Confocal microscope
A confocal microscope and microscope technology, applied in the field of confocal microscopes, can solve the problems of loss of measurement accuracy, difficulty in improving, difficulty in making a large numerical aperture, etc., and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and improving Z-direction resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0027] a. Dual-frequency interferometry scheme; b. Single-frequency polarization interferometry (with phase subdivision) scheme.
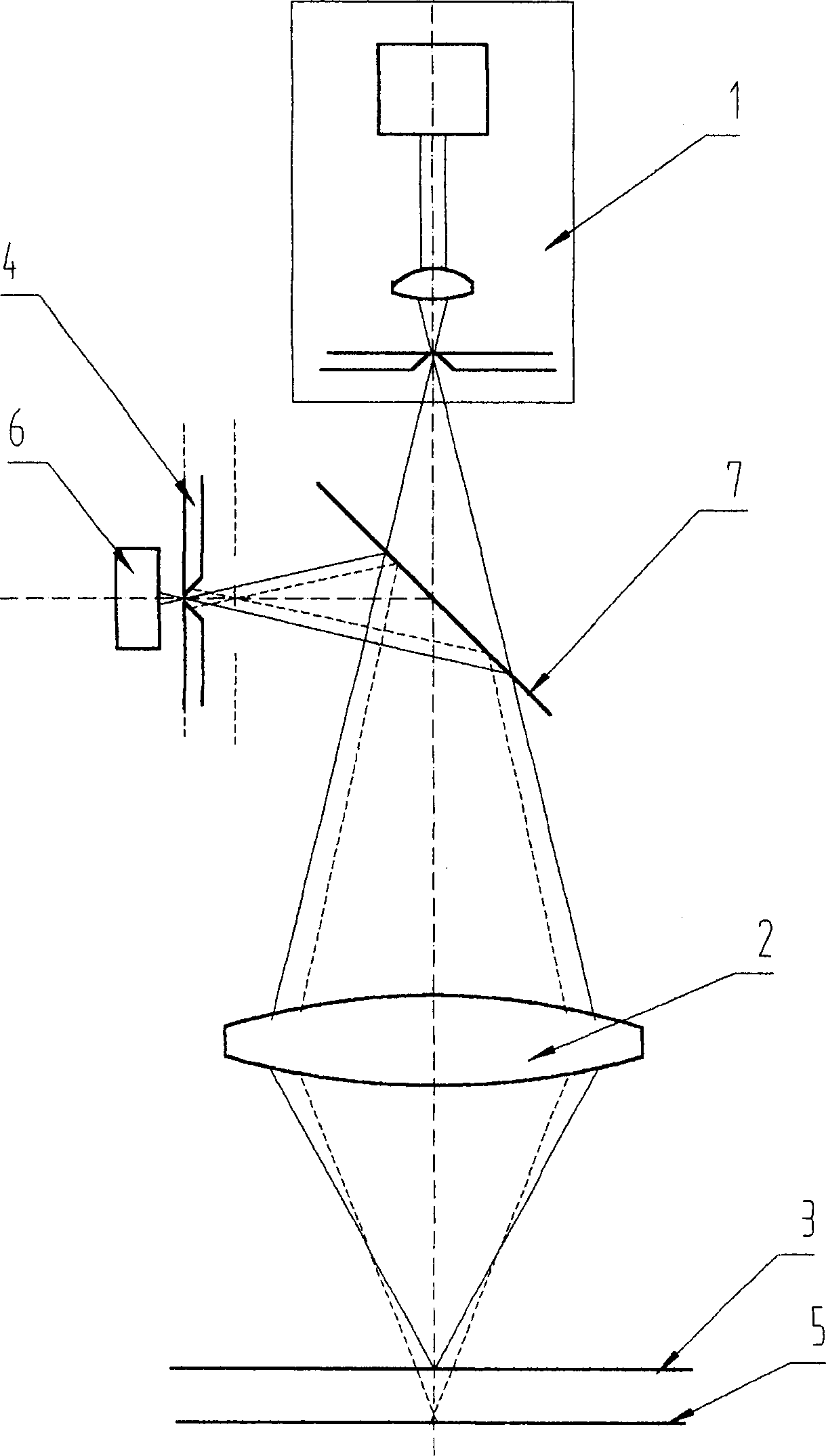
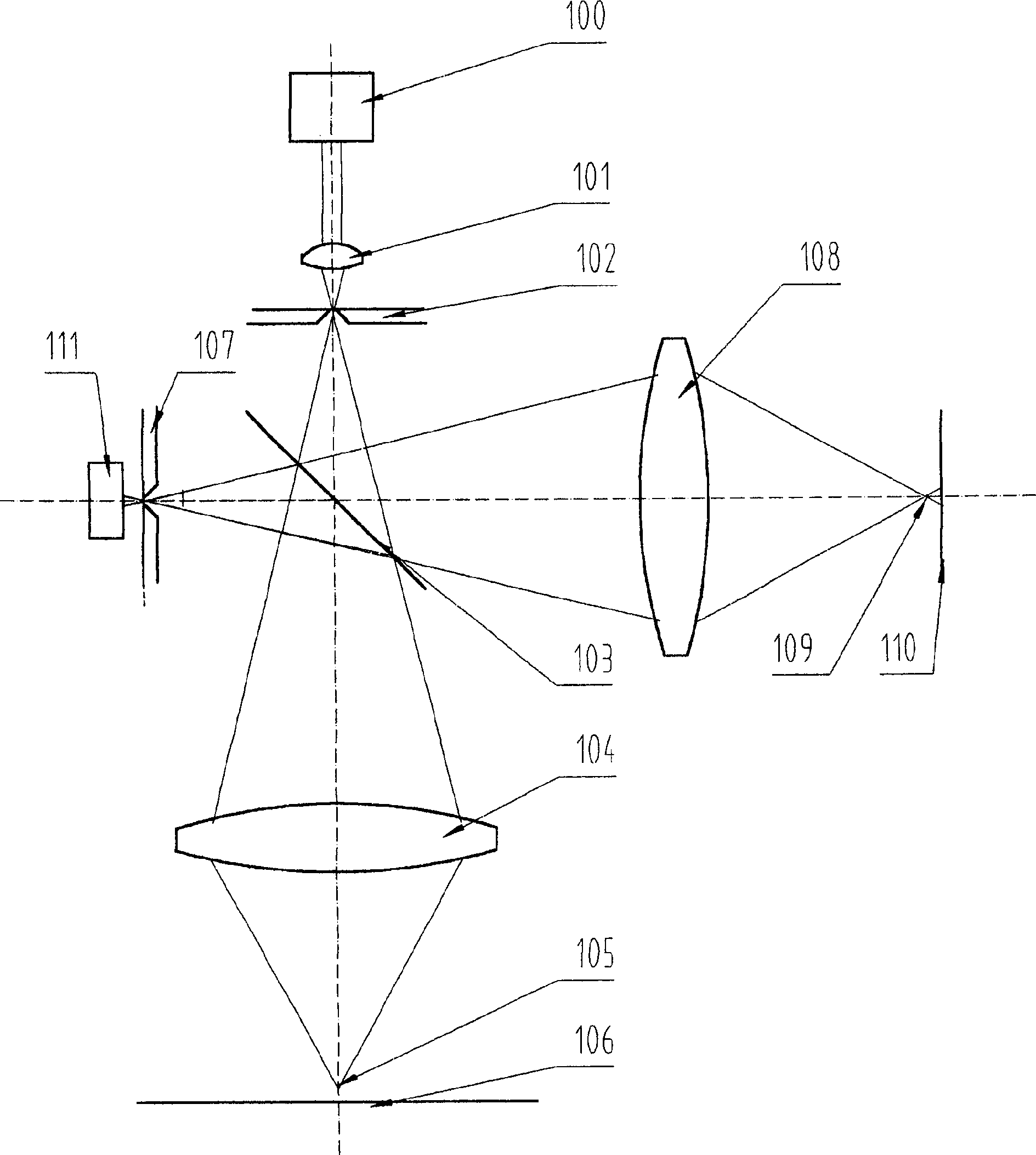
[0028] In each embodiment, in terms of specific geometrical optical paths, the following can be used: the optical path of the objective lens with infinite barrel length and the optical path of the objective lens with finite barrel length. In order to obtain the desired signal more reliably, in terms of the receiving optical path, the interference signal and the confocal signal can be received separately and mixed to receive two different structural forms. They are described as follows.
[0029] 1) Dual-frequency interference confocal microscope
[0030] see Figure 5 , using the dual-frequency laser 201 with two optical frequencies or wavelengths as the light source, a high-brightness point light source is formed on the pinhole of the diaphragm 203 through the condenser lens 202, and the light enters the beam splitter after passing through the co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com