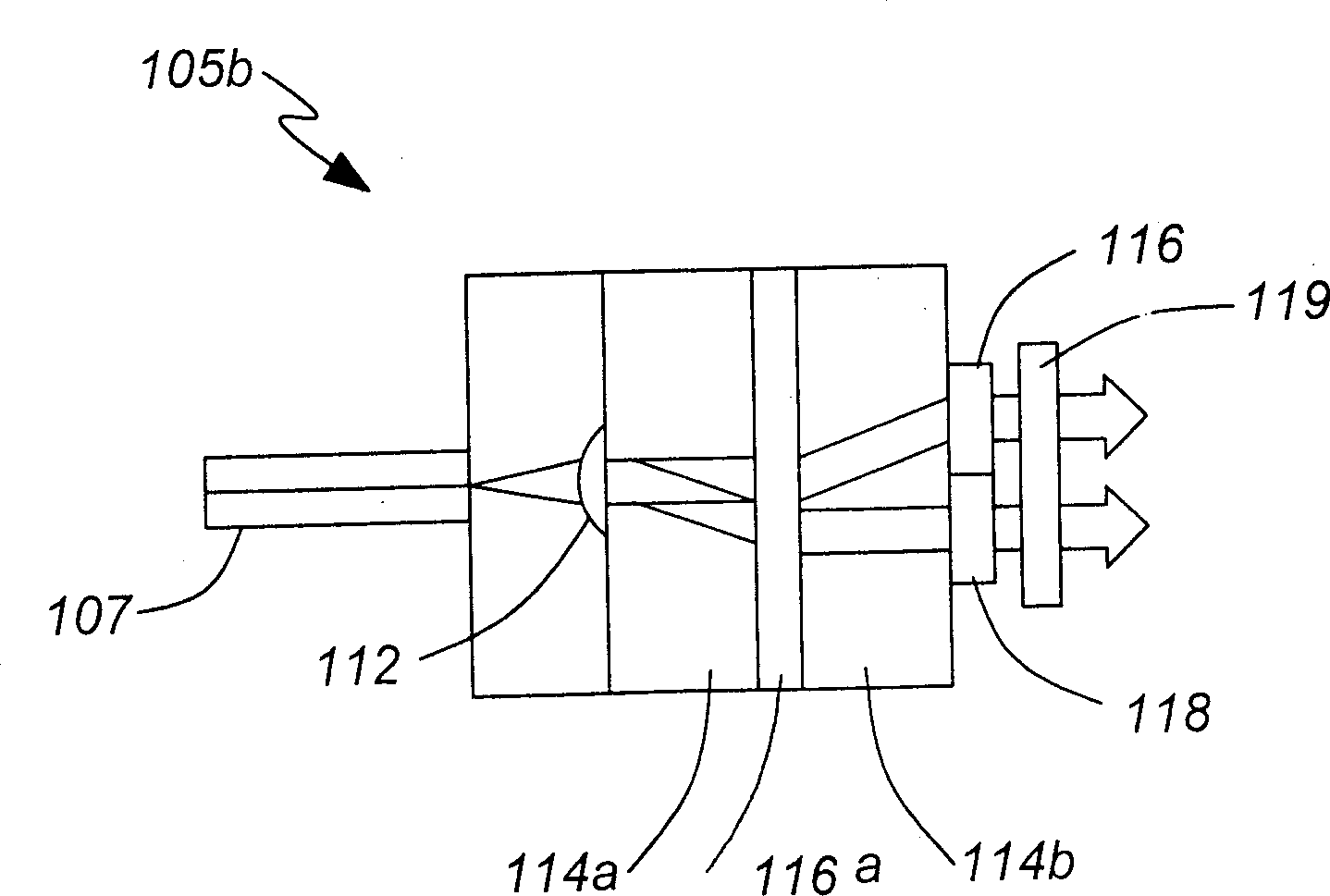
[0051] now refer to figure 1 , shows an optical device for rerouting and correcting optical signals according to the present invention, which can be used as a dynamic gain / channel equalizer (DGE) and / or a configurable optical add / drop multiplexer (COADM ).
[0052] The optical design includes a diffractive element 120 positioned at the focal plane between identical elements 110a and 110b each having an optical power. Two ports 102a and 102b are shown at the input / output ends, and the double-headed arrow indicates that light emitted to port 102a can be transmitted through the optical device and reflected back to input port 102a from which the light was emitted, or switched in a controllable manner to port 102b and vice versa. The input / output ports 102a and 102b are also disposed in the focal plane of the power device 110a coupled thereto. Although only two input / output ports are shown to facilitate understanding of the device, multiple such port pairs may alternatively be p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com