Nitric oxide inhibits rhinovirus infection
A technology of rhinoviruses and compounds, applied in the field of human rhinoviruses and virology, can solve problems such as effects to be studied
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Effect of cell passage: Preliminary studies have shown that repeated cell passage can have a significant effect on cytokine production in BEAS-2B cells. Although qualitatively the data obtained are always the same for each passage, cell passage has a progressive effect on the absolute levels of cytokines produced. For example, in 4 experiments using the same method of serial cell passage, the amount of IL-8 production decreased from 7690pg / ml to 3090pg / ml. Therefore, each experiment performed below was always performed in conjunction with an experiment using the same cell passage.
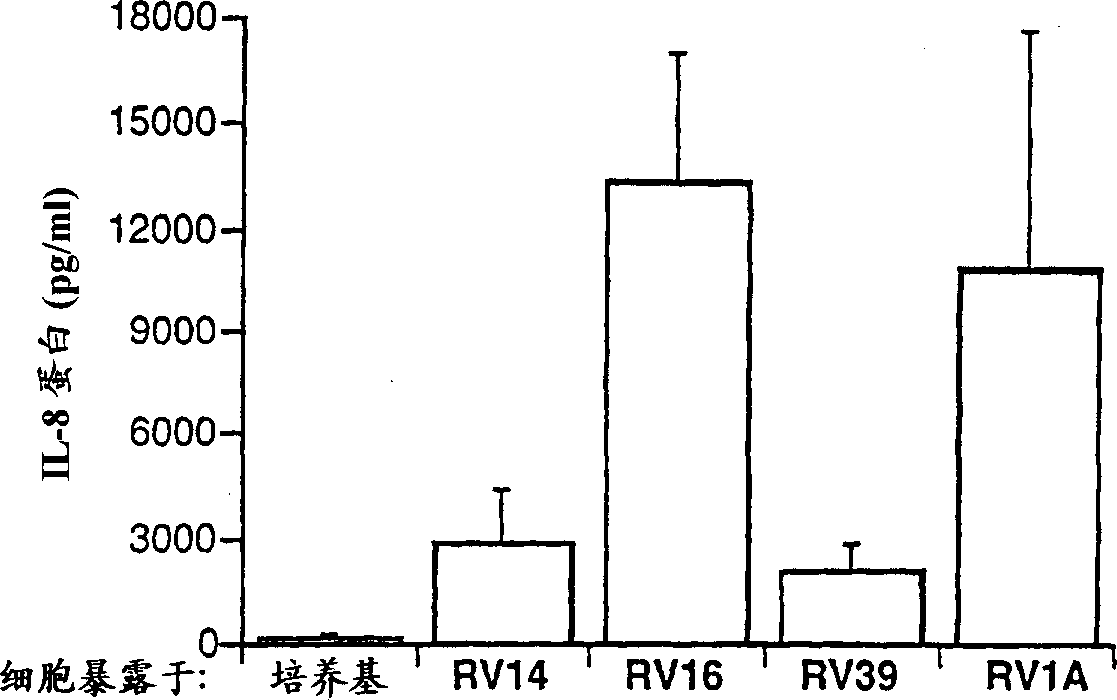
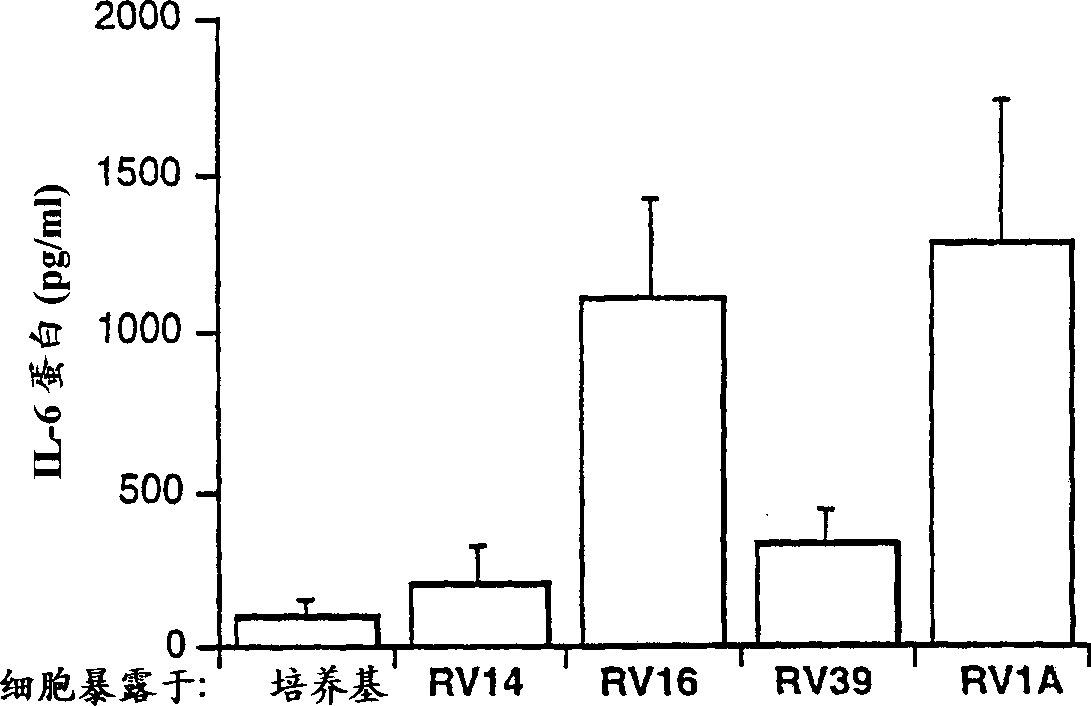
[0044] A comparison of the effects of several rhinovirus strains on cytokine production in BEAS-2B cells: The effects of four different rhinovirus strains at equal infectious doses on cytokine production were compared, using cell culture The object is BEAS-2B cells. Three of the virus strains used above are type 14, type 16 and type 19, which are members of the major group (major group) of...
Embodiment 2
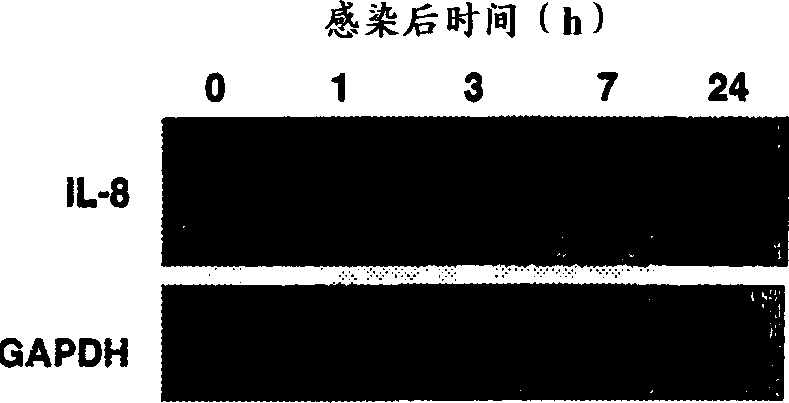
[0053] Kinetics of cytokine mRNA expression and protein secretion: Figure 2 shows that the mRNA levels of IL-8 and IL-6 were significantly increased within 1 hour after HRV-14 infection. At 24 hours post-infection, maximum expression had been reached for 3 hours but mRNA levels were still higher than uninfected controls. As mRNA was induced, IL-8 and IL-6 proteins in the supernatant were significantly increased. Cytokine production increased at 3 hours post-infection, reaching a maximum concentration at 24 hours. Notably, the time course of IL-8 and IL-6 production was faster after HRV-16 infection than after HRV-14 infection (Fig. 3). mRNA expression levels were highest within 1 hour post-infection and protein production was greatest within 7 hours. Consistent with the data shown above (FIG. 1), the amount of cytokines produced after HRV-16 infection was approximately 4-fold greater than after HRV-14 infection (FIG. 3 compared to FIG. 2). Since HRV-16 induces cytokine prod...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Virus titer after HRV-16 infection: The supernatant was collected at different time points after infection, and WI-38 cells were used for cytotoxicity experiments to determine the virus titer of HRV-16. Viruses could be detected in the culture medium about 7 hours after infection, and gradually increased during the period from 7 to 24 hours after infection (Table 1). Supernatants were collected during the second 24 hour post-infection period where virus levels approximated those observed after 24 hours (see Table 2 below). Indeed, this viral titer pattern was consistent with what was previously observed with HRV-14 (49).
[0056] Table 1
[0057] Human rhinovirus-16 infection from BEAS-2B cell cultures at different times
[0058] Virus content in the obtained supernatant
[0059] Time after infection Virus titer
[0060] (hour) (LogTCID 50 unit)*
[0061] 0 ND
[0062] 1 ND
[0063] 3 N...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com